What Are Carbon Mineralization Offsets and How Do They Work: The Big Picture
Affiliate Disclosure
Hey fellow impactful ninja ?
You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts.
Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click.
But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend.
Why do we add these product links?
First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide.
And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases.
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you.
And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you.
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you).
And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself.
What does this mean for me personally?
You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money.
Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go.
Stay impactful,
Carbon mineralization is currently one of the most direct ways we can remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from our atmosphere. In the scope of carbon offsets, mineralization could play a crucial role in reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. So, we had to ask: What are carbon mineralization offsets really, and could they help us mitigate climate change?
Carbon mineralization offsets are a specific type of carbon offset that remove carbon from the atmosphere. CO2 is either pumped into underground rock formations or exposed to certain rocks at the surface, where it is stored permanently in mineral form via a chemical reaction.
Keep reading to find out all about what carbon mineralization offsets are, how they work, what their project life-cycle is, how effective they are, their pros and cons, and how they can help mitigate climate change.
The Big Picture of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
Carbon offsets are reductions in carbon emissions that are used to compensate for carbon emissions occurring elsewhere. They are measured in tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalents and are bought and sold through international brokers, online retailers, and trading platforms on what is known as the global carbon offset market.
“Carbon Offset: a way for a company or person to reduce the level of carbon dioxide for which they are responsible by paying money to a company that works to reduce the total amount produced in the world, for example by reforestation”
Oxford Dictionary
Carbon mineralization is a form of technological carbon removal whereby atmospheric CO2 reacts with silicate material and rocks rich in calcium and magnesium (e.g., basalt rocks) to permanently lock away CO2 for thousands of years.
“Carbon mineralization: the process by which carbon dioxide becomes a solid mineral, such as a carbonate. It is a chemical reaction that happens when certain rocks are exposed to carbon dioxide”
The United States Geological Survey
For underground mineralization, CO2 is injected into wells that lead to igneous or metamorphic rock formations. For mineralization at the surface, CO2 is exposed to basalt rocks, ultramafic rocks, or mine tailings (mine waste).
| How are carbon offsets defined | Reductions in GHG emissions that are used to compensate for emissions occurring elsewhere. |
| What are carbon mineralization offsets | Carbon mineralization offsets are a specific type of carbon offset involving approaches that speed up the natural weathering process, whereby atmospheric CO2 reacts with silicate material and rocks rich in calcium and magnesium (e.g., basalt rocks). |
| How do direct carbon mineralization projects offset CO2 emissions | Carbon mineralization projects reduce CO2 emissions by supporting those mineralization practices that permanently lock away atmospheric carbon in rock formations for thousands of years. |
| When do carbon mineralization projects offset CO2 emissions | Carbon mineralization projects can speed up the natural weathering process by breaking down rocks into tiny pieces. For example, Carbfix achieves 95% permanent carbon mineralization in under two years. |
| What is the project life-cycle of carbon mineralization offsets | Building: The building of carbon mineralization offsets includes building mineralization power plants, identifying lands for injection or above-ground exposure, and actually injecting CO2 or spreading crushed rocks. Operating: There are very few CO2 emissions or waste products associated with operating and maintaining carbon mineralization projects, making the carbon footprint of this phase low. End-of-life: The end-of-life of carbon mineralization offset projects is not yet well documented because mineralization itself is a relatively new technology. But we do know that rates of carbon re-emission are very low given that mineralization is a permanent process. |
| How effective and efficient are carbon mineralization offsets | Effectiveness: Carbon mineralization offsets permanently and quickly remove CO2 from the atmosphere; however, they do not reduce your own carbon emissions, which can lead to greenwashing. Efficiency: Carbon mineralization offsets have low rates of carbon re-emission; however, they are also relatively expensive and are not yet scaled to compensate for our global emissions. |
| What are the best carbon mineralization offsets | The best carbon mineralization offsets are offered by Climeworks, Neustark, and greenSand which permanently store CO2 underground, in concrete, or in Olivine rocks, respectively. In addition, CarbonCure, CarbonBuilt, and Silicate lock away CO2 in concrete. |
What Are Carbon Mineralization Offsets
Carbon offsets are reductions in GHG emissions that are used to compensate for emissions occurring elsewhere. They are measured in tons of CO2 equivalents and are bought and sold through international brokers, online retailers, and trading platforms.
