How Sustainable Is Mahogany Wood? Here Are the Facts
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Mahogany – the exotic beauty of the tropical – has been the wood of choice for high-end furniture for centuries. It is native to tropical dry and wet forests, some of which host the most diverse wildlife in the world. As these forests and their biodiversity play a vital ecological role, we had to ask: How sustainable is it to cut down mahogany for our products?
Mahogany is fairly sustainable wood thanks to trees’ carbon sequestration, carbon storage in products, generally long product life, and carbon offset upon recycling. However, you have to watch out that it comes from a sustainable source too and not from illegal logging or monocropping.
In this article, we’ll go through the life-cycle of mahogany wood used for furniture and other household items. Then, we evaluate its sustainability, potentials, and shortfalls. And in the end, we’ll show you tips for buying sustainable mahogany.
Here’s How Sustainable Mahogany Wood Is
Mahogany is a hardwood desired for fine furniture, music instruments, and items subject to atmospheric conditions like boats or outdoor tables and chairs. Unfortunately, some mahogany species are endangered, making it unsustainable and, in some cases, illegal to trade their wood. However, when sourced from sustainably managed forests, wood is better for the environment than plastic.
“Sustainable: The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level | Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance”
Oxford Dictionary
To understand the sustainability of mahogany we assess the life-cycle of furniture products, such as tables or cabinets. This life-cycle assessment (LCA) is a method to evaluate the environmental impacts of each stage in a product’s life-cycle, from the making to the recycling. Over the years, companies have strategically used LCA to research and create more sustainable products.
In this article, we’ll use the cradle-to-grave perspective of the LCA, examining the five stages of the life-cycle of mahogany wood.
| The life-cycle stages of mahogany wood | Each stage’s sustainability |
| Growing of mahogany wood | Growing mahogany in its native tropical forests is sustainable when illegal and over-logging are under control and it is not grown in a monocropping forest. |
| Manufacturing of mahogany wood | Manufacturing mahogany wood has a relatively low carbon footprint and its wood waste can be recycled fully as by-products or biomass pellets to substitute fossil fuel in drying wood. |
| Transporting of mahogany wood | Transporting mahogany timber and furniture has a high carbon footprint, especially when furniture is sold in Europe and the U.S., far away from mahogany forests. |
| Usage of mahogany wood | The usage of mahogany wood is sustainable because the product usually lasts for a long time. |
| End-of-life of mahogany wood | The end-of-life of mahogany wood is sustainable as the product can be upcycled or recycled for biomass energy. |
We’ll say that mahogany wood can be sustainable. However, the actual environmental impact of a particular product, like a table or a guitar, depends on many factors, especially the forest management practices and the distance and mode of transportation. Let’s dive deeper into each stage and find out how it can be more sustainable.
How Sustainable Is the Growing Mahogany Wood
Growing mahogany in its native tropical forests is sustainable, but logging practices are a cause for concern. Mahogany forest plantations, such as those found in Asia, might lack biodiversity yet could be sustainably managed.
What Type of Wood Is Mahogany and What Does This Mean for Sustainability
Mahogany is a tropical hardwood tree, highly prized for high-end furniture material. Mahogany trees grow very tall at a rate relatively faster than hardwood trees in temperate-zone forests.
How Sustainable Does Mahogany Wood Grow
Growing mahogany is sustainable when proper forest management regarding logging and land use is in place.
Two common problems that raise alarms about the sustainability of harvesting mahogany wood are:
- Diminishing natural habitat: Lax forest management and illegal logging for the highly-priced mahogany has caused a significant decrease in forests where these species grow naturally. In one case, there is a 30% reduction in population in 60 years.
- Monocropping plantations: Because countries in South American have limited or banned the export of mahogany, plantations appear in places such as Fuji, Malaysia, or the Philippines. There are concerns over the biodiversity of these monocropping commercial operations. The acid soil that mahogany thrives on doesn’t support many other organisms, making these forests almost devoid of wildlife. Intensive monocropping also brings various diseases, making these trees vulnerable to weather factors, including the changing climate.
