Is All Renewable Energy Sustainable? Nearly…
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
A common misconception is that renewable energy sources will never run out. And while it is true that renewable resources naturally replenish themselves over time, they can only remain in infinite supply if we use the resources sustainably. Consuming the resources faster than they can replenish causes a renewable resource to become unsustainable and can lead to the eventual depletion of this resource. So we had to ask: Is all renewable energy sustainable?
Most renewable energy is sustainable but not all – depending on their rate of natural replenishment and environmental impact. Geothermal energy is the most sustainable renewable resource; solar, wind, hydro, and tidal energy can be sustainable; biomass energy, however, is generally not sustainable.
Knowing the difference between a renewable resource and a sustainable resource is important when making decisions regarding energy substitutes for fossil fuels. Not only should the energy be non-polluting, but it should aim to preserve the environment as much as possible. Below we will define both renewable and sustainable and examine the sustainability of the six most common renewable energy sources.
What Is the Difference Between Renewable and Sustainable Energy
Renewable and sustainable energy sources are alternatives to fossil fuels and aid in the fight against global climate change because they help curtail greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs). Knowing the difference between the two allows us to make better-informed decisions regarding our energy usage now and in the future.
“Renewable Energy: energy that is produced using the sun, wind, etc., or from crops, rather than using fuels such as oil or coal | types of energy that can be replaced naturally such as energy produced from wind or water”
Cambridge Dictionary
Renewable energy can be sustainable if the rate at which we harvest the resource remains below the rate at which the resource can naturally replenish itself. When we begin harvesting resources faster than they can be replenished, renewable energy becomes unsustainable.
“Sustainable: The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level | Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance”
Oxford Dictionary
Sustainable energy sources meet the needs of our current generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. They aim to limit GHGs while preserving the natural integrity of the environment.
To sum it up, renewable energy sources are flow-limited because there is a limited amount of energy available per unit of time. Renewable energy is sustainable as long as the rate of harvest stays below the rate of natural replenishment.
Which Renewable Energy Is Sustainable and Which Is Not
The six most common types of renewable energy are: solar, wind, hydro, tidal, geothermal, and biomass energy. They are a substitute for fossil fuels (e.g., coal and oil) that can reduce the effects of global warming by limiting global GHGs.
| Type of renewable energy | How sustainable is it? |
| Solar energy | Sustainable because it is non-polluting. Proper siting of solar farms is necessary to minimize environmental impacts. |
| Wind energy | Sustainable because it is non-polluting. Proper siting of wind farms is necessary to minimize environmental impacts. |
| Hydro energy | Dependent on the scale of energy generation. Low hydro is more sustainable than large hydro because it produces fewer GHGs and has a minute environmental impact. |
| Tidal energy | Sustainable because tidal is non-polluting and can have a minimal environmental impact depending on what technology is used. More research is needed before implementation. |
| Geothermal energy | Very sustainable because geothermal is non-polluting and it recycles the water used. |
| Biomass energy | Not sustainable because the rate of plant harvest often exceeds the rate of plant growth. Burning biomass also releases GHGs into the atmosphere. |
One of the best ways to preserve natural resources and maintain global ecosystems for future generations is to utilize renewable energy sources. Renewables can provide an infinite energy supply that is beneficial for the environment, but only if we use them sustainably. Harvesting, utilizing, operating, and building infrastructure for renewables are all areas where the energies could become unsustainable.
