Carbon Removal vs Carbon Avoidance: What’s the Difference?
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Carbon removal and carbon avoidance are two heavily debated methods of carbon emission reduction. Whether we remove the carbon that has already been emitted, avoid emitting more carbon than we already have, or do both, removal and avoidance are equally important in the fight against climate change. So, we had to ask: What’s the difference between carbon removal and carbon avoidance?
Carbon removal is the elimination of carbon emissions after they have entered our atmosphere. Carbon avoidance is the prevention of emitting carbon in the first place and can be divided into two categories, avoidance via carbon offsets and avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures.
In the fight against climate change, how can we tell the difference between carbon removal and carbon avoidance? Below we will define both terms, identify the key advantages and differences of each, explore how they operate and what impact they have on carbon emissions, and discuss why they are both important in the fight against climate change.
How Are Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance Defined
Carbon removal and carbon avoidance are two sustainability tools that can help individuals and organizations lower their carbon footprints. But since they are different mechanisms, understanding their differences is important.
What Does the Dictionary Say About Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance
Carbon removal, also referred to as negative emissions or carbon drawdown, is the process of eliminating carbon from the atmosphere.
“Carbon Removal: the process of removing CO2 from the atmosphere”
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Carbon removal can be split into 2 categories, technological and natural carbon removal.
- Technological removal: This involves specialized technology which extracts carbon from the atmosphere. A prominent example of this is Climeworks, a direct air capture who’s specialized machines take CO2 from the air, mix it with water, and pump it deep underground, turning the captured carbon into stone.
- Natural removal (carbon sequestration): Carbon is stored in vegetation (forests), soils, and oceans. Forests absorb 2.6 billion tons of CO2 every year, soil absorbs approximately 25% of all carbon emissions, and phytoplankton in our oceans absorb approximately 25% of all carbon emissions.
Overall, different carbon removal processes can include:
- Afforestation/reforestation: Planting new forests
- Soil carbon sequestration: Storing captured carbon in the soil
- Biochar: Creating charcoal and burying it or plowing it into fields
- Bioenergy: Capturing and sequestering carbon from biofuels and bioenergy plants
- Enhanced mineralization: Crushed rocks are spread over the land to absorb carbon
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): Machines suck carbon out of the atmosphere and store it in
geological formations underground
- Ocean-based Methods: Ocean alkalization/fertilization, artificial upwelling/dwelling
Carbon avoidance aims to prevent carbon from being released into the atmosphere.
“Avoidance: not doing something; preventing something from existing or happening”
Oxford Dictionary
Carbon avoidance can occur either via carbon offsets or via direct carbon reduction measures.
- Carbon offsets are measured in tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalents and are bought and sold through international brokers, online retailers, and trading platforms. The offsets that are classified as carbon avoidance measures include renewable energy and energy efficiency offsets. The former generates energy from renewable resources (i.e. solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass) rather than from fossil fuels. The latter develops products or systems that use less energy than conventional systems to perform the same task (i.e. LED light bulbs and efficient cooking stoves).
- Direct carbon reduction measures involve those that lower your carbon footprint. And a lower carbon footprint means less carbon is emitted into the atmosphere. Methods of direct carbon reduction include using less energy, switching to cleaner forms of energy other than fossil fuels, and reducing the waste you generate.
What Are the Differences Between and Advantages of Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance
Both carbon removal and carbon avoidance represent ways in which we can mitigate carbon emissions and global warming. But they are also different methods of climate action with different environmental impacts, making it important to understand their differences.
The main difference between carbon removal and carbon avoidance is that carbon removal removes the carbon that has already been emitted from our atmosphere. Carbon avoidance seeks to prevent carbon from being emitted in the first place.
Carbon removal is easier to track, calculate, and record because you are physically removing a set amount of carbon from the atmosphere. But it is also harder to implement the technology. Carbon avoidance is more difficult to quantify because it involves not putting carbon into the atmosphere. But it is easier to put into practice because it is easier not to do things than it is to do them.
