Carbon Credits vs Renewable Energy Credits (RECs): What’s the Difference?
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Carbon credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) are two important measures with the goal to help reduce global carbon emissions. However, they both work in different ways with different implications for your own carbon emissions. So we had to ask: What’s the difference between carbon credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)?
Carbon credits are tradable certificates or permits that set a maximum level of carbon emissions for industries, companies, or countries. Renewable Energy Credits are certificates that allow you to claim that the electricity you use came from a renewable resource with low or zero-carbon emissions.
In the fight against climate change, how can we tell the difference between carbon credits and RECs? Below we will define both terms, identify the key advantages and differences of each, explore how they operate and what impact they have on carbon emissions, and discuss why they are both important in the fight against climate change.
How Are Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Defined
Carbon credits and RECs are two sustainability tools that can help individuals and organizations lower their carbon footprints. But although they are often used in the same conversation, they are not interchangeable terms.
What Does the Dictionary Say About Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)
Carbon credits are tradable certificates or permits that give companies, industries, or countries the right to emit 1 tonne (1,000kg) of CO2 or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas (GHG).
“Carbon Credit: a unit used in carbon trading that represents the right of a business, factory, etc. to release 1000 kilograms of carbon dioxide into the environment”
Cambridge Dictionary
Carbon credits are a form of climate currency, meaning they are subject to supply and demand and can be bought and sold through a cap-and-trade market. This market limits how much total CO2 can be emitted. Cap-and-trade markets became established after the Kyoto Protocol, an international treaty, set a maximum amount of GHG emissions that could be released into the atmosphere, both globally and nationally.
Each entity operating under a cap-and-trade program is issued a certain number of carbon credits each year. They can purchase more if their emissions exceed what was issued, and they can sell unused credits to other entities if their emissions are less than what was issued.
But carbon credits are not the only available tool. Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) are another option to reduce carbon emissions.
“REC: a market-based instrument that represents the property rights to the environmental, social, and other non-power attributes of renewable electricity generation”
United States Environmental Protection Agency
RECs are also a form of climate currency, but they are used in the renewable energy market. RECs allow you to claim that the electricity you use came from a renewable resource (i.e., solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, or biomass) with low or zero-greenhouse gas emissions. For example, a corporation that has been mandated to generate a minimum level of energy from renewables can buy RECs instead of developing their own renewable sources or purchasing renewable energy from another provider.
RECs act as an accounting or tracking mechanism for renewable energies as they are incorporated into the power grid. Because we cannot distinguish energy generated from renewables and that produced by other sources, some form of tracking is required.
What Are the Differences Between and Advantages of Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)
Both carbon credits and RECs represent ways in which we can mitigate carbon emissions and global warming. But they are also different methods of climate action with different environmental impacts, making it important to understand their differences.
The main difference between carbon credits and RECs is that carbon credits cap carbon emissions whereas RECs create new energy from renewable resources. Also, purchasing RECs directly reduces your carbon footprint whereas carbon credits do not directly reduce your carbon footprint.
The following are key advantages of carbon credits:
- Caps on carbon emissions can be set strictly
- Unused credits can be traded to other companies
- Incentivizes companies to invest in greener technologies
The following are key advantages of RECs:
- Supports the renewable energy market
- Certified proof that you are using renewable energy without having to install the required infrastructure (i.e. solar panels)
- They can be uniquely numbered, tracked, and retired in the tracking system to prevent someone else from claiming it
How Do Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Impact Your Carbon Footprint
Knowing the similarities and differences between carbon credits and RECs is important when making a decision of which one to use.
| Carbon Credits | Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) | |
| How are carbon emissions reduced | Carbon credits cap how much CO2 can be emitted by an entity. This cap on emissions can be gradually reduced over time, leading to less and less overall emissions. | RECs create new energy from lower or zero-carbon sources, rather than from traditional fossil fuels. |
| Impact on own carbon emissions | Carbon credits do not directly reduce your carbon footprint. | Purchasing RECs directly reduces your carbon footprint. |
| Impact on global carbon emissions | Carbon credits mitigate the problem, but they do not work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions. | RECs mitigate the problem, but they do not work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions. |
| Environmental benefits | Carbon credits facilitate the switch to greener energy sources and promote energy independence. | RECs are non-polluting, low-maintenance, promote the decentralization of our energy supply, and create green jobs. |
| Overall effectiveness in reducing carbon emissions | Improper reporting and discrepancies in maximum GHG levels between countries limits carbon credit effectiveness on a global scale. | Market oversaturation and cheap prices limit REC effectiveness. RECs are also not additional. |
How Do Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Reduce Carbon Emissions
The goal of both carbon credits and RECs is to reduce carbon emissions to mitigate climate change.