Carbon mineralization offsets involve the process by which atmospheric CO2 reacts with silicate material and rocks rich in calcium and magnesium (e.g., basalt rocks) to form solid minerals.
How Are Carbon Offsets Defined
Carbon offsets play a crucial role in reducing our carbon footprint, the amount of CO2 emissions associated with an individual or an entity.
“Carbon footprint: the amount of greenhouse gasses and specifically carbon dioxide emitted by something (such as a person’s activities or a product’s manufacture and transport) during a given period”
Merriam Webster
Basically, a carbon footprint is the amount of carbon emitted by an activity or an organization. This includes GHG emissions from fuel that we burn directly (e.g., heating a home, driving a car) and GHG emissions from manufacturing the products that we use (e.g., power plants, factories, and landfills).
One way to reduce our carbon footprint is via the use of carbon offsets. These are mineralizations in GHG emissions that are measured in tons of CO2 equivalents and are bought and sold through international brokers, online retailers, and trading platforms.
“Carbon offset: a way for a company or person to reduce the level of carbon dioxide for which they are responsible by paying money to a company that works to reduce the total amount produced in the world, for example by planting trees”
Oxford Dictionary
When you hear the words “carbon offset”, think about the term “compensation”. Essentially, carbon offsets are mineralizations in GHG emissions that are used to compensate for emissions occurring elsewhere. Carbon offsets can range anywhere from a couple of hundred tons of CO2 per program per year to thousands of tons of CO2 per program per year.
How Are Carbon Mineralization Offsets Defined
Carbon mineralization is a form of technological carbon removal, the process of eliminating carbon from the atmosphere. More specifically, it is the removal of carbon from the atmosphere by sequestering it in permanent reservoirs.
“Carbon Removal: the process of removing CO2 from the atmosphere”
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Carbon mineralization, also referred to as enhanced weathering, refers to the process by which atmospheric CO2 reacts with silicate material and rocks rich in calcium and magnesium (e.g., basalt rocks).
“Carbon mineralization: the process by which carbon dioxide becomes a solid mineral, such as a carbonate. It is a chemical reaction that happens when certain rocks are exposed to carbon dioxide”
The United States Geological Survey
Carbon can be mineralized either by injecting CO2 into underground rock formations or exposing CO2 to broken pieces of rock at the Earth’s surface. Both approaches permanently lock away atmospheric carbon for thousands of years.
How Do Carbon Mineralization Offsets Work
Carbon mineralization includes approaches that aim to speed up the naturally occurring weathering process whereby atmospheric CO2 chemically reacts with certain types of rocks to form a solid mineral.
When certain rocks (e.g., basalt, ultramafic, mine tailings) are exposed to CO2, it triggers a chemical reaction that forms new carbonate material in the rocks. This locks away CO2 permanently with a limited possibility of re-emission, even if the rocks are broken.
How and When Do Carbon Mineralization Offsets Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
Carbon mineralization refers to the direct elimination of carbon from our atmosphere via its storage in geologic reservoirs. It is one way to mitigate the adverse effects of CO2 emissions that occur once they enter our atmosphere.
How Do Carbon Mineralization Offsets Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
Carbon mineralization projects reduce CO2 emissions by exposing certain rocks to CO2, which then converts the CO2 into solid minerals.
There are two main types of carbon mineralization:
- Injecting CO2 into underground rock formations
- Exposing CO2 to broken pieces of rock at the Earth’s surface
Underground, CO2 is injected into wells that lead to igneous or metamorphic rock formations. At the surface, CO2 is exposed to basalt rocks, ultramafic rocks, or mine tailings (mine waste). Both approaches permanently lock away atmospheric carbon for thousands of years.