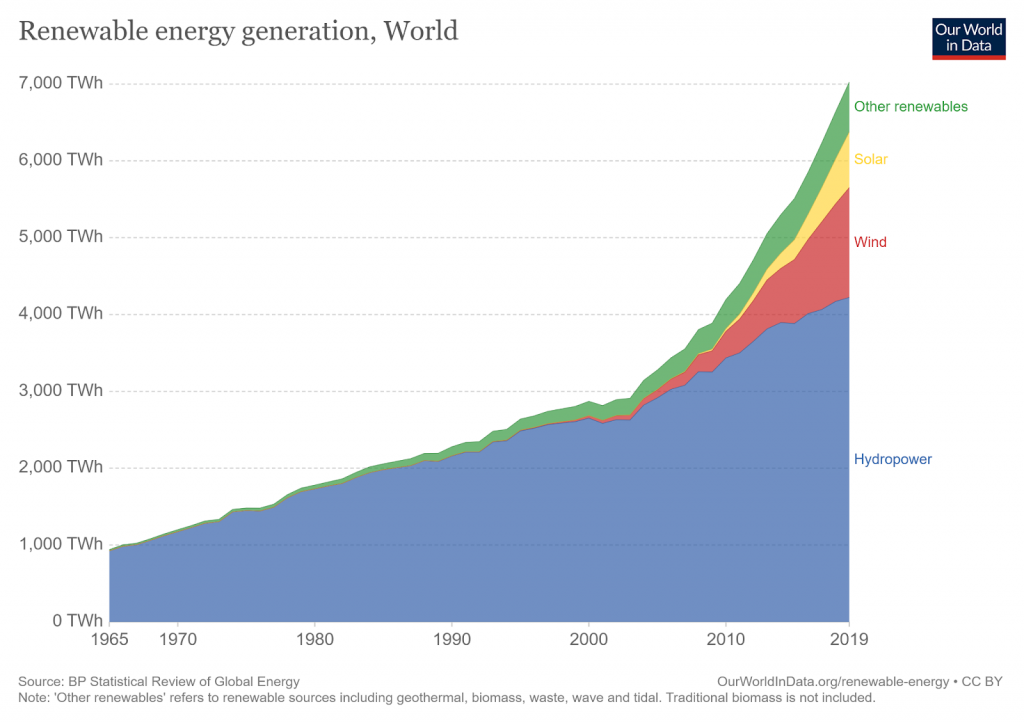
Below, we will evaluate the sustainability of the six most common renewables by focusing on their environmental sustainability. Environmental sustainability is defined as maintaining ecological integrity, balancing environmental systems, and consuming natural resources at a rate by which they can replenish themselves.
How Sustainable Is Solar Energy
Harnessing the power of the sun falls into two main categories:
- Photovoltaic (PV) solar cells: photovoltaic cells in solar panels absorb energy from sunlight, creating an electrical charge. This charge moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
- Concentrating solar thermal plants (CSP): mirrors reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect and convert solar energy into heat. This is utilized in very large power plants.
Solar energy is a renewable energy source because solar energy can be harnessed as long as the sun continues to shine. But just how sustainable is it?
The main concerns associated with solar energy are land use, water use, and hazardous materials.
- Land use: The scale of land degradation and habitat loss depends on the technology, site topography, and intensity of the solar resource. Siting large-scale solar farms on abandoned land and small-scale farms on top of buildings or homes can minimize negative environmental impacts.
- Water Use: Water is used to construct PV components, and CSPs require water for cooling. Wet-recirculating, once-through, and dry-cooling methods are used to reduce the amount of water used.
- Hazardous Materials: Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen fluoride, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, and acetone are all used to manufacture PV cells. If not handled and disposed of properly, they could present a serious risk to environmental and public health. Strict laws are in place to reduce the likelihood of this occurring.
Overall, solar energy is sustainable because it has minimal GHGs and does not negatively affect the environment, provided that proper siting and disposal methods are followed.
Solar power has a life-cycle global warming emission between 0.08 and 0.2 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour, while coal power plants have an estimated 1.4-3.6 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour emission.