- Carbon credits: Credits represent indirect emission reductions. Putting a cap on emissions and decreasing this cap over time reduces carbon emissions over time, preventing CO2 from entering the atmosphere.
- RECs: RECs represent indirect emission reductions. Purchasing RECs supports renewable energy generation from a low or zero-emissions resource.
When you hear the words “carbon credit”, think about the term “allowance”. Carbon credits represent the maximum amount of CO2 an entity is allowed to emit. This cap on CO2 emissions slowly decreases over time, forcing entities to emit less and less CO2 to stay within the boundaries of the cap. Companies with high levels of emissions can continue to operate, but only at an increased cost.
When you hear the word “REC”, think about the term “renewable energy”. RECs can reduce the demand for “dirty”, fossil-fueled energies by bolstering the renewable energy market. RECs represent the creation of renewable energy to be supplied to our power grid. For example, if you consume 100 MWh per year, then you should purchase 100 RECs to ensure that all of the electricity you use is sourced from renewable energy sources.
What Impact Do Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Have on Your Own Carbon Emissions
One of the best ways we can aid in the fight against global climate change is to reduce our carbon footprint. And to do this we first have to reduce our carbon emissions.
- Carbon credits: Carbon credits do not directly reduce your carbon footprint.
- RECs: Purchasing RECs directly reduces your carbon footprint.
Carbon credits do not directly reduce your own carbon emissions. Setting a limit on how much carbon emissions are allowed is an indirect method of emissions reduction because companies can continue to emit as long as they pay the price. Coupled with direct measures of emission reductions, such as reducing individual energy usage and consumption, carbon credits can become more effective.
RECs directly reduce your own carbon emissions. When you purchase a REC, you source your energy from renewable resources rather than from fossil fuels. Since renewables have a lower carbon footprint than fossil fuels, your carbon footprint decreases as you use RECs.
What Impact Do Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Have on Global Carbon Emissions
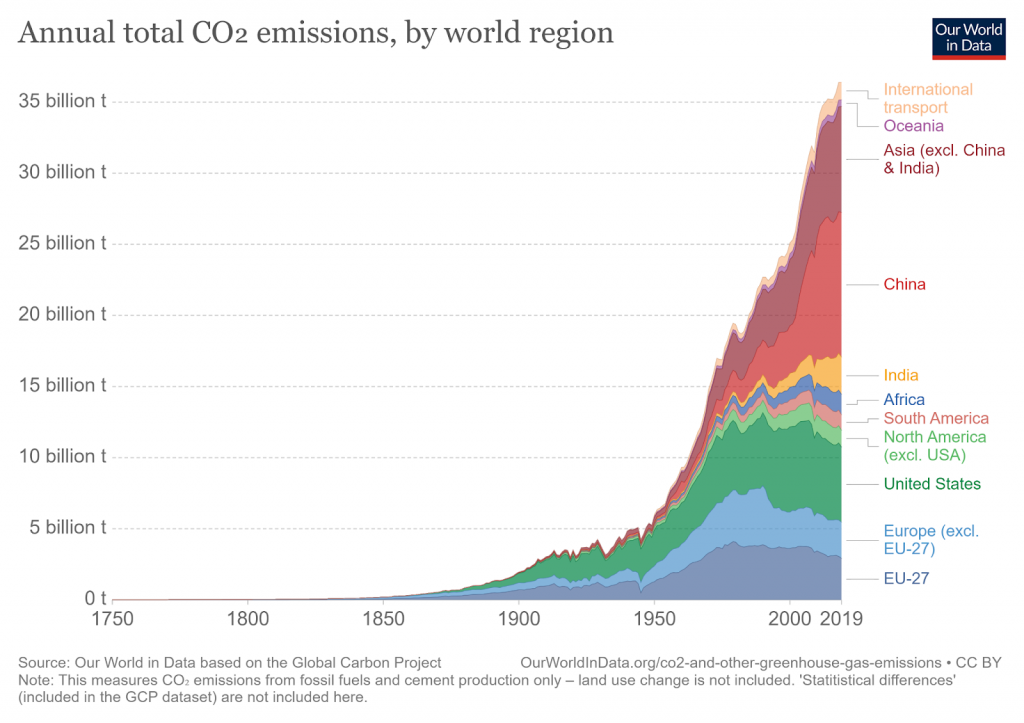
Every year we pump over 36 billion tons of CO2 into the atmosphere, fueling climate change. This causes temperature and sea-level rise, melting of sea ice, changing precipitation patterns, and ocean acidification. Carbon credits and RECs aim to reduce global emissions and mitigate these negative environmental effects.
- Carbon credits: Carbon credits mitigate the problem, but they don’t work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions.
- RECs: RECs allow you to purchase renewable energy, but it is not a guarantee that carbon emissions are avoided.