When Do Carbon Mineralization Offsets Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
Carbon mineralization is a natural process that occurs over millions of years. Carbon mineralization projects aim to speed up this process by breaking down silicate rocks into tiny pieces, thereby skipping slow weathering processes.
For example, Carbfix achieves 95% permanent carbon mineralization in under two years. And in comparison, newly planted trees for reforestation offsets could take upwards of 20 years to capture the amount of CO2 that most carbon offset programs promise.
When comparing this to other methods of carbon removal like planting trees, we find that carbon mineralization reduces CO2 emissions faster and more permanently.
- For example, a newly planted tree could take upwards of 20 years to capture the amount of CO2 that most carbon offset programs promise.
- Also, there is always the risk of, e.g., droughts, wildfires, tree diseases, and deforestation wiping out newly planted trees, negating any carbon reduction benefits.
What Could Prevent Carbon Mineralization Offsets From Being Realized
Carbon mineralization offsets are one of the most expensive methods of carbon removal, are not yet scaled to compensate for our global emissions, and do not reduce your own emissions, which can lead to greenwashing.
Behind direct carbon capture (DCC), carbon mineralization offsets are one of the most expensive offsets out of all of the carbon removal methods. Mineralization offsets currently range anywhere from $82 – $1,200 per ton of CO2, depending on the type of technology, type of energy source, and scale of the operation. In comparison, reforestation offsets cost approximately $50 per ton.
Carbon mineralization offsets are also not yet scaled enough to keep pace with our global carbon emissions. Because there are relatively few companies engaged in carbon mineralization on a commercial level, the amount of carbon they can sequester is limited.
Lastly, purchasing a carbon offset does not directly reduce your carbon footprint. It only makes others reduce their carbon footprint to compensate for your carbon footprint.
If emissions are only offset and not reduced from the source, this could lead to greenwashing, when the consumer is deceived into thinking they are offsetting their emissions but in reality, they are not.
What Is the Project Life-Cycle of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
To fully understand carbon mineralization offsets, we must assess each stage of its life cycle. This life-cycle assessment (LCA) is a method to evaluate the environmental impacts of products and materials. Over the years, companies have strategically used LCA to research and create more sustainable products. So, we had a look at the LCA for carbon mineralization offsets!
Building of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
The building of carbon mineralization offsets includes building mineralization powerplants, identifying lands for injection or above-ground exposure, and actually injecting CO2 or spreading crushed rocks.
Carbon mineralization plants for CO2 injection are most effective in locations where there is excess renewable energy available along with ample natural storage options for the CO2.
For example, the greatest potential for mineralization underground and at the surface in the US is in the pacific northwest, specifically Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. Some East and West Coast states also have the potential for mineralization via mine tailings.
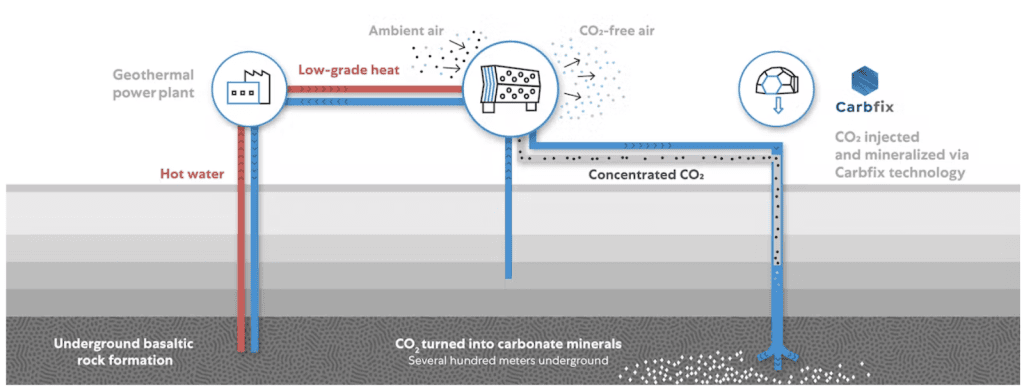
Iceland is also a hotspot for mineralization due to ample geothermal energy coupled with large underground basalt rock formations. Carbfix’s Hellisheiði Powerplant is a prime example of this.