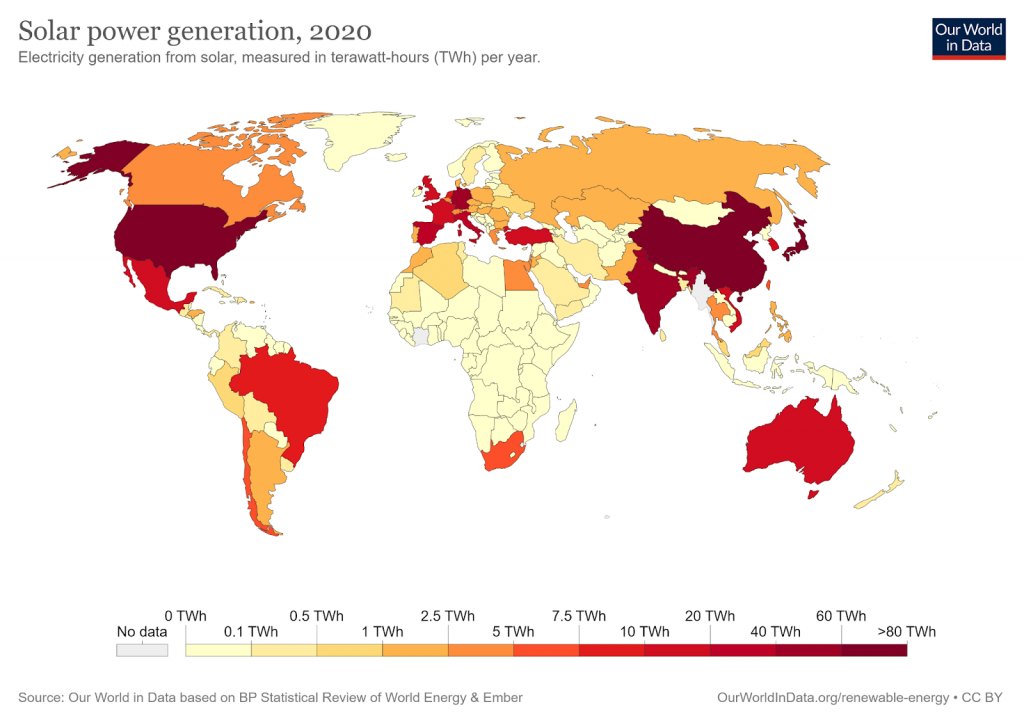
The U.S. generated 3% of its energy from solar in 2020, which is an increase from 0.1% in 2010.
How Sustainable Is Wind Energy
Wind is a form of solar energy that is caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface, irregularities of the earth’s surface, and the earth’s rotation. To harness wind energy, the wind turns the turbine blades around a rotor, which spins a generator to create electricity. An average annual wind speed of 9 miles per hour (mph) or 4 meters per second (m/s) for small turbines and 13mph (5.8m/s) for utility-scale turbines is necessary to economically harness wind energy.
Wind energy is a renewable energy source because as long as the wind blows, its power can be harnessed. But just how sustainable is it?
The three main concerns associated with wind energy are land use, wildlife impact, and public health.
- Land use: wind farms take up a substantial amount of land, but the areas between and around turbines can be used for livestock grazing, agriculture, highways, and hiking trails. The amount of land disturbed when a turbine is constructed is minimal, and they can be sited on abandoned lands to further reduce land impacts.
- Wildlife Impact: turbine blades are large and pose a threat to flying wildlife such as birds and bats. While this is true, the threat is quite minimal. Extensive research and technological advances have reduced turbine-caused wildlife death. For example, turbines are kept motionless when wind speeds are low because bats are most active at these speeds.
- Public Health: turbines can cause mechanical and aerodynamic noise pollution when constructed close to residential areas. Siting wind farms in remote locations or on abandoned lands can reduce this effect.
Overall, wind energy is sustainable because it does not emit greenhouse gases and land use, wildlife impact, and public health concerns are mitigated by proper planning and siting of wind farms.
Wind turbines have a life-cycle global warming emission between 0.02 and 0.04 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour, while coal power plants have an estimated 1.4-3.6 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour emission.
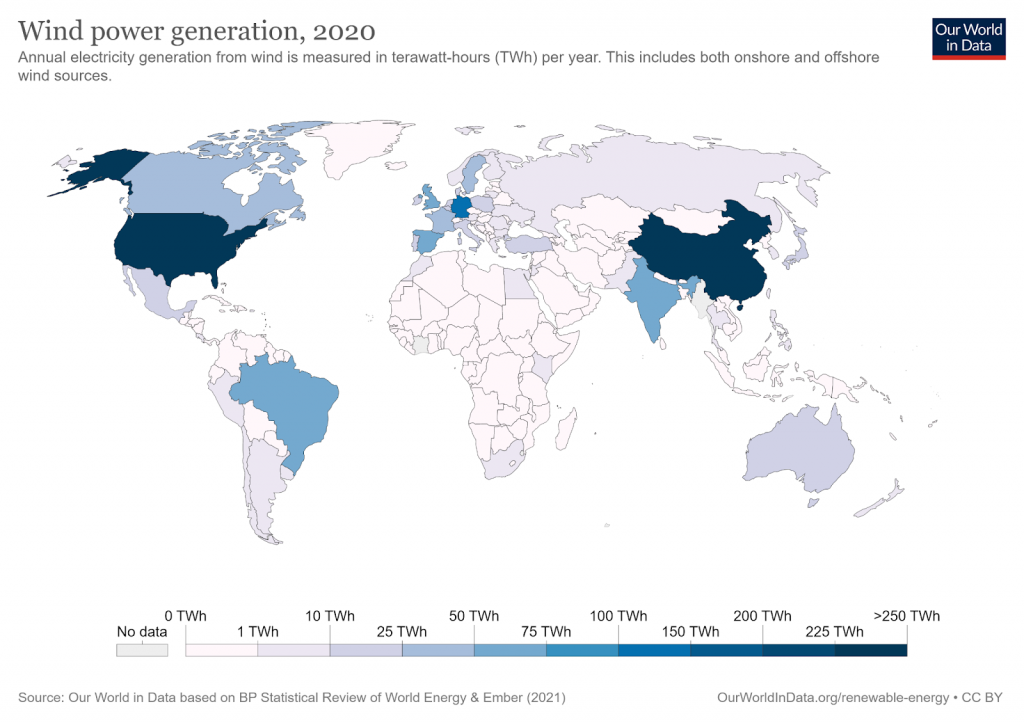
The U.S. produced 24% of its renewable energy from wind energy in 2019.
