How Sustainable Is Hardboard (HDF)? Here Are the Facts
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Hardboard, also called High-Density Fiberboard (HDF), is made with exploded wood fibers salvaged from wood chips and shavings. This engineered wood is an excellent way to recycle wood waste collected from sawmills into a reasonably strong and affordable material. Though the wet wood fibers can be bound using heat and pressure, synthetic resins are often used. So we had to ask: How sustainable is it to buy products made out of hardboard?
Hardboard is largely sustainable thanks to the timber trees’ carbon sequestration. Synthetic resins used in some varieties of hardboard are, however, not environmentally friendly. When natural-based resins are used, hardboards are biodegradable and recyclable and, thus, sustainable.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the life-cycle of hardboard (HDF) used in furniture, flooring, and house-building projects. Then, we evaluate its sustainability, potential, and shortfalls. And in the end, we’ll show you tips for buying sustainable High-Density Fiberboard panels.
Here’s How Sustainable Hardboard (HDF) Is
HDF panels could be made and consumed sustainably if manufacturers source environmentally friendly components and consumers arrange to recycle HDF furniture properly. Wood is mostly a sustainable material because of timber trees’ carbon sequestration potential. And using wood waste increases the material’s environmental benefits. Though most glues contain toxic chemicals, there are natural-based bonding alternatives, which are more environmentally friendly.
“Sustainable: The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level | Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance”
Oxford Dictionary
To understand the sustainability of HDF, we assess the life-cycle of panels made with this wood composite. This life-cycle assessment (LCA) is a method to evaluate the environmental impacts of each stage in a product’s life-cycle, from the making to the recycling. Over the years, companies have strategically used LCA to research and create more sustainable products.
In this article, we’ll use the cradle-to-grave perspective of the LCA, examining the five stages of the life-cycle of furniture and flooring made with hardboard material. However, you will also find some cradle-to-gate data where relevant.
| The life-cycle stages of HDF panels | Each stage’s sustainability |
| Sourcing of HDF components | Sourcing waste material for HDF panels can be sustainable thanks to timber trees’ carbon sequestration and the utilization of chips and shavings in sawmills. On the other hand, some hardboards use resins that contain toxic chemicals. When natural materials are sourced as bonding agents in hardboards, the end products are much more environmentally friendly. |
| Manufacturing of HDF | Manufacturing HDF panels can have a significant carbon footprint due to the energy needed to run machinery to process the wood waste and make the resin (when used). |
| Transporting of HDF components | Transporting can be another carbon-intensive stage in the life-cycle of HDF furniture due to the emissions associated with operating the hauling vehicles. Transporting points include taking timber to sawmills, delivering wood waste to HDF factories, then bringing HDF furniture to stores. HDF panels made with wood waste from local sawmills have a lower carbon footprint than HDF panels containing imported woods, providing they are both sold in the US. |
| Usage of HDF | Using HDF wood furniture can be sustainable thanks to the carbon capture during the products’ long life. |
| End-of-life of HDF | The end-of-life stage for HDF furniture and flooring is not as sustainable as natural wood because most HDF panels are non-biodegradable. However, HDF can be recycled, which is the most sustainable scenario for its end-of-life stage. |
We’ll say that HDF can be a sustainable material because of its nature as a by-product made from wood waste. However, the actual environmental impact of a particular product depends on many factors. These include the type of wood waste, the bonding components, the transportation distances, and the type of hauling vehicles. Let’s dive deeper into each stage and find out how it can be more sustainable.
How Sustainable Is the Sourcing Hardboard (HDF) Components
Sourcing waste material for HDF panels can be sustainable thanks to timber trees’ carbon sequestration and the utilization of chips and shavings in sawmills. On the other hand, some hardboards use resins that contain toxic chemicals. When natural materials are sourced as bonding agents in hardboards, the end products are much more environmentally friendly.