When mahogany trees are grown in sustainably managed forests, the carbon sequestration and the short duration of growth means using the wood could be more sustainable than plastic.
- Carbon sequestration: The Hondura Big Leaf Mahogany can grow as much as 150 feet high, being on the top level of the tropical forest, as it doesn’t grow well in the shade. The tree trunk can be as big as 10 to 12 feet in diameter. Their large size means high carbon sequestration over their lifetime of 350 years and more.
- The short duration of growth: In its natural habitat in tropical forests, mahogany grows relatively fast at about 3 to 4 feet per year. That is about three times faster than an average white oak tree. As a result, a mahogany tree can reach the legal, commercial size in 50 years when it provides fine quality wood for high-end furniture.
Where Is Mahogany Wood Usually Grown
Mahogany trees of genus Swietenia are considered “genuine mahogany.” They grow natively in the Americas, throughout the Caribbean, and Central and South America. Distantly related species of Swietenia are found in Africa and Asia but are considered as providing wood of inferior quality to genuine mahogany (yet still expensive).
The genus Swietenia consists of three species (and their hybrids):
- Swietenia macrophylla, native to Central and South America: Commonly known as big-leaf mahogany, this species grows in dry and wet tropical forests of southern Mexico, along the north Atlantic slope of Central America, and down to Brazil. It’s also found in Colombia, Peru, and Bolivia, and on Cape Verde Islands.
- Swietenia mahogani, native to the Caribbean and southern Florida: The common names for this species are Caribbean, Cuba, West Indies, and sometimes true mahogany.
- Swietenia humilis, native to seasonally dry forests in the Pacific coastal region of Central America: It is commonly known as Pacific mahogany or Honduran mahogany.
The big-leaf, the most traded genuine mahogany, is listed on the Convention on Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, known as CITES. It means the trading of these species requires governmental verification regarding its legality and sustainability. The other two species are now commercially extinct due to uncontrolled harvesting and illegal logging.
Genuine mahogany has been logged and exploited for wood supply in other markets like the U.S. and Europe since the 1500s. In addition, a 2004 study has found that Bolivia no longer has commercially viable mahogany across 79% of its range. Also Peru’s mahogany native habit has halved, and a further 28% will be logged out within a decade.
When countries like Brazil and Bolivia implemented export bans, illegal logging became severe problems as both demand and price increased. “How to extract mahogany sustainably” is still a challenge in the region.
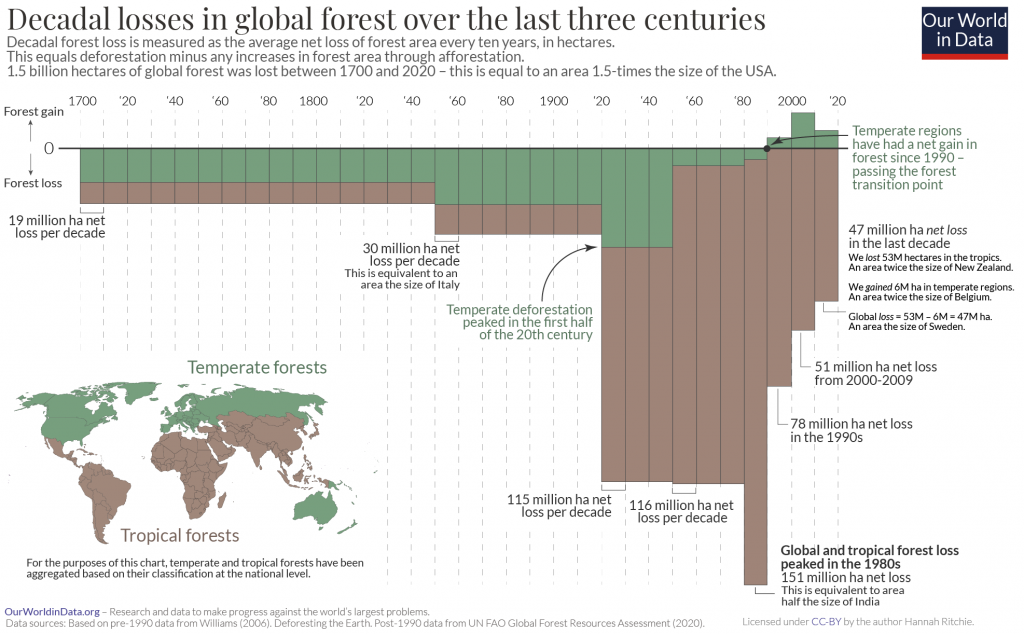
Such tropical forest loss for commercial products has devastating consequences. In total, logging of forestry products from plantations accounts for 26% of forest loss, which is a combination of deforestation and forest degradation. However, the loss in bio-diverse forests in tropical climates is more significant (and sometimes less properly recorded) than in temperate, well-managed logging forests.