The following are key advantages of carbon removal:
- Removes carbon from the atmosphere permanently
- Reduces atmospheric carbon dioxide levels
The following are key advantages of carbon avoidance:
- A proactive rather than reactive way of dealing with carbon emissions
- Avoidance via carbon offsets promotes renewable energy and energy efficiency
- Avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures cuts carbon emissions at their source
How Do Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance Impact Your Carbon Footprint
Knowing the similarities and differences between carbon removal and carbon avoidance is important when making a decision of which one to use.
| Carbon Removal | Carbon Avoidance | |
| How are carbon emissions reduced | Carbon removal represents indirect emission reductions. Carbon is eliminated after the emissions have already entered our atmosphere. | Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets and direct carbon reduction measures prevents carbon from entering the atmosphere. |
| Impact on own carbon emissions | Carbon removal does not directly reduce your carbon footprint. | Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets does not directly reduce your carbon footprint. Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures does directly reduce your carbon footprint. |
| Impact on global carbon emissions | Carbon removal mitigates the problem, but it does not work at the core issue of reducing overall carbon emissions. | Carbon avoidance via offsets does not work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions. Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures does work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions. |
| Environmental benefits | Carbon removal improves air quality, protects ecosystems, and aids in climate change mitigation. | Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets and direct carbon reduction measures improves air quality, protects ecosystems, and aids in climate change mitigation. |
| Overall effectiveness in reducing carbon emissions | Cost and storage capacity limits affect carbon removal effectiveness on a global scale. | The effectiveness of carbon avoidance via carbon offsets depends on the type of project and if the project is realized, additional, permanent, meets certain key criteria and project standards, and does not engage in greenwashing. Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures is effective because it cuts emissions at their source. |
How Do Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance Reduce Carbon Emissions
The goal of both carbon removal and carbon avoidance is to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change.
- Carbon removal: Carbon removal represents indirect emission reductions.
- Carbon avoidance: Carbon avoidance via offsets represents indirect emission reductions. Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures represents direct emission reductions.
Carbon removal still permits the combustion of fossil fuels at current rates, it just eliminates the carbon after it has entered our atmosphere. The carbon can then be stored permanently in land or ocean-based reservoirs.
For carbon avoidance via carbon offsets, the offsets represent the reduction, avoidance, destruction or sequestration of the equivalent of a ton of carbon in one place to “offset” an emission taking place somewhere else. Purchasing carbon offsets funds carbon emission reduction projects which prevent CO2 from entering the atmosphere.
For carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures, you prevent carbon from being emitted by switching to practices that emit less or even zero carbon. For example, biking to work and sourcing your energy from renewables.
What Impact Do Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance Have on Your Own Carbon Emissions
One of the best ways we can aid in the fight against global climate change is to reduce our carbon footprint. And to do this we first have to reduce our carbon emissions.
- Carbon removal: Carbon removal does not directly reduce your carbon footprint.
- Carbon avoidance: Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets does not directly reduce your carbon footprint. But carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures does directly reduce your carbon footprint.
Carbon removal does not directly reduce your own carbon emissions. It is an indirect method of emission reduction, and knowing there is an option to essentially erase our emissions after we cause them negates any incentive of reducing emissions of our own accord.
Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets does not directly reduce your own carbon emissions. Offsets only make others reduce their carbon emissions to compensate for your emissions.
Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures does directly reduce your own carbon emissions. Choosing to directly reduce your carbon output reduces your carbon footprint. And this means less carbon is emitted into the atmosphere.