What Is Hardboard (HDF) Made Of And What Does This Mean for Sustainability
Exploded wood fibers from chips and shavings are the main components for HDF panels. These fibers can be bound using water under high temperatures and pressures, but extra bonding agents are often used. We will first look at the sustainability of wood. Then, bonding agents often used in hardboards will be assessed for their sustainability.
How Sustainable is the Wood Used for Hardboard (HDF) Panels
As implied in the name, high-density fiberboard panels are made with wood fibers extracted from the chips and shavings accumulated in sawmills. Fiberboard, which also includes MDF (Medium-Density Board) and cellulosic fiberboard, exploits the fibrous nature of wood to engineer strong wood-based products. Thus, HDF panels tend to last longer than particle board, which is a wood composite made differently using wood particles.
Sourcing wood for HDF panels doesn’t contribute to deforestation because the input is otherwise waste material (not virgin wood). However, timber harvesting practices remain an important factor. If the wood chips come from illegally cut logs, then any hardboards made with them are not sustainable.
How Sustainable Are the Bonding Agents Used for HDF Panels
Wood fibers in hardboards can be bound together using no extra chemicals but water and heat. In this case, the final products are 100% natural. The sustainability of the wood will be the only concern in the sourcing stage.
However, manufacturers often use resins to bind the exploded wood fibers. This is a similar practice to other wood composite panels: MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) and particle board (Low-Density Fiberboard). Thus, hardboard has another name as High-Density Fiberboard.
When resins are used as the bonding agent, the nature of the final HDF panels alters depending on the type of resin used.
HDF glues can be either synthetic or natural-based. The former comes from non-renewable resources and negatively impacts the environment (and potentially people’s health). The latter are alternatives being developed to make more sustainable hardboards.
Let’s dive deeper into each group of adhesives.
The synthetic glue – phenolic resin or urea-formaldehyde resin – comes from non-renewable resources (i.e., oil and gas). These adhesives are also used in other engineered panels: plywood, MDF, and particle board.
There are several problems with phenolic glues, but the most concerning issues are health risks and recycling challenges.
These glues contain formaldehyde, which releases potentially harmful gas (Volatile Organic Compounds) into the air over a period of time. This process is called “off-gassing,” and a high-level exposure can cause skin rashes, shortness of breath, wheezing, and changes in lung function.
Not all glues containing formaldehyde have the same level of off-gassing in terms of quantity and duration. Phenolic resin has a much lower emission than urea-formaldehyde resin.
Though formaldehyde at a high level is toxic, the off-gas release is often very small once the adhesive is set and cured. Engineered wood panels with added formaldehyde are safe to use once it has time to air out and/or sealed (with an appropriate coating).
Alternative adhesives use plant-based substitutes, such as lignin, tannin, or starch. These natural-based glues tend to be better for the environment for two main reasons:
- No risk of letting off Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- The possibilities of final hardboard products being biodegradable and recyclable
This cradle-to-gate life-cycle assessment of hardboards compared different glues used in hardboards. The results indicated that HDF panels made with plant-based adhesives have lesser (negative) impacts on the environment than hardboards made with phenol resin (so-called conventional hardboards). For example, carbon emissions of hardboard panels using lignin-based adhesive are 32% lower than the carbon emissions of conventional hardboards.
Where Are Hardboard (HDF) Components Usually Sourced From
The wood component used to make hardboards comes from sawmills or forests’ waste materials. Because it is essentially a by-product, making HDF doesn’t affect tree populations. However, the harvesting method still matters because cutting down trees illegally or unsustainably can result in biodiversity loss regarding the tree species and wild animals that feed and shelter in the woods.
Biodiversity loss regarding tree species
One example is when loggers only cut down the biggest and tallest trees. That pattern would cause a reduction in the genetic diversity and quality of the trees within the stand, leading to gradual degradation of tree quality.
Biodiversity loss regarding forest animals
Cutting down trees also disrupts the forests’ wild animals, which depend on the forest for food and shelter. In this aspect, wood from short-lived trees is generally more sustainable because long-lived trees support more wildlife.