Mahogany trees grown in Africa are not of the genus Swietenia but genus Khaya. They grow natively in Africa, primarily found in the Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Nigeria. Though African mahogany is not considered the same quality as genuine mahogany, the wood is still sourced at a high price, especially with the restricted export from Latin American countries.
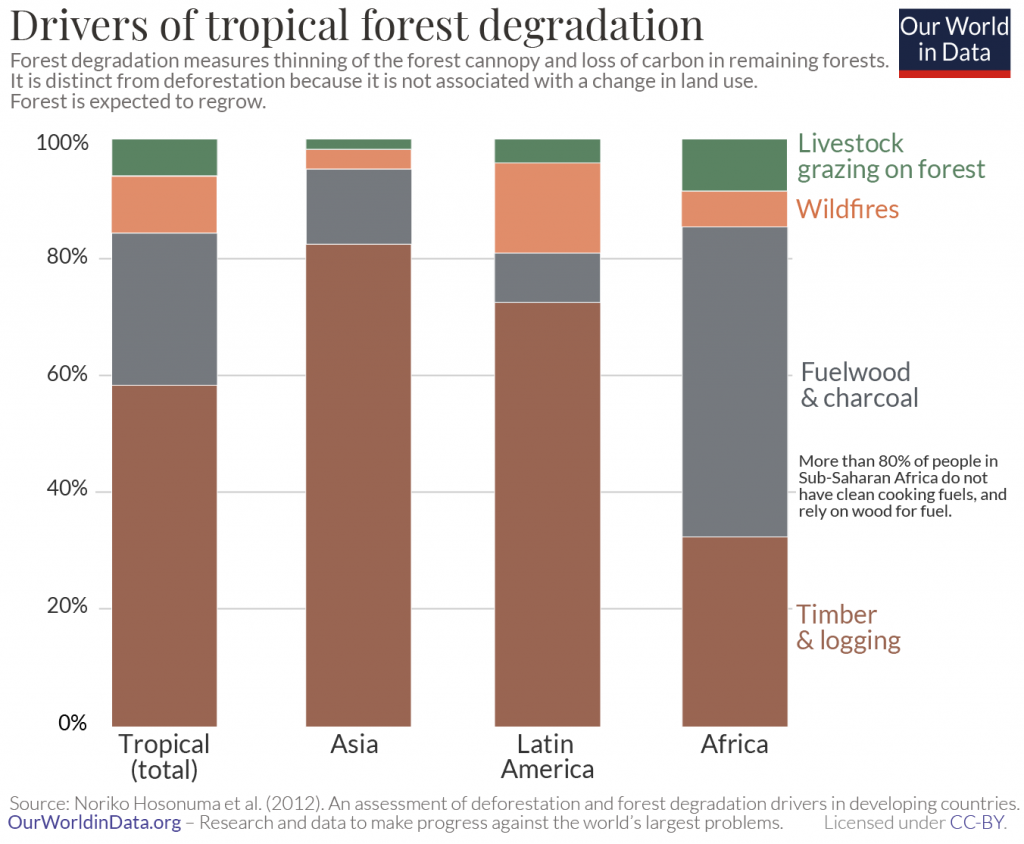
These species are either over logged as some African countries allow such practice or heavily targeted by illegal loggers. Logging in Africa is the key factor to the increase in illicit trading of bushmeat. Animals are hunted by loggers, either for themselves as food while camping or for selling as bushmeat. Loggers bulldoze new roads into pristine forests, clearing away the wildlife habitat, threatening the population of endangered species, including chimps, gorillas, and pangolins.