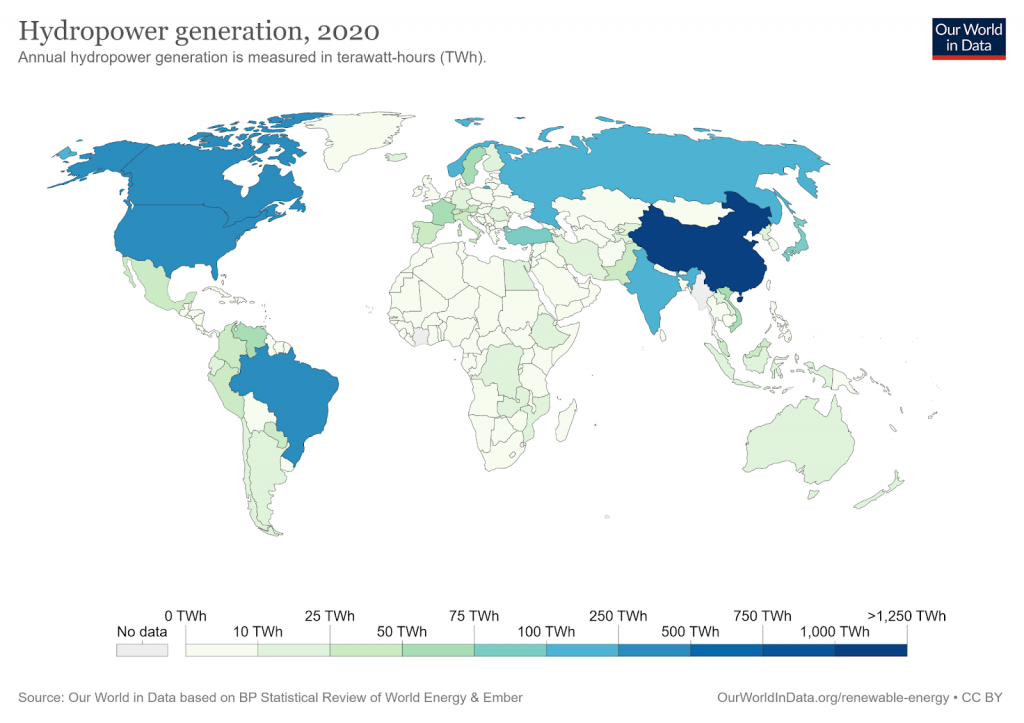
How Sustainable Is Hydro Energy
To harness energy from water, flowing water turns turbines and spins a generator to generate electricity. Hydropower can be divided into two main categories depending on how many megawatts of power are generated.
- Low-Impact Hydropower (Low Hydro): projects that generate 10 MW or less of power. On a small scale, hydropower produces very few greenhouse gases and has little to no environmental impact. Installing small turbines in irrigation canals, water-treatment plant outfalls, and existing hydroelectric facilities mitigates possible emissions and environmental impact.