An oak tree, for example, arguably supports more wildlife than any other tree species in Northern America. (A white oak tree can live up to 600 years and a red oak tree 500 years.)
Some softwood species in the redwood and the pine family are among the oldest living tree species on earth.
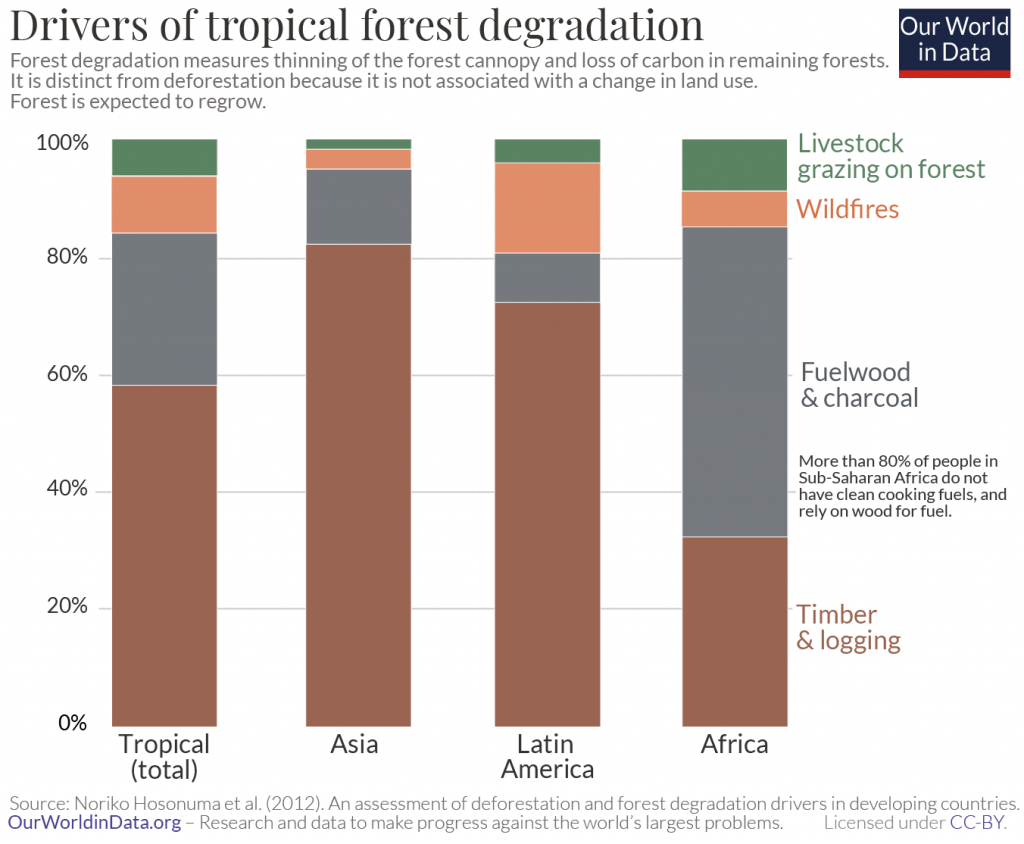
The ecological impact of logging varies depending on a tree’s native forests and the forestry management practices. The more biodiverse the forests, such as tropical rainforests in South America or Southeast Asia, the higher the cost of biodiversity loss. These bio hotspots also face rampant illegal logging and unsustainable logging, often due to lax management, to make matters worse.
The rule of thumb for you as a consumer to tackle problems caused by illegal logging is to source sustainable woods. We will point you in the right direction with hardboards at the end of this article.