Operating and Maintaining of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
There are very few CO2 emissions or waste products associated with operating and maintaining carbon mineralization projects, making the carbon footprint of this phase low.
In general, there is no long-term monitoring or maintenance required for carbon mineralization projects after the chemical reaction between the rocks and CO2 is initiated. CO2 emissions at this stage are associated with the operation and maintenance of the carbon mineralization plants.
Although carbon mineralization facilities that inject CO2 underground require energy to operate, they can re-emit only small amounts of CO2 if powered by low-carbon energy sources. For example, Carbfix’s Hellisheiði Powerplant runs on geothermal energy, which emits 38 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced. Compare this to coal power plants, which emit 820 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced.
Also, injecting CO2 underground can require large amounts of water. Water usage will depend on the type of plant, as well as local temperature and humidity. Carbfix addresses this concern by sourcing its water from the reservoir in which injection occurs so that it can be circulated and reused.
Lastly, the operating/maintaining stage is also where the offsetting promised by mineralization projects occurs. When CO2 reacts with basalt rocks, ultramafic rocks, or mine tailings, the chemical reaction that follows converts CO2 into carbonate, permanently removing it from the surrounding air.
End-of-Life of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
The end-of-life of energy-efficiency offsets would include the end-of-life of the technology or anything that negates the project’s effectiveness.
The end-of-life of carbon mineralization offset projects is not yet well documented because mineralization itself is a relatively new technology. But we do know that rates of carbon re-emission are very low given that mineralization is a permanent process.
For example, greenSand Olivine rocks permanently store carbon and will only release that carbon back into the atmosphere if the temperature exceeds 1,600 degrees. In addition, even if the rocks are broken, the carbon will remain trapped inside. This makes mineralization effective at reducing CO2 emissions.
Carbfix: An Example Project of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
Since 2017, Carbfix has been working with Climeworks, a direct air capture company based in Zurich, Switzerland. After Climeworks’ specialized machines directly capture CO2 from the air, Carbfix then turns the captured CO2 into stone in less than two years.
Carbfix first dissolves the captured CO2 in water to create a slurry, before injecting it underground where it reacts with basalts and other reactive rock formations to form solid minerals (carbonates) via natural processes. These carbonates remain stable for thousands of years, making the process permanent. To date, Carbfix has injected over 70,000 tons of CO2 at their Icelandic site.
How Effective and Efficient Are Carbon Mineralization Offsets
In terms of effectiveness, carbon mineralization offsets permanently and quickly remove CO2 from the atmosphere; however, they do not reduce your own carbon emissions, which can lead to greenwashing.
In terms of efficiency, carbon mineralization offsets have low rates of carbon re-emission; however, they are also relatively expensive and are not yet scaled to compensate for our global emissions.
Carbon mineralization offsets are effective at mitigating climate change because they:
- Permanently lock away CO2 for thousands of years with no long-term monitoring required
- Reduce emissions quicker than natural weathering processes and other nature-based solutions
However, carbon mineralization offsets can also lack effectiveness because they do not reduce your own carbon emissions, which can lead to greenwashing. This occurs when emissions are only offset and not reduced from the source, and the consumer is deceived into thinking they are offsetting their emissions but in reality, they are not.
Carbon mineralization offsets are efficient at reducing CO2 emissions because they are a permanent process that has very low rates of CO2 re-emission. In addition, even if the rocks are broken, the carbon will remain trapped inside.
However, carbon mineralization offsets can also lack efficiency because they are one of the most expensive offsets out of all of the carbon removal methods, behind direct carbon capture (DCC). They are also not yet scaled to compensate for our global carbon emissions, although they could be scaled up to capture 2-4 billion tons of CO2 per year by 2050.