- Large Hydropower (Large Hydro): facilities with a generating capacity of more than 30 megawatts (MW). The construction of large hydroelectric facilities and biomass decomposition in the reservoirs produces GHGs (e.g. carbon dioxide and methane), although the rate of emissions is much lower than that of fossil fuels. Also, dams that create reservoirs can obstruct fish migration, alter the water temperature and chemistry, and flood out adjacent lands.
Hydro energy is a renewable energy source because the water cycle is a continuous process that recharges itself. But just how sustainable is it?
The overall sustainability of hydropower depends on the scale at which it is generated.
- Low hydro is more sustainable than large hydro because it produces fewer GHGs and has a minute environmental impact. However, the amount of energy that can be generated from low hydro is less than what can be generated from large hydro.
- Large hydro is less sustainable than low hydro because it produces more GHGs and has the potential to alter the natural state of the environment. However, it can contribute significantly higher amounts of energy to the power grid because it operates on a larger scale.
The life-cycle global warming emission for low hydro is between 0.01 and 0.03 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour, while coal power plants have an estimated 1.4-3.6 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour emission. Large hydro emission is approximately 0.06 in arid regions but maybe over 0.5 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour in tropical regions.
How Sustainable Is Tidal Energy
The gravitational pull of the sun and moon coupled with the rotation of the earth creates tides in the ocean. Tidal turbines, barrages, and lagoons use the rise and fall of tides to spin a generator to produce electricity. A minimum tidal range of 10 feet is required to economically harness energy.
Tidal energy is renewable because the rotation of the earth and the gravitational pull of the sun and moon will continue until the end of time. But just how sustainable is it?
Tidal streams, barrages, and lagoons are the three ways to generate electricity from tides, and each comes with its own set of environmental impacts.
- Stream: turbines are placed in tidal streams. The machines are large and can disrupt the tides. The size of the turbine and the location of the tidal stream will dictate the level of environmental impact.
- Barrage: a barrage (dam) is placed across a river, bay, or estuary. The barrage gates open as the tide rises and close at high tide, creating a lagoon. The water is then released through the turbines which spin a generator to create electricity. Barrages cause significant land disruption within the tidal range, and the change in water and salinity levels within the lagoon can harm plant and animal life. Also, turbines in barrages move fast and can kill marine life in their blades.
- Lagoon: a body of ocean water is partially enclosed by a man-made barrier. Lagoons function in the same manner as a barrage, but they generate continuous power and can also be constructed along a coastline. Lagoons provide a minimal level of environmental impact but also generate the least amount of energy. They can be constructed with natural materials like rock and would easily allow marine life to pass through.
Overall, lagoons are the most sustainable form of tidal energy, followed by tidal streams and lastly by barrages.
