How Sustainable Is Wood Plastic Composite? Here Are the Facts
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Wood plastic composites (WPCs) are engineered wood products that recycle wood flour or fibers from different stages of other timber products. Using wood waste is a telltale sign of their sustainability. However, the majority of WPCs contain fossil-based, non-biodegradable polymers. Also, composite panels’ synthetic additives raise some health and environmental alarms. So we had to ask: How sustainable is it to buy products made out of wood plastic composite?
Wood plastic composites (WPCs) are largely sustainable because the used wood waste keeps the trees’ carbon sequestration and doesn’t contribute to more deforestation. However, they are most sustainable if their plastic component is recycled or bio-based and their additives are natural-based.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the life-cycle of wood plastic composites used in windows, flooring, and decking. Then, we evaluate its sustainability, potential, and shortfalls. And in the end, we’ll show you tips for buying sustainable wood plastic composites (WPCs).
Here’s How Sustainable Wood Plastic Composite Panels Are
Wood plastic composites could be made and consumed sustainably if manufacturers source environmentally friendly components and consumers arrange appropriate recycling when disposing of these products.
Wood is largely a sustainable material because of timber trees’ carbon sequestration potential. And using wood waste for WPCs increases the material’s environmental benefits.
“Sustainable: The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level | Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance”
Oxford Dictionary
To understand the sustainability of wood plastic composite, we assess the life-cycle of products made with these types of material. This life-cycle assessment (LCA) is a method to evaluate the environmental impacts of each stage in a product’s life cycle, from the making to the recycling. Over the years, companies have strategically used LCA to research and create more sustainable products.
In this article, we’ll use the cradle-to-grave perspective of the LCA, examining the five stages of the life-cycle of wood plastic composite panels. However, you will also find some cradle-to-gate data where relevant.
| The life-cycle stages of wood composite panels | Each stage’s sustainability |
| Sourcing of wood composite panels’ components | Sourcing wood material for wood plastic composites can be sustainable thanks to timber trees’ carbon sequestration and wood waste utilization. Using recycled polymers reduces carbon footprint and negative ecological impacts regarding the thermoplastic part. Lastly, it is possible to have biodegradable WPCs when components are derived entirely from bio-based materials. |
| Manufacturing of wood composite panels | Manufacturing wood plastic composites can have a significant carbon footprint due to the energy needed to run machinery to process the wood waste and make the synthetic polymers and additives (when used). |
| Transporting of wood composite panels’ components | Transporting can be another carbon-intensive stage in the life-cycle of wood plastic composites due to the emissions associated with operating the hauling vehicles, from forests to manufacturing facilities to customers. WPCs made with wood waste from local sawmills would have a lower carbon footprint than ones containing imported woods. |
| Usage of wood composite panels | Using wood plastic composites can be sustainable thanks to the carbon capture storage in the products. |
| End-of-life of wood composite panels | The end-of-life stage for wood plastic composites is not as sustainable as natural wood because most of these products are non-biodegradable. However, many products can be recycled. Also, some 100% bio-based WPCs are bio-degradable, which is the most sustainable scenario for the end-of-life stage. |
We’ll say that wood plastic composites can be made more environmentally friendly using wood waste and recycled or bio-based plastics. However, the actual environmental impact of a particular product depends on many factors. These include the kind of wood waste, the origin of the plastic component, and the additives. Also, the transportation distances and the type of hauling vehicles matter. Let’s dive deeper into each stage and find out how it can be more sustainable.
How Sustainable Is the Sourcing of Wood Plastic Composite Components
Sourcing wood material for wood plastic composites can be sustainable thanks to timber trees’ carbon sequestration and wood waste utilization. Using recycled polymers reduces carbon footprint and negative ecological impacts regarding the thermoplastic part. Lastly, it is possible to have biodegradable WPCs when components are derived entirely from bio-based materials.
What Are Wood Plastic Composites Made Of And What Does This Mean for Sustainability
In the most simplistic sense, wood plastic composite contains three components:
- Wood flour or fiber (i.e., the wood part)
- Thermoplastics (i.e., the plastic part)
- Additives (to bind the wood and plastic parts, strengthen the product, fill the gap, etc.)
We will look at each of these for their sustainability.