How Could You Offset Your Own Carbon Footprint With Carbon Mineralization Offsets
The market for carbon offsets was small in the year 2000, but by 2010 it had already grown to represent nearly $10 billion worldwide. The voluntary carbon offset market (VCM) is where everyday consumers can purchase carbon offsets to offset their carbon emissions, and the Ecosystem Marketplace predicts the VCM can grow to $50B by the year 2050.
Carbon mineralization takes advantage of natural chemical processes and can permanently and quickly remove carbon from the atmosphere, locking it away for thousands of years. Because it has the potential to store large amounts of carbon, it is predicted to make up an increasing share of the VCM. Below are our favorite carbon mineralization offsets.
| Carbon Mineralization Offset Company | Quick Facts |
| Climeworks | Carbon offset purchases support the practice of direct CO2 removal, where specialized machines remove CO2 directly from the air and store it in rock formations underground. |
| Neustark | Neustark removes CO2 from the atmosphere and stores it in recycled concrete, and they cut new CO2 emissions by reducing the use of traditional cement. |
| greenSand | greenSand uses Olivine rocks, which trap CO2 when they come into contact with water. For every ton of CO2 purchased, greenSand spreads 1 ton of Olivine, which can in turn absorb 1 ton of CO2. |
| InPlanet | InPlanet accelerates the natural process of enhanced weathering by grinding and spreading silicate rocks on tropical soils. The silicate rocks capture and store carbon for thousands of years and help regenerate tropical soils by acting as a long-term fertilizer. |
| CarbonCure | CarbonCure’s technology allows concrete producers to inject captured CO2 into fresh concrete during mixing. The CO2 then reacts with the concrete mix and is chemically converted into a mineral, where it is permanently stored for thousands of years. |
| UNDO | UNDO accelerates the natural process of enhanced weathering by spreading crushed basalt rock on farmlands. The rock absorbs CO2 and locks it away in mineral form for thousands of years. |
| Heirloom | Heirloom’s technology captures CO2 through an accelerated process of natural mineralization, whereby minerals absorb CO2 from the air. The CO2 is then injected underground and stored permanently. |
| CarbonBuilt | Carbonbuilt takes CO2 generated by industrial processes and transforms it into precast concrete. |
| Arca | Arca is a startup speeding up the natural process of weathering. They partner with mines and transform mine tailings into giant carbon sinks capable of extracting and permanently storing large amounts of CO2. |
| Silicate | Silicate is a startup leveraging the carbon removal potential of surplus concrete. They grind surplus concrete to dust so that it can be spread on farmlands. The crushed concrete reacts with carbonic acid in the soil to remove CO2 from the air. |
How Can Carbon Mineralization Offsets Help Mitigate Climate Change
Climate change is a severe and long-term consequence of fossil fuel combustion. Carbon mineralization offsets can help mitigate climate change because they permanently eliminate fossil-fuel-derived carbon from our atmosphere which, if left untreated, can remain there for tens of thousands of years and exacerbate the negative effects of climate change.
How Is Climate Change Defined
Climate change is arguably the most severe, long-term global impact of fossil fuel combustion. Every year, approximately 33 billion tons (bt) of CO2 are emitted from burning fossil fuels. The carbon found in fossil fuels reacts with oxygen in the air to produce CO2.
“Climate change: changes in the earth’s weather, including changes in temperature, wind patterns and rainfall, especially the increase in the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere that is caused by the increase of particular gasses, especially carbon dioxide.”
Oxford Dictionary
Atmospheric CO2 fuels climate change, which results in global warming. When CO2 and other air pollutants absorb sunlight and solar radiation in the atmosphere, it traps the heat and acts as an insulator for the planet. Since the Industrial Revolution, Earth’s temperature has risen a little more than 1 degree Celsius (C), or 2 degrees Fahrenheit (F). Between 1880-1980 the global temperature rose by 0.07C every 10 years. This rate has more than doubled since 1981, with a current global annual temperature rise of 0.18C, or 0.32F, for every 10 years.