More research needs to be performed on tidal systems, but estimates for the life-cycle global warming emission of tidal energy are below 0.05 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour, while coal power plants have an estimated 1.4-3.6 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour emission.
The Rance Tidal Power Station in France and the Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station in South Korea are among the few commercial-sized tidal power plants currently in operation.
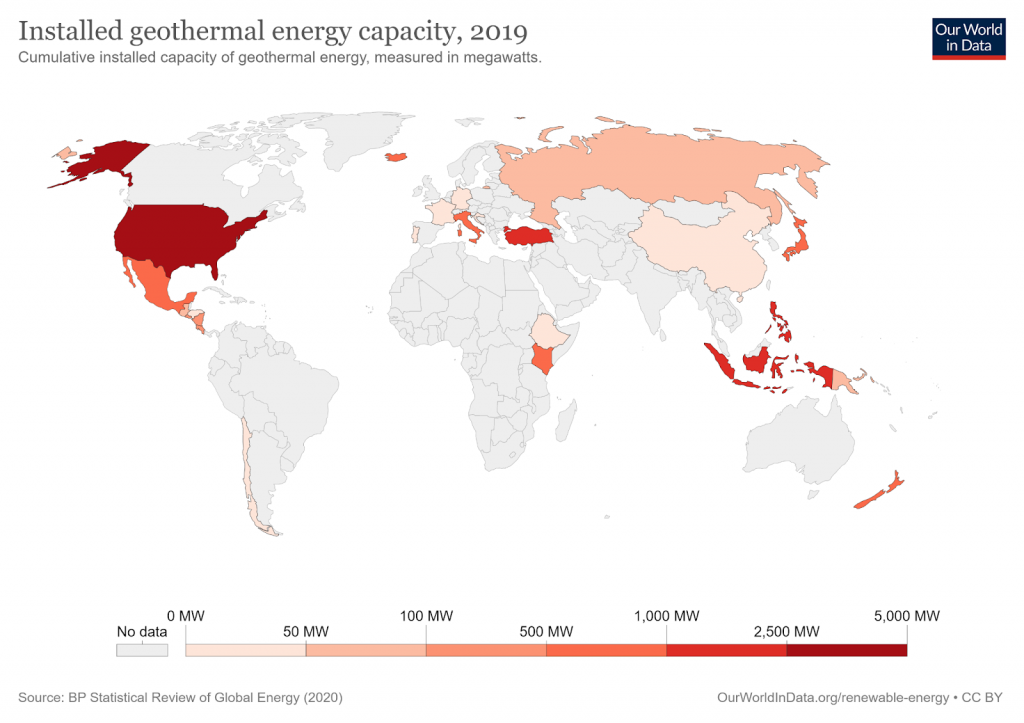
How Sustainable Is Geothermal Energy
The decay of radioactive materials in the rock and fluid of the earth’s core produces geothermal energy. Drilling down to hot water reservoirs up to a mile below the surface creates steam that rotates a turbine, which spins a generator to generate electricity. Geothermal is found along major tectonic plate boundaries where volcanoes are located.
Geothermal energy is renewable because the Earth has an almost unlimited supply of heat generated by its core. But just how sustainable is it?
Geothermal power plants produce a minute amount of greenhouse gases, emitting 97% fewer sulfur compounds and 99% less carbon dioxide than fossil fuel plants of comparable size. Scrubbers are also utilized to remove hydrogen sulfide stored in geothermal reservoirs, further cutting down on emissions. The three main types of geothermal power plants are dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle plants. All three harvest water from the earth’s core in the same manner, by drilling down to reservoirs and extracting the hot water to produce steam. Negative environmental impacts are minimized by only drilling to shallow depths, siting power plants away from major fault lines, properly disposing of hazardous waste captured by the scrubbers, and recycling the geothermal steam and water via re-injection into the ground.
Overall, geothermal energy is sustainable because it produces low levels of GHGs and does not adversely affect the environment.
Geothermal systems have a life-cycle global warming emission of approximately 0.2 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour, while coal power plants have an estimated 1.4-3.6 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour emission.
How Sustainable Is Biomass Energy
To harvest biomass energy, wood, agricultural crops, biogenic materials, animal manure, and human sewage are burned to release stored chemical energy. Biomass is incredibly versatile and can be used to produce fuel, energy, and everyday products that contain plastics.
Biomass energy is a renewable energy source because it can be replenished by planting trees and agricultural crops. But just how sustainable is it?
Existing biomass power plants emit more CO2 from their smokestacks than coal plants. Replacing coal with biomass inevitably releases more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and replacing older trees with saplings reduces the amount of carbon stored in a forest.
Overall, biomass is not as sustainable as it appears to be at first glance. For biomass to be sustainable, the rate of harvest must not exceed the rate of forest growth. In reality, this rarely happens. Also, it could take anywhere from decades to well over a century before we start receiving the climate benefits provided by biomass, which is well outside the timeframe of averting our current climate crisis.