Mahogany trees of related species to Swietenia have also been found in plantations across Asia, like India, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand. However, despite their economic benefits, such forests don’t support wildlife and are vulnerable to climate change. Moreover, they are not sustainable as they take up the land where tropical rainforests could grow and thrive.
How Sustainable Is the Manufacturing of Mahogany Wood Into Furniture
Turning mahogany wood into furniture has a relatively low carbon footprint because wood waste can be recycled fully as by-products or biomass pellets to offset the carbon emissions during harvesting and processing. Significant reduction in carbon emissions can also come from using fossil-free energy.
The first step of manufacturing mahogany furniture involves cutting down trees and turning them into lumber in a sawmill. In one calculation, diesel utilized in harvesting the African mahogany Khaya wood to the mill accounts for 27% of all total carbon emissions up to delivering timber for furniture manufacturing. The actual emission of this step depends on how energy is generated to operate sawing machinery.
The next step is to dry lumber and turn it into furniture. Mahogany dries rapidly, which reduces the energy required for kiln drying. Besides, a significant part of the necessary energy can come from burning wood waste. At least 90% of all thermal energy used for kiln drying in the U.S. hardwood sector is derived from biomass.
How Sustainable Is the Transporting of Mahogany Wood
Transporting is a carbon-intensive stage in the life-cycle of mahogany furniture due to the emissions associated with operating the hauling vehicles that take timber to sawmills and factories, then furniture to stores.
The emission during this stage depends on the type of vehicles used, the fuel they need, and the distance the wood travels. For example, in one calculation, diesel utilized in transporting the African mahogany Khaya wood to the sawmill accounts for 21% of all total carbon emissions up to delivering timber for furniture manufacturing. In this case, much diesel is used due to transporting logs over long distances, on bad roads using low efficient trucks.
After the furniture is made, it is then transported to the stores. If the consumer market is in Europe or the U.S., far away from native mahogany forests, the transporting emission is much higher than when it is traded locally.
Calculations made by the Norwegian Forest and Landscape Institute showed that smaller wood hauling trucks emitted more CO2 per transported cubic meters of timber: 1,25 times more than larger wood hauling trucks, 1,3 times more than sea vessels, and six times more than freight trains. The cost efficiency is higher when the distance increases and emissions are reduced when using biofuels.
How Sustainable Is the Usage of Mahogany Wood
Using mahogany wood furniture can be sustainable thanks to the carbon capture during the products’ long life.
Mahogany wood is resistant to rot, mold, and other decay organisms, making it a stand-out option also for outdoor furniture. Because mahogany has no pockets or grooves, it is immune to water damage. It is up to 70% more stable than any other form of hardwood like oak or balsa. Outdoor furniture made from mahogany can last up to 40 years.
When wood is decayed, either naturally in the forest or because of damage caused by usages at home, the carbon stored in the wood is released back to the atmosphere. Therefore long-lasting furniture can be considered as a good way of keeping the carbon out of the atmosphere. If the wood is then reclaimed for making another piece of furniture, its positive carbon storage environmental impact is even higher.
How Sustainable Is the End-of-Life of Mahogany Wood
The end-of-life stage for mahogany furniture is sustainable when the wood is reused or burned for energy.
There are a few scenarios for wood products – furniture, flooring, and household items – at the end of their life.
They can end up in landfills and don’t decompose. In this case, it keeps its role as carbon storage.
Wood products can also be upcycled and reused, extending their role as carbon storage and reducing the CO2 emitted as much as four times when comparing, for example, a recovered hardwood flooring with a new one.