As outlined in the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement, we must cut current GHG emissions by 50% by 2030 and reach net zero by 2050.
How Do Carbon Offsets Generally Help Mitigate Climate Change
Levels of carbon in our atmosphere that cause climate change have increased as a result of human emissions since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in 1750. The global average concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today registers at over 400 parts per million. Carbon offsets can help prevent these levels from increasing even more.
When you hear the words “carbon offset”, think about the term “compensation”. Essentially, carbon offsets are reductions in GHG emissions that are used to compensate for emissions occurring elsewhere.
Carbon offsets that meet key criteria and verified project standards, are additional and permanent, and are part of projects that are carried out until the end of their lifespan have the best chance of reducing carbon emissions and therefore reducing climate change.
When we offset CO2 we also slow the rate of global temperature rise, which in turn minimizes the effects of climate change.
How Do Carbon Mineralization Offsets Specifically Help Mitigate Climate Change
Carbon mineralization can specifically help mitigate climate change because it eliminates atmospheric carbon, which when emitted, can remain in our atmosphere for a long period of time. Whether via underground injection, concrete, or mine tailings, the process of carbon mineralization permanently locks away CO2 for thousands of years.
What Are The 5 Pros and 4 Cons of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
Carbon mineralization offsets are permanent, have a low rate of carbon re-emission, reduce emissions quickly, protect the biosphere, and can help offset emissions that cannot be reduced otherwise.
Carbon mineralization offsets are one of the most expensive methods of carbon removal, are not yet scaled to compensate for our global emissions, may induce seismic activity, and do not reduce your own emissions, which can lead to greenwashing.
What Are the 5 Pros of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
Carbon mineralization offsets have various pros that make them effective at sequestering carbon from our atmosphere.
| 5 Pros of Carbon Mineralization Offsets | Quick Facts |
| #1: Carbon mineralization offsets are permanent | Carbon mineralization offsets are a specific type of carbon offset that store carbon permanently in geological reservoirs. For example, Carbfix turns captured CO2 into stone, a process that locks away CO2 for thousands of years with no long-term monitoring required. |
| #2: Carbon mineralization offsets have a low rate of carbon re-emission | Because carbon mineralization is a permanent process, rates of carbon re-emission are very low. For example, greenSand Olivine rocks permanently store carbon and will only release that carbon back into the atmosphere if the temperature exceeds 1,600 degrees. |
| #3: Carbon mineralization offsets reduce CO2 emissions quickly | Enhanced weathering speeds up the natural carbon mineralization process by breaking down silicate rocks into tiny pieces, thereby skipping slow weathering processes. For example, Carbfix achieves 95% permanent carbon mineralization in under two years. |
| #4: Carbon mineralization offsets protect the biosphere | Removing carbon emissions from the atmosphere via carbon mineralization would lead to improved public health in terms of asthma, respiratory allergies, airway diseases, and lung cancer. It also promotes healthy ecosystems, which have been linked with cleaner air, water, and food. |
| #5: Carbon mineralization offsets can help offset carbon emissions that can’t be reduced otherwise | We already have governmental-level policies in place to reduce carbon emissions, but carbon mineralization offsets allow us to reduce emissions from activities where sustainable alternatives are not yet widely available. |
What Are the 4 Cons of Carbon Mineralization Offsets
Understanding the drawbacks of carbon mineralization offsets is important when implementing this strategy on a large scale in order to mitigate climate change.