How Sustainable is the Wood Used for Wood Plastic Composites
The wood component in WPCs is generally in the sawdust form or small fibers. Wood accounts for between 50 to 70% of the total weight of the WPC.
In most cases, wood fiber or flour is utilized from waste materials – chips and shaving leftover after sawing lumber for other products. Maple, oak, or pine are common types of sawdust.
Small pieces of virgin wood are sometimes used to make large panels of WPCs. Smaller trees don’t provide lumber in the oversize occasionally needed in construction. Consequently, wood plastic composites are the solution.
Utilizing wood waste is favorable for the environment because it doesn’t contribute to deforestation.
Using smaller pieces of wood (instead of cutting down bigger, older trees) has lesser negative ecological impacts. The reason is that big, old trees play a more significant role in supporting wildlife.
Timber harvesting practices remain important in both scenarios (using wood waste or small virgin wood pieces). If the wood chips come from illegally cut logs, then WPCs made with them are not sustainable.
Though it might be difficult to find the origin of the wood source, a good indicator of the sustainability of this component is to check the sustainability certificates available. We will point you in the right direction in the later section.
Materials such as bamboo, rice straw, rubberwood, and sugarcane bagasse, have been used as alternatives to wood to manufacture composite panels. However, we only cover polymer composites reinforced with wood flour/fiber in this article.
How Sustainable Are the Thermoplastics Used for Wood Plastic Composites
Wood plastic composites use thermoplastics – a kind of polymer. Here are some thermoplastics commonly used in WPCs:
The biggest share in the WPC market is Polyethylene (PE), of which manufacturing depends heavily on fossil fuels. Other fossil-based plastics used in WPCs are PVC, PP, and PS.
Sourcing fossil-based polymers leads to an increased carbon footprint in WPCs. In comparison, composite wood panels like the Masonite hardboard can be manufactured entirely from wood fibers.
- Though most thermoplastics used in WPCs are derived from fossil fuels, there are also 100% bio-based options.
- Too, using recycled plastics results in more sustainable WPCs.
For example, PLA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and renewable thermoplastic derived from corn starch. Also, bio-based polyethylene (from sugar cane and bio-based polyamides from castor have become increasingly commercially available.
WPCs made with these types of thermoplastics can be all-natural and, in some cases, biodegradable. Research showed that sourcing bio-based polymers improved sustainability and carbon footprint compared to conventional wood plastic composites.
Another alternative is to use recycled plastics to make new WPCs. A life-cycle assessment of WPCs showed that using secondary material (recycled plastics) in new WPCs is an ecologically superior alternative to WPC incineration
How Sustainable Are the Additives Used for Wood Plastic Composites
Additives are used to bind wood fibers and thermoplastic polymers, strengthening the end products and creating desired features.
Different types of additives are used depending on the polymers and the manufacturing products. However, regarding sustainability, they can be divided into bio-based materials and synthetic materials.
Synthetic additives used in wood plastic composites often come from non-renewable resources (i.e., oil and gas) and carry several problems, including health risks and recycling challenges.
For example, common binding agents tend to contain formaldehyde, which releases potentially harmful gas (Volatile Organic Compounds) into the air over a period of time. This process is called “off-gassing,” and a high-level exposure can cause skin rashes, shortness of breath, wheezing, and changes in lung function.
Not all glues containing formaldehyde have the same level of off-gassing in terms of quantity and duration. Phenolic resin has a much lower emission than urea-formaldehyde resin.
Though formaldehyde at a high level is toxic, the off-gas release is often very small once the adhesive is set and cured. Engineered wood panels with added formaldehyde are safe to use once it has time to air out and/or sealed (with an appropriate coating).
The use of synthetic materials results in non-biodegradable end-products.
Alternative additives use natural substances from plants or animals.
Natural-based solutions tend to be better for the environment for two main reasons:
- No risk of letting off Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- The possibilities of wood composite panels being biodegradable and recyclable
Where Are Wood Plastic Composite Components Usually Sourced From
Using wood waste to make wood plastic composites doesn’t contribute to further deforestation. However, the harvesting method still plays a significant role in the overall sustainability of WPCs.