What Impact Do Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance Have on Global Carbon Emissions
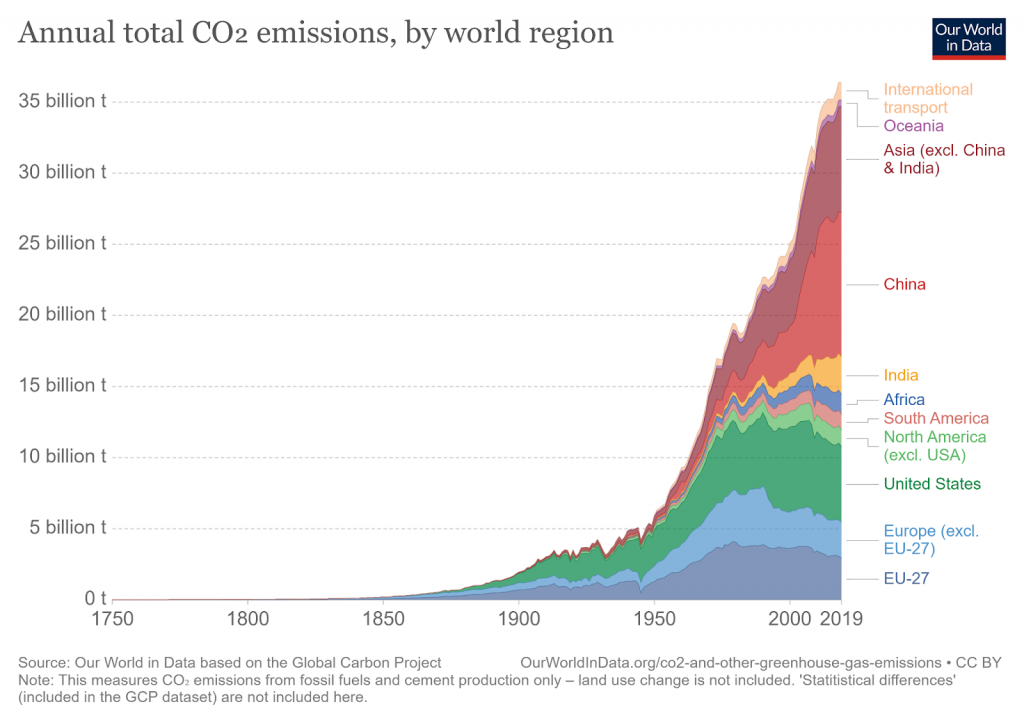
Every year we pump over 36 billion tons of CO2 into the atmosphere, fueling climate change. This causes temperature and sea-level rise, melting of sea ice, changing precipitation patterns, and ocean acidification. Carbon removal and carbon avoidance aim to reduce global emissions and mitigate these negative environmental effects.
- Carbon removal: Carbon removal mitigates the problem, but it does not work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions.
- Carbon avoidance: Carbon avoidance via offsets does not work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions. But carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures does work at the core issue of reducing overall CO2 emissions.
Carbon removal does not have a significant impact on global carbon emissions. To contribute substantially to the fight against climate change, global carbon removal capacity would need to reach 10 gigatons (Gt) of carbon by 2050 and 20 Gt of carbon for each year from 2050 to 2100. Currently, carbon removal processes contribute negligibly to this amount. Thus there remains a substantial gap between what we currently have and what is needed to reduce our emissions to the Paris Climate Agreement target levels for carbon removal.
Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets does not have a significant impact on global carbon emissions. This is because, in comparison to our 36 billion tons of CO2 emissions, carbon offsets for only ~1 billion tons of CO2 have been listed for sale on the voluntary market. Meaning that only about 0.8-1% of our annual CO2 emissions are offset.
Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures does have a significant impact on global carbon emissions. For example, if we stopped burning fossil fuels today we would be preventing the emission of billions of tons of carbon into the atmosphere every year. But even on a smaller scale, using cold water when washing clothes and switching to energy-efficient lightbulbs decreases carbon emissions.
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered the largest decrease in energy-related carbon emissions since World War II, a decrease of 2 billion tonnes. However, emissions rebounded quickly and rose by 6% in 2021 to 36.3 billion tonnes, their highest ever level. This indicates that the earth is still warming at an accelerated rate, and still not enough is being done to implement direct carbon reduction measures.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance
Using carbon removal and carbon avoidance can reduce our consumption of and reliance on fossil fuels (i.e., coal, oil, and natural gas) which can reduce the effects of global warming by limiting global greenhouse gas emissions. But they also come with various environmental benefits.
- Carbon removal: Carbon removal improves air quality, protects ecosystems, and aids in climate change mitigation.
- Carbon avoidance: Carbon avoidance via carbon offsets and direct carbon reduction measures improves air quality, protects ecosystems, and aids in climate change mitigation.
Carbon removal and carbon avoidance aid in climate change mitigation because they both aim to reduce the amount of carbon emissions in our atmosphere. Levels of carbon emissions increased exponentially to more than 35 billion tons per year at the end of the 20th century. And the global average amount of carbon in the atmosphere today registers at over 400 parts per million. The more carbon there is in our atmosphere, the more the global temperature rises, and the more serious climate change becomes. Rising global temperatures can wreak havoc on our environment, so the more we remove or avoid emitting carbon, the more we slow the rates of sea-level rise, ice melting, extreme weather occurrences, and ocean acidification.