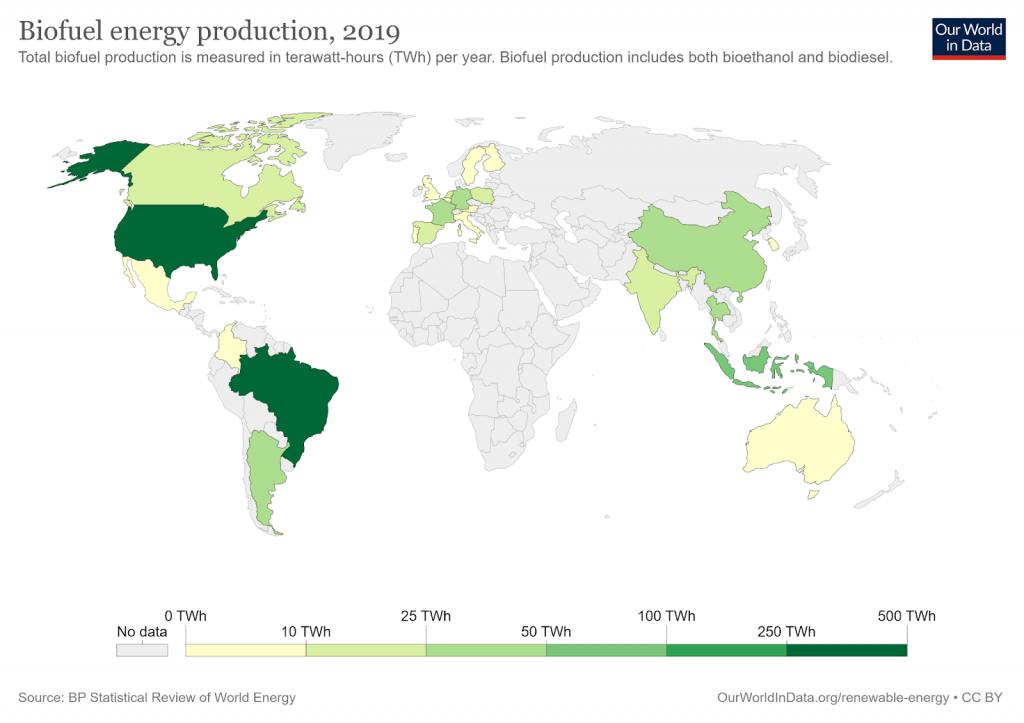
In 2019, the U.S. generated 5% of its total energy from biomass in the industrial, transportation, residential, electric power, and commercial sectors.
Which Energy Sources are the Most and Least Sustainable?
Renewable energy is sustainable when we preserve our natural resources. When we exploit resources faster than the planet can handle and replenish, renewables become unsustainable.
When taking into account the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions profile and level of environmental impact, we get the following six most common types of renewable energy ranked in terms of most to least sustainable:
| Geothermal energy | takes the top spot in terms of sustainability because its GHG emissions are drastically lower than that of coal, and preventative measures such as water recycling minimize environmental impacts. |
| Solar and wind energy | are sustainable because they have low levels of GHG emissions, but they also have the potential to negatively impact the environment if preventative measures are not taken. |
| Hydro energy | can be sustainable if low hydro is utilized because the GHG emissions and environmental impact are minimal. Large hydro carries higher levels of GHG and can disturb the aquatic environment. |
| Tidal energy | and its impact on the environment needs to be researched more before it can be implemented on an economic scale. But it is non-polluting. |
| Biomass energy | claims the last spot on the list because burning it releases substantial amounts of GHG emissions, and forest clearcutting causes significant environmental damage. |
Final Thoughts
Knowing the difference between renewable and sustainable is important when discussing substitute energy sources that could replace fossil fuels. If we want to become a more sustainable society and preserve what we have now for future generations to use, we must implement renewable resources. But more than that, we have to make sure we are utilizing renewable resources sustainably. If we are not careful and overuse our resources, we cannot provide for future generations.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Our World in Data: Renewable Energy
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Renewable Energy Explained
- McGill: What is Sustainability?
- Impactful Ninja: Sustainable vs Unsustainable – What’s the Difference?
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Renewable Energy Explained – Types and Usage
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: How Does Solar Work?
- Solar Energy Industries Association: Solar Industry Research Data
- Union Of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Solar Power
- Union of Concerned Scientists: How it Works – Water for Power Plant Cooling
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: How Do Wind Turbines Work?
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Wind Explained – Where Wind Is Harnessed
- Union Of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Wind Power
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Environmental Impacts and Siting of Wind Projects
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: How Hydropower Works
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Types of Hydropower Plants
- Synapse Energy Economics Inc.: Hydropower Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Hydropower and the environment
- Union Of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Hydropower
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Hydropower Explained
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Hydropower Explained – Tidal Power
- National Geographic: Tidal Energy
- Union of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Hydrokinetic Energy
- TWI: What is Geothermal Energy? How Does it Work?
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Geothermal Electricity Production Basics
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Geothermal Explained – Use of Geothermal Energy
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Geothermal Explained – Geothermal Energy and the Environment
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Geothermal Explained – Geothermal Power Plants
- Brittanica: Geothermal – Environmental Effects And Economic Costs
- Union of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Geothermal
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Biomass Explained
- Natural Resources Defense Council: How the Biomass Industry Sent “Sustainability” Up in Smoke