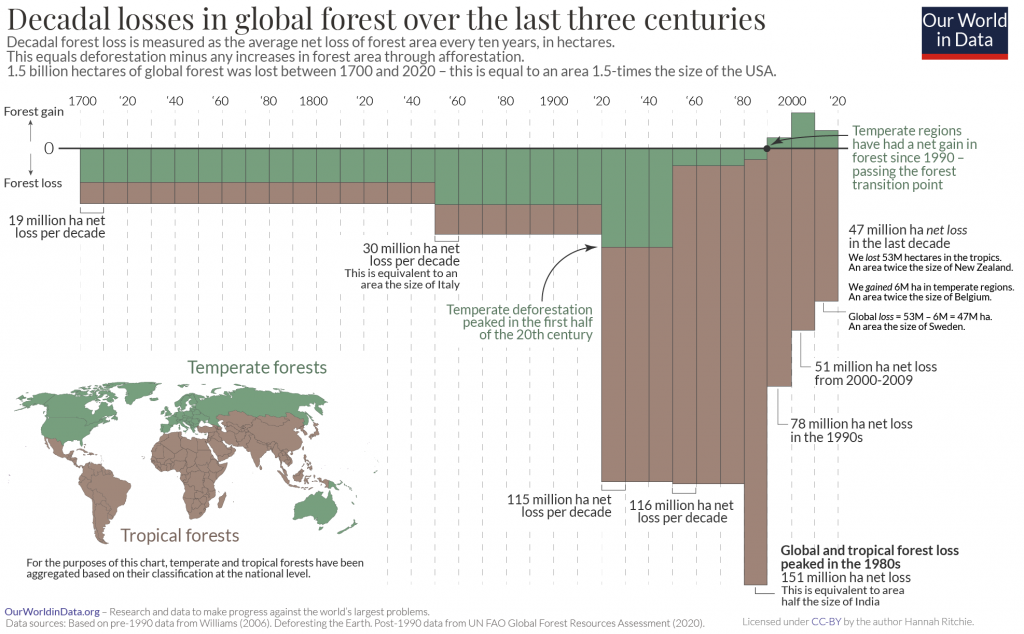
In total, logging of forestry products from plantations accounts for 26% of forest loss, a combination of deforestation and forest degradation. However, in tropical climates, the loss in bio-diverse forests is more significant (and sometimes less properly recorded) than that in temperate, well-managed logging forests.
How Sustainable Can Hardboard (HDF) Panels Be Sourced
Wood is generally considered a sustainable material because it is renewable. The growing and regrowing of wood also help mitigate the climate crisis through carbon sequestration.
As a tree grows, it absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere while releasing oxygen. The tree acts as a carbon sink during its lifespan. The longer the lifespan, the more carbon a tree uptakes and keeps out of the atmosphere.
Being a carbon sink means that they are taking greenhouse gasses out of the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the climate crisis. Carbon is then stored in branches, the trunk, and the root system. The bigger and taller a tree gets, the more it can hold.
During this growing stage, timber trees uptake carbon, generally a lot more than emissions from fuel consumption during forest management processes, including regeneration, thinning, and harvest.
According to a Cradle-to-Gate Life-Cycle Assessment of US wood composite panels, the carbon uptake for 1 m3 of hardwood panels (comprising 94% wood fibers and 6% resin) is 1355 kg CO2–eq. Because the carbon emissions calculated for all the cradle-to-gate processes total 659 kg CO2–eq, the studied hardboard material has a negative carbon footprint.
A negative carbon footprint is generally the case for High-Density Fiberboards thanks to carbon sequestration at the forestry stage. Also, hardboard panels are made mostly with wood waste, which furthers the environmental benefits of using wood.
How Sustainable Is the Manufacturing of Hardboard (HDF) Panels
Manufacturing HDF panels can have a significant carbon footprint due to the energy needed to run machinery to process the wood waste and make the resin (when used).