In another end-of-life scenario, products like a mahogany table can be burned for biomass energy displacing coal or natural gas in generating electricity. For example, in one calculation, burning a hardwood floor at the end of life can offset 75% of biomass energy consumed when making it.
How Can You Buy Mahogany Wood More Sustainably
The key to sustainably buying any wood is to check on relevant environmental and original certifications. Reliable certifications for sustainable woods are:
An FSC certification ensures that the mahogany wood comes from responsibly managed forests that provide environmental, social, and economic benefits.
PEFC’s approaches to sustainable forest management are in line with protecting the forests globally and locally and making the certificate working for everyone. Getting a PEFC certification is strict enough to ensure the sustainable management of a forest is socially just, ecologically sound, and economically viable but attainable not only by big but small forest owners.
Because there is a high risk of illegal or over logging for mahogany, both the genuine species and the African alternative, make sure you only buy mahogany with an FSC or PEFC certification. You should adhere to the same principle when buying mahogany furniture sourced from plantations across Asia.
Why Is It Important to Buy More Sustainable Wood
Buying sustainable wood also means helping to prevent illegal or unsustainable logging, which harms the forests’ biosystems and accelerates climate change.
Logging of forestry products from plantations accounts for 26% of forest loss. Cutting down trees for wood has a lesser impact on carbon storage than digging up the whole forest floor and turning it into farms or mines. However, if logging is not sustainably managed, it can badly damage wildlife.
When logging happens in tropical forests – the bio hotspots of our planet – the biodiversity loss can be much more damaging. Subtropical and tropical forests are packed with unique wildlife – endemic mammals, birds, and amphibians. The displacement of such wildlife during poorly managed logging would be a major contributor to global biodiversity loss.
Sustainable management of forests also means that trees are cut down for timber only when they are mature. These trees will then be able to regrow and eventually replace the loss of canopy, absorb carbon from the atmosphere and reduce the effect of climate change.
Final Thoughts
Making furniture from mahogany wood is sustainable as long as the material comes from sustainably managed forests. Mahogany is a tropical timber that has been exploited for a long time for high-end furniture demand in Europe and America. Though both local governments and international groups are making conservation efforts, the risk of illegal and over-logging still looms over tropical forests and their biodiverse wildlife. The sustainable approach is to buy mahogany furniture only if you are certain that it comes from a sustainable source, use it for as long as you can, upcycle the material to extend its usage, and arrange for it to be fully recycled.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Reuters: Ditch metal and plastic and turn to wood to save the planet, says U.N.
- Science Direct: Life-cycle assessment (LCA)
- MIT SMR: Strategic Sustainability Uses of Life-Cycle Analysis
- European Environment Agency: cradle-to-grave
- Tree Plantation: MAHOGANY TREE, endangered tropical hardwood
- Wildlife Journal: Why your tree planting isn’t helping the Philippine environment
- RAINFOREST ALLIANCE: Big-Leaf Mahogany
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is White Oak Wood? Here Are the Facts
- FAO: SWIETENIA AND CEDRELA IN THE NEOTROPICS
- GLOBAL TREES CAMPAIGN: Big-Leaf Mahogany
- CITES: CITES trade controls to take effect for mahogany
- ECOLOGY AND SOCIETY: Impacts of Unsustainable Mahogany Logging in Bolivia and Peru
- Our World in Data: Deforestation and Forest Loss
- Rainforest Relief: Bushmeat: Logging’s Deadly 2nd Harvest
- Academic Journals: Environmental assessment of tropical African mahogany (Khaya)
- Bailie: Proper Drying of Tropical Lumber Makes a Difference
- American Hardwood: Environmental Life Cycle Assessment
- Science Norway: Larger logging trucks give less CO2 emissions
- Sloane & Sons: Choosing the Best Material for Outdoor Furniture
- Laurel Crown: Mahogany as Outdoor Furniture
- Research Gate: Life cycle primary energy and carbon analysis of recovering softwood framing lumber and hardwood flooring for reuse
- Our World in Data: Epidemic Mammal Species