| 4 Cons of Carbon Mineralization Offsets | Quick Facts |
| #1: Carbon mineralization offsets are one of the most expensive methods of carbon removal | Mineralization offsets currently range anywhere from $82 – $1,200 per ton of CO2, depending on the type of technology, type of energy source, and scale of the operation. In comparison, reforestation offsets cost approximately $50 per ton. |
| #2: Carbon mineralization offsets are not yet at a scale where they can compensate for our global carbon emissions | Because there are relatively few companies engaged in carbon mineralization on a commercial level, the amount of carbon they can sequester is limited. Also, processes, standards, and technologies still need to be developed to ensure proper monitoring, verification, and reporting of carbon sequestration. |
| #3: Carbon mineralization offsets may have negative environmental effects | Water contamination and seismic activity are potential risks associated with carbon mineralization, although further research is needed. |
| #4: Carbon mineralization offsets do not reduce your own carbon emissions, which can lead to greenwashing | If emissions are only offset and not reduced from the source, this could lead to greenwashing, when the consumer is deceived into thinking they are offsetting their emissions but in reality, they are not. |
What Are Better Alternatives to Carbon Mineralization Offsets
If used correctly, carbon mineralization offsets can provide environmental, economic, and social benefits beyond reducing carbon emissions. They have the potential to instigate meaningful environmental change and begin to reverse some of the effects of climate change.
However, we can’t let this method be a guilt-free way to reduce carbon emissions. Carbon mineralization offsets must be used in conjunction with direct carbon reduction measures until the industry has time to develop, refine, and make the technology more affordable.
These reduction measures don’t have to involve drastic changes either. Actions that may seem minor can have a significant impact because those small changes add up! You can reduce your carbon footprint in three main areas of your life: household, travel, and lifestyle.
Reduce your household carbon footprint:
- Wash with cold water: Washing clothes in cold water could reduce carbon emissions by up to 11 million tons. Approximately 90% of the energy is used to heat the water, so switching to cold saves also saves energy.
- Replace incandescent bulbs with fluorescent bulbs: Fluorescent bulbs use 75% less energy than incandescent ones, saving energy and thus reducing electricity demand and GHG emissions.
Reduce your travel carbon footprint:
- Fly less: Aviation accounts for around 1.9% of global carbon emissions and 2.5% of CO2. Air crafts run on jet gasoline, which is converted to CO2 when burned.
- Walk or bike when possible: The most efficient ways of traveling are walking, bicycling, or taking the train. Using a bike instead of a car can reduce carbon emissions by 75%. These forms of transportation also provide lower levels of air pollution.
Reduce your lifestyle carbon footprint:
- Switch to renewable energy sources: The six most common types of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydro, tidal, geothermal, and biomass energy. They are a substitute for fossil fuels that can reduce the effects of global warming by limiting global carbon emissions and other pollutants.
- Recycle: Recycling uses less energy and deposits less waste in landfills. Less manufacturing and transportation energy costs means fewer carbon emissions generated. Less waste in landfills means less CH4 is generated.
- Switch from single-use to sustainable products: Reusing products avoids resource extraction, reduces energy use, reduces waste generation, and can prevent littering.
- Eat less meat and dairy: Meat and dairy account for 14.5% of global GHG emissions, with beef and lamb being the most carbon-intensive. Globally, we consume much more meat than is considered sustainable, and switching to a vegan or vegetarian diet could reduce emissions.
- Take shorter showers: Approximately 1.2 trillion gallons of water are used each year in the United States just for showering purposes, and showering takes up about 17% of residential water usage. The amount of water consumed and the energy cost of that consumption are directly related. The less water we use the less energy we use. And the less energy we use, the less of a negative impact we have on the environment.
Because carbon mineralization offsets are an indirect way and not a direct way of reducing emissions, they alone will not be enough to reduce global carbon emissions significantly. Direct measures of emission reductions, such as reducing individual energy use and consumption, are better alternatives to carbon mineralization offsets.
Final Thoughts
Carbon mineralization offsets are a specific type of carbon offset that remove carbon from the atmosphere. CO2 is either pumped into underground rock formations or exposed to certain rocks at the surface, where it is stored permanently in mineral form via a chemical reaction. CO2 reduction occurs quickly, making mineralization an effective and efficient way to reduce CO2 emissions.