There are several methods of making hardboards, known as wet-, dry- and semi-dry. These methods vary by the use of water and different resin. However, there are typically seven steps from wood chips to final HDF panels:
- Pulpwood processing: Cutting wood chips into the required sizes
- Fiber preparation: Making wood fibers by steaming and refining chips at a high temperature
- Resin application: Adding the right type of resin at the right moment depending on the processing method
- Fiber drying: Drying fibers to the desired moisture content
- Mat formation: Forming panels from dried fibers
- Cold and hot pressing: Using pressure and temperature to make the final product
During these manufacturing steps, the need for fuel consumption comes from operating machinery, such as refiner, dryer, blender, and etc.
Making glues also involves fuel consumption.
When fossil fuels are needed to run machinery or generate electricity, it adds to the total carbon emissions. However, renewable energy can be used during these processes. Possible sources of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass.
According to a Cradle-to-Gate Life-Cycle Assessment of US wood composite panels, renewable resources accounted for about two-thirds of the total energy consumption in manufacturing hardboards, with biomass being the main source (66%).
In the same assessment, carbon emissions for manufacturing HDF accounted for 93% of the total amount released in all stages from cradle to gate. Still, manufacturing emission is only about 45% of the carbon uptake during forestry.
How Sustainable Is the Transportation of Hardboard (HDF)
Transporting can be another carbon-intensive stage in the life-cycle of HDF furniture due to the emissions associated with operating the hauling vehicles. Transporting points include taking timber to sawmills, delivering wood waste to HDF factories, then bringing HDF furniture to stores.
HDF panels made with wood waste from local sawmills have a lower carbon footprint than HDF panels containing imported woods, providing they are both sold in the US.
Calculations made by the Norwegian Forest and Landscape Institute showed that smaller wood hauling trucks emitted more CO2 per transported cubic meters of timber: 1.25 times more than larger wood hauling trucks, 1.3 times more than sea vessels, and six times more than freight trains. Therefore, the sustainable transportation option would be rail or large trucks running on biofuel. You can check with your HDF suppliers how their products are transported and opt for the more sustainable option.
A Cradle-to-Gate Life-Cycle Assessment of North American Hardboard found a total carbon footprint of 658.48 kg CO2–eq, including:
- Forestry operation: 17.43 kg CO2-eq
- Wood residue production: 29.43 kg CO2-eq
- Hardboard production: 611.62 kg CO2-eq
Compared with other US wood composite panels, hardboards have a lower carbon footprint than MDF, yet higher than particle boards. The emissions during manufacturing and transportation, cradle-to-gate, of the composite panels are as follows:
- Hardboard: 659 kg CO2–eq
- Particle board: 403 kg CO2–eq
- MDF: 759 kg CO2–eq
The assessment also looked into other building materials like cement, steel, plastic, and glass. The carbon footprint calculated for those non-wood materials is much higher than for wood composite panels. In the case of steel vs. hardboard, it is about 20 times higher.
How Sustainable Is the Usage of Hardboard (HDF)
Using HDF furniture can be sustainable thanks to the carbon capture storage in the products.
Though HDF is a wood-based material, it is not as durable as natural wood. Hardboard is, however, superior to MDF and particle board regarding strength, durability, and water resistance. These boards have a lifespan of 30 to 40 years.
Some hardboards are biodegradable, while some others can be recycled at designated centers, extending the carbon storage role of this engineered wood.
How Sustainable Is the End-of-Life of Hardboard (HDF)
The end-of-life stage for HDF furniture and flooring is not as sustainable as natural wood because some hardboards are non-biodegradable. However, most of these boards can be recycled, which is the most sustainable scenario for its end-of-life stage.
There are two scenarios for HDF products – furniture or flooring – at the end of their life:
- They can end up in landfills and don’t decompose. In this case, it keeps its role as carbon storage.
- Wood products can also be upcycled and reused, extending their role as carbon storage and reducing the fossil CO2 emitted as much as four times when comparing, for example, a recovered hardwood flooring with a new one. New wood products often travel much further to their markets, compared with recovered wood products. The latter is typically made in urban centers and sold locally, which lowers the transportation environmental burdens.