Both also generate environmental benefits because they can help reduce overall CO2 emissions, leading to improved public health and healthier ecosystems. Offsets can reduce the instances of asthma, respiratory allergies, airway diseases, and lung cancer caused by carbon emissions. And healthy ecosystems have been linked with cleaner air, water, and food.
How Effective Are Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance in Reducing Carbon Emissions
Carbon removal and carbon avoidance can be effective at reducing carbon emissions under certain conditions.
- Carbon removal: Cost and storage capacity limits affect carbon removal effectiveness on a global scale.
- Carbon avoidance: The effectiveness of carbon avoidance via carbon offsets depends on the type of project and if the project is realized, additional, permanent, meets certain key criteria and project standards, and does not engage in greenwashing. Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures is effective because it cuts emissions at their source.
The main factors affecting carbon removal effectiveness are the cost and storage capacity limits, which depend on the removal method. For example, planting trees is one of the cheapest and most natural ways to remove carbon from the atmosphere, but storage capacity is limited by available land and can be negatively impacted by deforestation. On the other hand, direct air capture is more expensive than planting trees ($250-$650 per 1,000kg compared to $50 per 1,000kg), but the storage capacity is vastly greater.
Carbon removal is also a reactive, rather than proactive, way of dealing with emissions. In this manner, we can continue to use fossil fuels at an accelerated rate. Removal technologies are expensive to implement, and there will be little economic incentive to use them until the cost of emitting carbon rises enough to prompt behavioral changes.
The overall effectiveness of carbon avoidance via carbon offsets depends on various factors. Renewable energy offsets are generally more effective than energy efficiency offsets. But most importantly, carbon offsets must be realized to be effective. When offsets do not get realized they do not offset any carbon, and we don’t reduce any emissions. The main problem with carbon offsets is that the number of sellers on the voluntary carbon market exceeds the buyers by about 600-700 million tons. Meaning that only about 300-400 million tons of CO2 offsets actually get realized.
Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures is effective because it cuts emissions at their source. And cutting emissions at the source is the fastest way to decrease global emissions, thereby mitigating the effects of global warming.
Why Are Both Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance Important to Fight Climate Change
Carbon removal and carbon avoidance via carbon offsets are important to fight climate change because they are both ways to reduce carbon emissions. They mitigate the effects of climate change, which has a positive cascade effect on public health and plant and animal diversity. In addition, it boosts the global economy and leads to innovative, more environmentally-friendly solutions.
However, neither should be seen as a panacea for climate change. Relying on either one exclusively is impractical because they are reactive (indirect) rather than proactive (direct) ways of dealing with emissions.
Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures, on the other hand, is a direct way of dealing with carbon emissions. And in the long term, direct methods are much more effective.
What are Better Alternatives to Carbon Removal and Carbon Avoidance
If used correctly, carbon removal and carbon avoidance via carbon offsets can provide environmental, economic, and social benefits that go beyond reducing carbon emissions. They have the potential to instigate meaningful environmental change and begin to reverse some of the effects of climate change.
However, we can’t let these methods become a guilt-free way to reduce carbon emissions. Carbon removal and carbon avoidance via carbon offsets must be used in conjunction with carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures until the industry has time to invest, develop, and refine more sustainable innovations.
These reduction measures don’t have to involve drastic changes either. Actions that may seem small can have a big impact because those small changes add up! You can reduce your carbon footprint in three main areas of your life: household, travel, and lifestyle.
Reduce your household footprint:
- Wash with cold water: Washing clothes in cold water could reduce carbon emissions by up to 11 million tons. Approximately 90% of the energy is used to heat the water, so switching to cold saves also saves energy.
- Replace incandescent bulbs with fluorescent bulbs: Fluorescent bulbs use 75% less energy than incandescent ones, saving energy and thus reducing electricity demand and greenhouse gas emissions.
Reduce your travel footprint:
- Fly less: Aviation accounts for around 1.9% of global carbon emissions and 2.5% of CO2. Air crafts run on jet gasoline, which is converted to CO2 when burned.
- Walk or bike when possible: The most efficient ways of traveling are walking, bicycling, or taking the train. Using a bike instead of a car can reduce carbon emissions by 75%. These forms of transportation also provide lower levels of air pollution.