Carbon credits do not have a significant impact on global carbon emissions. Although they may incentivize companies to reduce their CO2 emissions, the immediate effect of reducing emissions under the cap-and-trade system is to benefit a company’s bottom line. The direct goal of carbon permits is not to reduce greenhouse emissions or support sustainable energy projects, but rather for companies to make money.
RECs do not have a significant impact on global carbon emissions because they do not curtail energy from fossil fuels or limit their production. They simply bolster the renewable energy market and increase renewable energy supply to the power grid.
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered the largest decrease in energy-related carbon emissions since World War II, a decrease of 2 billion tons. However, emissions rebounded quickly at the end of 2020, with levels in December ending 60 million tons higher than those in December 2019. This indicates that the earth is still warming at an accelerated rate, and not enough is being done to implement clean energy practices.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)
Using carbon credits and RECs can reduce our consumption of and reliance on fossil fuels (i.e., coal, oil, and natural gas) which can reduce the effects of global warming by limiting global GHGs. But they also come with various environmental benefits.
- Carbon credits: Carbon credits facilitate the switch to greener energy sources and promote energy independence.
- RECs: Renewable energy is mostly non-polluting, low-maintenance, promotes the decentralization of our energy supply, and creates green jobs.
Carbon credits incentivize companies to switch to greener energy sources including solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy. They do not emit CO2, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxides, or mercury into the atmosphere, soil, or water. And these pollutants are known to contribute to the thinning of the ozone layer, global sea-level rise, and the melting of our world’s glaciers.
Switching from fossil fuels to green energy also promotes energy independence. Being able to produce your electricity without the aid of foreign countries is an important step in becoming more self-sufficient.
RECs generate environmental benefits associated with the fact that the energy was produced via renewable resources without burning fossil fuels. Renewable energy has environmental benefits because it is sustainable, meaning that the energy sources are in infinite supply and we can keep harvesting them for many years to come. The renewable energy sector supplied approximately 12 million jobs globally in 2020, and jobs continue to increase as we start to realize just how beneficial renewable energy is for our environment.
How Effective Are Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) in Reducing Carbon Emissions
Carbon credits and RECs can be effective at reducing carbon emissions under certain conditions.
- Carbon credits: Improper reporting and discrepancies in maximum GHG levels between countries limits carbon credit effectiveness on a global scale.
- RECs: Market oversaturation and cheap prices limit REC effectiveness. RECs are also not additional.
Carbon credits have faced criticism because most industries lack the technology that monitors and determines their amount of CO2 emissions. This makes it easier for companies to cheat on their emissions reports and say they are emitting less than they actually are. Also, different countries have different standards and caps for CO2 emissions. If the cap is set too high, then companies are not incentivized to reduce emissions. But set the cap too low, and companies will be overly burdened to reduce emissions. And the extra cost will be passed down to consumers as a result.
The overall effectiveness of RECs depends on their price and the state of the market. The more that RECs are in demand, the more renewable energy must be generated. The more renewable energy that is generated, the less reliant we can be on fossil fuels. But the main problems with RECs are that the market is oversaturated due to the thundering success of the renewable energy market, and that RECs are so cheap to buy that they are not a big enough revenue source to make a difference on a large power project. RECs are not additional because most projects receiving REC revenue now would have been built regardless. In short, we should think of buying RECs as supporting renewable energy rather than curtailing fossil fuels.
Why Are Both Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) Important to Fight Climate Change
Carbon credits and RECs are important to fight climate change because they are both ways to reduce your carbon footprint. Reducing your carbon footprint is important because it mitigates the effects of climate change, which has a positive cascade effect on public health and plant and animal diversity. In addition, this boosts the global economy and leads to innovative, more environmentally-friendly solutions.
However, carbon credits and RECs should not be used as a Panacea for climate change. Relying on credits solely is impractical because the immediate effect of reducing emissions under the cap-and-trade system is to benefit a company’s bottom line. And relying on RECs solely is impractical because they are so cheap that they have become irrelevant to the financing and investment decisions of the power industry.
In the long term, direct methods of carbon footprint reduction are much more effective. Reducing your household, travel, and lifestyle carbon footprint can go a long way in the fight against climate change!
What are Better Alternatives to Carbon Credits and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)
If used correctly, carbon credits and RECs can provide environmental, economic, and social benefits that go beyond reducing carbon emissions. They have the potential to instigate meaningful environmental change and begin to reverse some of the effects of climate change.
However, we can’t let these two methods be a guilt-free way to reduce carbon emissions. Carbon credits and RECs must be used in conjunction with carbon reduction measures until the industry has time to invest, develop, and refine more sustainable innovations.
These reduction measures don’t have to involve drastic changes either. Actions that may seem small can have a big impact because those small changes add up! You can reduce your carbon footprint in three main areas of your life: household, travel, and lifestyle.