100% natural hardboards can be recycled fully. On the other hand, HDF panels containing synthetic resins require the kind of facilities that are not always available at household recycling. However, some local Household Waste Recycling Centers will take composite wood panels, so make sure you check in your region.
How Can You Buy Hardboard (HDF) More Sustainably
As far as the wood component in High-Density Fibreboard is concerned, relevant environmental and original certifications would help you to pick a sustainable option. Reliable certifications for sustainable woods are:
An FSC certification ensures that the wood in your hardboard panels comes from responsibly managed forests that provide environmental, social, and economic benefits.
PEFC’s approaches to sustainable forest management are in line with protecting the forests globally and locally and making the certificate work for everyone. Getting a PEFC certification is strict enough to ensure the sustainable management of a forest is socially just, ecologically sound, and economically viable but attainable not only by big but small forest owners.
Regarding glues, there are more environmentally friendly options that you can choose. Whenever possible, go for HDF that is made with formaldehyde-free adhesive. This will lower the toxicity and volatile organic compound emissions into the environment.
Similarly, if you are to seal your HDF furniture (to lower the risk of VOC emissions), pick the most environmentally friendly options available.
Why Is It Important to Buy More Sustainable Wood
Buying sustainable wood also means helping to prevent illegal or unsustainable logging, which harms the forests’ biosystems and accelerates climate change.
Logging of forestry products from plantations accounts for 26% of forest loss. Cutting down trees for wood has a lesser impact on carbon storage than digging up the whole forest floor and turning it into farms or mines. However, if logging is not sustainably managed, it can badly damage wildlife.
When logging happens in tropical forests – the bio hotspots of our planet – the biodiversity loss can be much more damaging. Subtropical and tropical forests are packed with unique wildlife – endemic mammals, birds, and amphibians. The displacement of such wildlife during poorly managed logging would be a major contributor to global biodiversity loss.
Sustainable management of forests also means that trees are cut down for timber only when they are mature. These trees will then be able to regrow and eventually replace the loss of canopy, absorb carbon from the atmosphere and reduce the effect of climate change.
Final Thoughts
You can buy hardboards as an alternative to solid wood. It is an excellent way of utilizing wood waste. However, you need to ensure that the wood used in your High-Density Fiberboard is from sustainably managed forests. Also, opt for the hardboard option with no-added formaldehyde to reduce toxic gases in the environment. Most importantly, use HDF products for as long as possible, upcycle the material to extend its usage, and arrange for it to be recycled.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Science Direct: Life-cycle assessment (LCA)
- MIT SMR: Strategic Sustainability Uses of Life-Cycle Analysis
- European Environment Agency: cradle-to-grave
- Science Direct: Cradle-to-Gate Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is MDF wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is particle wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Plywood? Here Are the Facts
- ATSDR: Formaldehyde and Your Health
- My Chemical-Free House: Is Plywood Toxic? (Non-Toxic Alternatives)
- TINY ECO HOME LIFE: Is Plywood Sustainable & What Impact Does It Have On The Environment?
- Science Direct: Environmental assessment of green hardboard production coupled with a laccase activated system
- The New York Times; Why You Should Plant Oaks
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is White Oak Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Red Oak Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Redwood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Pine Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Our World in Data: Deforestation and Forest Loss
- Composite Panel: Life cycle assessment of Particleboard, Medium Density Fiberboard, and Hardboard/Engineered Wood Siding & Trim
- US Forest Service:A comparison of hardboards manufactured by semidry-, dry-, and wet-formed processes
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Biomass Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- CORRIM: ENVIRONMENTAL PRODUCT DECLARATION – NORTH AMERICAN HARDBOARD
- Timber Blogger: What is Hardboard Siding? | Maintenance, Pros, and Cons
- Research Gate: Life cycle primary energy and carbon analysis of recovering softwood
- Forest Stewardship Council
- Program for Endorsement of Forest Certification
- Our World in Data: Epidemic Mammal Species