Cutting down trees, especially if done illegally or unsustainably, can result in biodiversity loss regarding the tree species and wild animals that feed and shelter in the woods.
Biodiversity loss regarding tree species
One example is when loggers only cut down the biggest and tallest trees. That pattern would cause a reduction in the genetic diversity and quality of the trees within the stand, leading to gradual degradation of tree quality.
Biodiversity loss regarding forest animals
Cutting down trees also disrupts the forests’ wild animals, which depend on the forest for food and shelter. In this aspect, wood from short-lived trees is generally more sustainable because long-lived trees support more wildlife.
Some softwood species in the redwood and the pine family can live for many thousands of years. A white oak tree can live up to 600 years and a red oak tree 500 years.
Conversely, some timber species have much shorter lifespans: less than two decades, like a mango tree, or a couple of centuries, like an aspen tree. Alternatively, species like bamboo can be cut after a few years of planting because they regrow quickly.
Besides, the ecological impact of logging varies depending on a tree’s native forests and the forestry management practices. The more biodiverse the forests, such as tropical rainforests in South America or Southeast Asia, the higher the cost of biodiversity loss. These bio hotspots also face rampant illegal logging and unsustainable logging, often due to lax management, to make matters worse.
Here is the list of woods from tropical forests, some of which are the world’s richest in biodiversity. You need to purchase these woods with caution, whether it is in the form of natural wood or wood composite panels:
The rule of thumb for you as a consumer to tackle problems caused by illegal logging is to source sustainable woods. We will point you in the right direction with wood plastic composite at the end of this article.
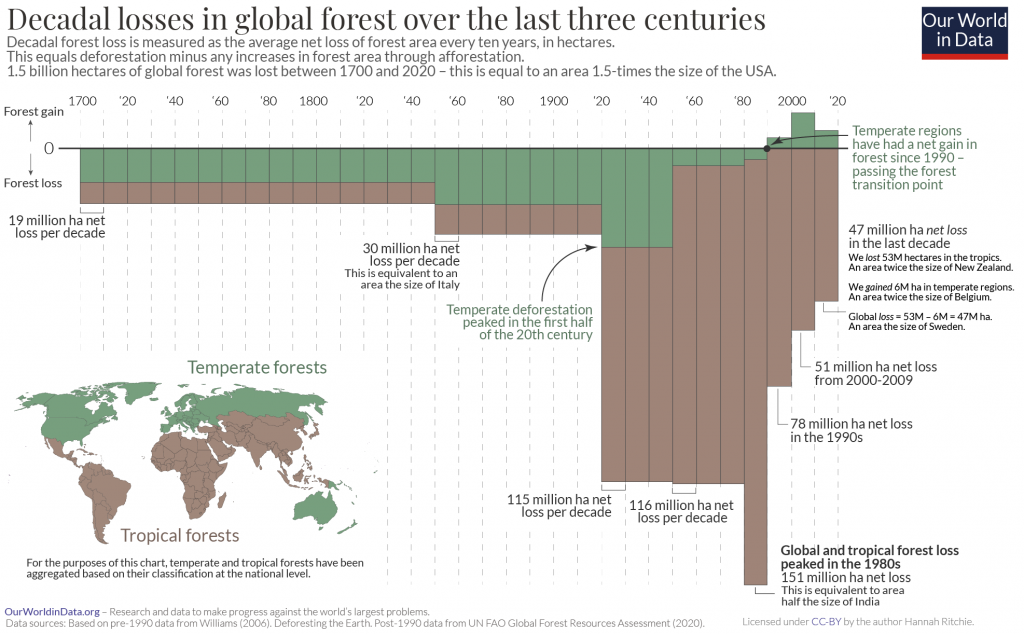
In total, logging of forestry products from plantations accounts for 26% of forest loss, a combination of deforestation and forest degradation. However, in tropical climates, the loss in bio-diverse forests is more significant (and sometimes less properly recorded) than that in temperate, well-managed logging forests.
How Sustainably Can Wood Plastic Composite Panels Be Sourced
Wood is generally considered a sustainable material because it is renewable. The growing and regrowing of wood also help mitigate the climate crisis through carbon sequestration.
As a tree grows, it absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere while releasing oxygen. The tree acts as a carbon sink during its lifespan. The longer the lifespan, the more carbon a tree uptakes and keeps out of the atmosphere.