Reduce your lifestyle footprint:
- Switch to Renewable Energy Sources: The six most common types of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydro, tidal, geothermal, and biomass energy. They are a substitute for fossil fuels that can reduce the effects of global warming by limiting global carbon emissions and other pollutants.
- Recycle: Recycling uses less energy and deposits less waste in landfills. Less manufacturing and transportation energy costs means fewer carbon emissions generated. Less waste in landfills means less CH4 is generated.
- Switch from single-use to sustainable products: Reusing products avoids resource extraction, reduces energy use, reduces waste generation, and can prevent littering.
- Eat less meat and dairy: Meat and dairy account for 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with beef and lamb being the most carbon-intensive. Globally, we consume much more meat than is considered sustainable, and switching to a vegan or vegetarian diet could reduce emissions.
- Take shorter showers: Approximately 1.2 trillion gallons of water are used each year in the United States just for showering purposes, and showering takes up about 17% of residential water usage. The amount of water consumed and the energy cost of that consumption are directly related. The less water we use the less energy we use. And the less energy we use, the less of a negative impact we have on the environment.
Final Thoughts
In short, carbon removal is not the same thing as carbon avoidance. Carbon removal occurs after the emitted carbon has already entered our atmosphere. Carbon avoidance, divided into avoidance via carbon offsets and avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures, seeks to prevent carbon from being emitted in the first place. Carbon removal is reactive, whereas carbon avoidance is proactive, in terms of dealing with carbon emissions.
Both are tools in our sustainability toolbox that can be used to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change. We should not rely on carbon removal or carbon avoidance via carbon offsets to be a cure-all for our environmental problems. Carbon avoidance via direct carbon reduction measures is much more effective in reducing emissions both in the short and long term.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- American University: What is Carbon Removal?
- South Pole: Carbon Offsets Explained
- Climeworks: Homepage
- Climeworks: Direct air capture to help reverse climate change
- ClientEarth: What is a carbon sink?
- Columbia Climate School: Can Soil Help Combat Climate Change?
- World Economic Forum: The oceans are absorbing more carbon than previously thought
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Offsets and RECs: What’s the Difference?
- David Suzuki Foundation: Are carbon offsets the answer to climate-altering flights?
- Smartgrid.gov: Renewable energy – The Smart Grid
- Carbon Offset Guide: Energy Efficiency
- Greenbiz: Understanding Carbon Offsets
- GreenBiz: REC vs. Carbon Offset: Do You Know the Difference?
- Our World in Data: CO2 emissions
- National Wildlife Federation: Climate Change
- World Resources Institute: Carbon Removal
- US Department of Energy – Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management: Carbon Dioxide Removal FAQs
- Yale Environment 360: Is the ‘Legacy’ Carbon Credit Market a Climate Plus or Just Hype?
- International Energy Agency: After steep drop in early 2020, global carbon dioxide emissions have rebounded strongly
- International Energy Agency: Global CO2 emissions rebounded to their highest level in history in 2021
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Coal Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Oil Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Natural Gas? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Carbon Offsets 101
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Climate Change – Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Asthma, Respiratory Allergies and Airway Diseases
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Cancer
- Carbon Brief: Climate change will hit ‘endemic’ plants and animals the hardest, study warns
- World Economic Forum: Carbon removal – the Three Conditions to Make it Successful
- Britannica: Carbon Offset
- Terrapass: Carbon Offset Projects
- Edie: Carbon offsetting – How are businesses avoiding greenwashing on the road to net-zero?
- World Resources Institute: Direct Air Capture – 6 Things to Know
- CNBC: Carbon capture technology has been around for decades — here’s why it hasn’t taken off
- The Ocean Foundation: Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
- Cold Water Saves: Washing Laundry In Cold Water Protects A Lot More Than Just Our Clothing.
- Energy Information Administration: Renewable Energy Explained
- Energy Star: Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs (CFLs) and Mercury
- Our World in Data: Where in the world do people have the highest CO2 emissions from flying?
- Our World in Data: Which form of transport has the smallest carbon footprint?
- Zero Waste Europe: Reusable vs Single Use Packaging
- Carbonbrief: Interactive – What is the climate impact of eating meat and dairy?
- Stop Waste: Recycling and Climate Protection
- Impactful Ninja: Is Taking Long Showers Bad for the Environment?
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Showerheads