Reduce your household footprint:
- Wash with cold water: Washing clothes in cold water could reduce carbon emissions by up to 11 million tons. Approximately 90% of the energy is used to heat the water, so switching to cold saves also saves energy.
- Replace incandescent bulbs with fluorescent bulbs: Fluorescent bulbs use 75% less energy than incandescent ones, saving energy and thus reducing electricity demand and greenhouse gas emissions.
Reduce your travel footprint:
- Fly less: Aviation accounts for around 1.9% of global carbon emissions and 2.5% of CO2. Air crafts run on jet gasoline, which is converted to CO2 when burned.
- Walk or bike when possible: The most efficient ways of traveling are walking, bicycling, or taking the train. Using a bike instead of a car can reduce carbon emissions by 75%. These forms of transportation also provide lower levels of air pollution.
Reduce your lifestyle footprint:
- Switch to Renewable Energy Sources: The six most common types of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydro, tidal, geothermal, and biomass energy. They are a substitute for fossil fuels that can reduce the effects of global warming by limiting global carbon emissions and other pollutants.
- Recycle: Recycling uses less energy and deposits less waste in landfills. Less manufacturing and transportation energy costs means less carbon emissions generated. Less waste in landfills means less CH4 is generated.
- Switch from single-use to sustainable products: Reusing products avoids resource extraction, reduces energy use, reduces waste generation, and can prevent littering.
- Eat less meat and dairy: Meat and dairy account for 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with beef and lamb being the most carbon-intensive. Globally, we consume much more meat than is considered sustainable, and switching to a vegan or vegetarian diet could reduce emissions.
- Take shorter showers: Approximately 1.2 trillion gallons of water are used each year in the United States just for showering purposes, and showering takes up about 17% of residential water usage. The amount of water consumed and the energy cost of that consumption are directly related. The less water we use the less energy we use. And the less energy we use, the less of a negative impact we have on the environment.
Final Thoughts
In short, carbon credits are not the same thing as RECs. Carbon credits are tradable certificates or permits that give companies, industries, or countries the right to emit 1 tonne (1,000kg) of CO2. RECs are certified proof that energy was created from renewable resources rather than from fossil fuels. They are not a guarantee that any particular amount of fossil fuel electricity generation was avoided. And they are also not a guarantee that any particular amount of carbon emissions was avoided.
Both are tools in our sustainability toolbox that can be used to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change. But we should not rely on either or both to be a cure-all for our environmental problems. Direct measures of carbon emission reduction are much more effective in reducing emissions both in the short term and in the long term.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- One Tree Planted: Carbon Credits Vs Carbon Offsets – What’s the Difference?
- Environmental Defense Fund: How cap and trade works
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: What is the Kyoto Protocol
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Offsets and RECs: What’s the Difference?
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
- National Geographic: Renewable Resources
- OurWorldofEnergy: Recent Controversy Over Renewable Energy Credits
- Investopedia: Renewable Energy Certificate (REC)
- World Resources Institute: Carbon Tax vs. Cap-and-Trade – What’s a Better Policy to Cut Emissions?
- Energy Sage: Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)
- GreenBiz: REC vs. Carbon Offset – Do You Know the Difference?
- CarbonCredits.com: The ultimate Guide to Understanding Carbon Credits
- 8BillionTrees: Renewable Energy Certificates vs Carbon Offset Credits (2022 Updates)
- Our World in Data: CO2 emissions
- National Wildlife Federation: Climate Change
- Harmony Fuels: What Is The Difference Between Carbon Offsets And Carbon Credit?
- International Energy Agency: After steep drop in early 2020, global carbon dioxide emissions have rebounded strongly
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Coal Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Oil Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Natural Gas? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: What is Green Power?
- White House Archives: Fact Sheet – Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
- Terrapass: How do RECs work?
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Renewable Energy – The Clean Facts
- International Renewable Energy Agency: Renewable Energy and Jobs – Annual Review 2021
- Investopedia: Cap and Trade Definition
- Vox: RECs, which put the “green” in green electricity, explained
- The Ocean Foundation: Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
- Cold Water Saves: Washing Laundry In Cold Water Protects A Lot More Than Just Our Clothing.
- Energy Information Administration: Renewable Energy Explained
- Energy Star: Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs (CFLs) and Mercury
- Our World in Data: Where in the world do people have the highest CO2 emissions from flying?
- Our World in Data: Which form of transport has the smallest carbon footprint?
- Zero Waste Europe: Reusable vs Single Use Packaging
- Carbonbrief: Interactive – What is the climate impact of eating meat and dairy?
- Stop Waste: Recycling and Climate Protection
- Impactful Ninja: Is Taking Long Showers Bad for the Environment?
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Showerheads