Being a carbon sink means that they are taking greenhouse gasses out of the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the climate crisis. Carbon is then stored in branches, the trunk, and the root system. The bigger and taller a tree gets, the more it can hold. (Carbon accounts for 50% of a tree’s dry weight).
During this growing stage, timber trees sequester carbon, generally a lot more than emissions from fuel consumption during forest management processes, including regeneration, thinning, and harvest.
According to a study of wood plastic composites containing bio-based polymers, the amount of CO2 generated by the processing of the composite material is partially or completely compensated by the carbon uptake during the growth phase of the plants used as raw materials.
How Sustainable Is the Manufacturing of Wood Plastic Composites
Manufacturing wood plastic composites can have a significant carbon footprint due to the energy needed to run machinery to process the wood waste and make the synthetic polymers and additives (when used).
The manufacturing methods for WPCs vary depending on the wood and plastic components as well as the coupling technologies. However, it typically involves some of the following steps:
- Recovering and prepping wood fibers into the required sizes
- Manufacturing polymers or recovering waste plastics
- Mixing the two components, using additives such as colorants, coupling agents, blowing agents, reinforcing agents, foaming agents, and lubricants depending on the desired end product
The manufacturing of some polymers depends heavily on fossil fuels. This is the reason why WPCs are typically not as environmentally friendly as composites made mostly with wood fibers.
During these manufacturing steps, there is also the need for fuel consumption to operate machinery, such as refiner, dryer, blender, etc.
When fossil fuels are needed to run machinery or generate electricity, it adds to the total carbon emissions. However, renewable energy can be used during these processes. Possible sources of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass.
How Sustainable Is the Transportation of Wood Plastic Composites
Transporting can be another carbon-intensive stage in the life-cycle of wood plastic composites due to the emissions associated with operating the hauling vehicles, from forests to manufacturing facilities to customers.
WPCs made with wood waste from local sawmills would have a lower carbon footprint than ones containing imported woods.
Here is a list of popular woods that can be hauled from the US forests:
| Hardwoods | Softwoods |
| Aspen | Cedar |
| Ash | Douglas fir |
| Basswood | Pine |
| Beech | Spruce |
| Birch | Redwood |
| Black cherry | |
| Elm | |
| Hickory | |
| Maple (soft and hard) | |
| Oak (white and red) | |
| American Tulipwood | |
| Walnut | |
| Willow |
Because of their various weights, some American woods have a higher transporting carbon footprint than others. Check our articles for individual woods for the specifics.
And here are examples of imported woods, which travel long distances to reach the US market:
Calculations made by the Norwegian Forest and Landscape Institute showed that smaller wood hauling trucks emitted more CO2 per transported cubic meters of timber: 1.25 times more than larger wood hauling trucks, 1.3 times more than sea vessels, and six times more than freight trains. Therefore, the sustainable transportation option would be rail or large trucks running on biofuel. You can check with your suppliers how their wood composite panels are transported and opt for the more sustainable option.
How Sustainable Is the Usage of Wood Plastic Composites
Using wood plastic composites can be sustainable thanks to the carbon capture storage in the products.
WPCs have excellent resistance to cracking and splitting. These composite products can last longer than equivalent solid woods in outdoor environments because they are stronger and less prone to humidity-induced buckling. Similarly, WPCs are often used as a replacement for MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) and particle boards in high humidity areas.
Some varieties of wood plastic composites are biodegradable, while some others can be recycled at designated centers, extending the carbon storage role of this wood plastic composite.
How Sustainable Is the End-of-Life of Wood Plastic Composites
The end-of-life stage for wood plastic composites is not as sustainable as natural wood because most of these products are non-biodegradable. However, many products can be recycled. Also, some 100% bio-based WPCs are bio-degradable, which is the most sustainable scenario for the end-of-life stage.
There are some scenarios for wood plastic composite panels at the end of their life:
- They can end up in landfills and don’t decompose. In this case, it keeps its role as carbon storage.
- Some WPCs are made entirely from biomaterials and can be left to decompose naturally at the end of life.
- Some WPCs can be recycled. Reusing the thermoplastic polymer(s) improves the overall sustainability of WPCs.