Although carbon mineralization offsets can instigate meaningful change, they should not be seen as the only solution to climate change. They are effective at reducing CO2 in the short-term, but in the long term they fail to reduce CO2 enough. Offsets, in general, also do not reduce your own carbon emissions, which can lead to greenwashing.
When used in conjunction with direct CO2 reduction measures, carbon offsetting can be much more effective. We should reduce our own carbon footprint as much as possible first, and only then choose the most effective carbon mineralization offsets.
Stay impactful,
Sources
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Offsets and RECs -What’s the Difference?
- Britannica: Carbon Offset
- David Suzuki Foundation: Are carbon offsets the answer to climate-altering flights?
- The Economist: Carbon Mineralisation – Permanently CO2 by hastening reaction with minerals
- World Resources Institute: Carbon Removal
- US Geological Survey: Making minerals – how growing rocks can help reduce carbon emissions
- Impactful Ninja: What Are Carbon Mineralization Offsets and How Do They Work? The Big Picture
- Impactful Ninja: Why is a Carbon Footprint Bad for the Environment?
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: System of Registries
- Carbfix: Protecting Our Climate by Turning CO2 Into Stone
- GreenPeace: The biggest problem with carbon offsetting is that it doesn’t really work
- Impactful Ninja: Direct Carbon/Air Capture Offsets Explained: All You Need to Know
- Climeworks: Subscriptions
- greenSand: Certificate – CO₂ Compensation
- World Resources Institute: Direct Air Capture – 6 Things to Know
- Science Direct: Life-cycle assessment (LCA)
- MIT SMR: Strategic Sustainability Uses of Life-Cycle Analysis
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint Fossil Fuels? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint Geothermal Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Climeworks: Homepage
- Climeworks: Direct air capture: our technology to capture CO₂
- Carbfix: Homepage
- Carbfix: Proven
- Climeworks: How direct air capture and storage (DAC+S) works
- Edie: Carbon offsetting – How are businesses avoiding greenwashing on the road to net-zero?
- greenSand: Olivine Research & Evidence
- American University: Fact Sheet – Enhanced Mineralization
- Carbon Offset Guide: Voluntary Offset Programs
- Ecosystem Marketplace: Voluntary Carbon Markets Top $1 Billion in 2021 with Newly Reported Trades
- Columbia Climate School: Can Removing Carbon From the Atmosphere Save Us From Climate Catastrophe?
- Impactful Ninja: Best Carbon Mineralization Offsets
- Neustark: Homepage
- greenSand: Homepage
- InPlanet: Homepage
- CarbonCure: Homepage
- UNDO: Homepage
- Heirloom: Homepage
- CarbonBuilt: Homepage
- Arca: Homepage
- Silicate: Homepage
- World Nuclear Association: Carbon Emissions from Electricity
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Global Warming 101
- myclimate: What does “net zero emissions” mean?
- United Nations Convention Framework on Climate Change: The Paris Agreement
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Climate Change – Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
- Terrapass: Carbon Offset Projects
- Carbon Offset Guide: Additionality
- Carbon Offset Guide: Permanence
- American University: Fact Sheet – Carbon Removal
- Impactful Ninja: Carbon Mineralization Offsets: All 5 Pros and 4 Cons Explained
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Asthma, Respiratory Allergies and Airway Diseases
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Cancer
- Carbon Brief: Climate change will hit ‘endemic’ plants and animals the hardest, study warns
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: Paris Climate Agreement
- The Ocean Foundation: Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
- Energy Information Administration: Renewable Energy Explained
- Energy Star: Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs (CFLs) and Mercury
- Our World in Data: Where in the world do people have the highest CO2 emissions from flying?
- Zero Waste Europe: Reusable vs Single Use Packaging
- Carbonbrief: Interactive – What is the climate impact of eating meat and dairy?
- Stop Waste: Recycling and Climate Protection
- Impactful Ninja: Is Taking Long Showers Bad for the Environment?
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Showerheads
- Impactful Ninja: 4 Main Reasons Why Reducing Your Carbon Footprint is Important