How Can You Buy Wood Plastic Composites More Sustainably
As far as the wood component is concerned, relevant environmental and original certifications would help you to pick a sustainable option. Reliable certifications for sustainable woods are:
An FSC certification ensures that the wood in your WPCs comes from responsibly managed forests that provide environmental, social, and economic benefits.
PEFC’s approaches to sustainable forest management are in line with protecting the forests globally and locally and making the certificate work for everyone. Getting a PEFC certification is strict enough to ensure the sustainable management of a forest is socially just, ecologically sound, and economically viable but attainable not only by big but small forest owners.
Regarding plastics and additives, there are more environmentally friendly options that you can choose. Whenever possible, go for bio-based, degradable materials.
Why Is It Important to Buy More Sustainable Wood
Buying sustainable wood also means helping to prevent illegal or unsustainable logging, which harms the forests’ biosystems and accelerates climate change.
Logging of forestry products from plantations accounts for 26% of forest loss. Cutting down trees for wood has a lesser impact on carbon storage than digging up the whole forest floor and turning it into farms or mines. However, if logging is not sustainably managed, it can badly damage wildlife.
When logging happens in tropical forests – the bio hotspots of our planet – the biodiversity loss can be much more damaging. Subtropical and tropical forests are packed with unique wildlife – endemic mammals, birds, and amphibians. The displacement of such wildlife during poorly managed logging would be a major contributor to global biodiversity loss.
Sustainable management of forests also means that trees are cut down for timber only when they are mature. These trees will then be able to regrow and eventually replace the loss of canopy, absorb carbon from the atmosphere and reduce the effect of climate change.
Final Thoughts
You can buy wood plastic composite as an alternative to solid wood and engineered wood panels like MDF or LDF. WPCs are an excellent way of utilizing wood waste. However, you need to ensure that the wood component comes from sustainably managed forests. Also, opt for the increasingly-available options of either bio-based or recycled polymers. Most importantly, use wood plastic composites for as long as possible, upcycle the material to extend its usage, and arrange it to be recycled appropriately.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Science Direct: Thermoplastics
- Science Direct: Life-cycle assessment (LCA)
- MIT SMR: Strategic Sustainability Uses of Life-Cycle Analysis
- European Environment Agency: cradle-to-grave
- Science Direct: Cradle-to-Gate Assessment
- Sicience Direct: Biopolymers: Applications and Trends
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Maple Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Pine Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Science Direct: Polyethylene
- Science Direct: Polyvinyl chloride
- Science Direct: Polylactic Acid
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Engineered (Composite) Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Hardboard (HDF)? Here Are the Facts
- Science Direct: Sustainable wood-plastic composites from bio-based polyamide 11 and chemically modified beech fibers
- SpringerLink: Life–Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Plastic–Wood Composites
- ATSDR: Formaldehyde and Your Health
- My Chemical-Free House: Is Plywood Toxic? (Non-Toxic Alternatives)
- TINY ECO HOME LIFE: Is Plywood Sustainable & What Impact Does It Have On The Environment?
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Redwood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is White Oak Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Red Oak Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Mango Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Aspen Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Bamboo “Wood”? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Mahogany Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Ipe Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Cumaru Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Tigerwood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Rosewood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Meranti Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Cocobolo Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Ebony Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Merbau Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Wenge Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Teak Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Our World in Data: Deforestation and Forest Loss
- Science Direct: Sustainable wood-plastic composites from bio-based polyamide 11 and chemically modified beech fibers
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Solar Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Wind Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Hydropower Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Geothermal Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Biomass Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Ash Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Basswood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Beech Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Birch Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Black Cherry Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Elm Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Hickory Wood? Here Are the Facts
- mpactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Tulipwood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Walnut Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Willow Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Cedar Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Douglas Fir Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Pine Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Spruce Wood? Here Are the Facts
- Science Norway: Larger logging trucks give less CO2 emissions
- Science Direct: Tribology of Natural Fiber Polymer Composites (Second Edition)
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is MDF? Here Are the Facts
- Impactful Ninja: How Sustainable Is Particle Board (LDF)? Here Are the Facts
- Forest Stewardship Council
- Program for Endorsement of Forest Certification
- Our World in Data: Epidemic Mammal Species