Nuclear Power: All 7 Pros and 4 Cons Explained
Affiliate Disclosure
Hey fellow impactful ninja ?
You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts.
Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click.
But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend.
Why do we add these product links?
First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide.
And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases.
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you.
And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you.
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you).
And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself.
What does this mean for me personally?
You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money.
Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go.
Stay impactful,
Nuclear power accounts for roughly 10% of the world’s electricity generation. It can play an important role in the global energy transformation and help transition away from fossil fuels, but it comes with drawbacks as with any other energy source. So, we had to ask: What are the pros and cons of nuclear power?
The main pros of nuclear power include a low carbon footprint, air quality protection, high energy density, few waste products, and energy independence. However, the main con of nuclear power is that it produces nuclear waste with varying levels of radioactivity.
Keep reading to find out all about what the pros and cons of nuclear power are, how effective and efficient it is, how it can mitigate climate change, and how safe or dangerous it is.
The Big Picture of Nuclear Power
In general, nuclear power is generated when neutrons either divide or fuse, which releases heat, produces steam, spins a turbine, and drives generators to produce electricity.
The two ways we can generate nuclear power are via nuclear fission (when neutrons divide) or nuclear fusion (when neutrons fuse).
How Is Nuclear Power Defined
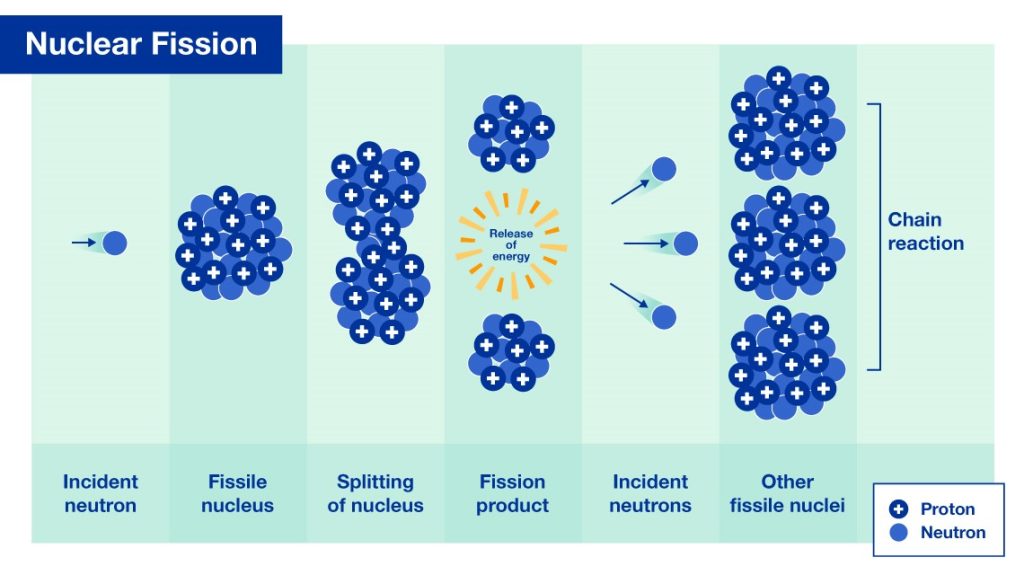
Nuclear fission is the generation of energy produced when splitting apart the nucleus of an atom.
“Nuclear fission: a nuclear reaction in which a heavy nucleus splits spontaneously or on impact with another particle, with the release of energy.”
Cambridge Dictionary
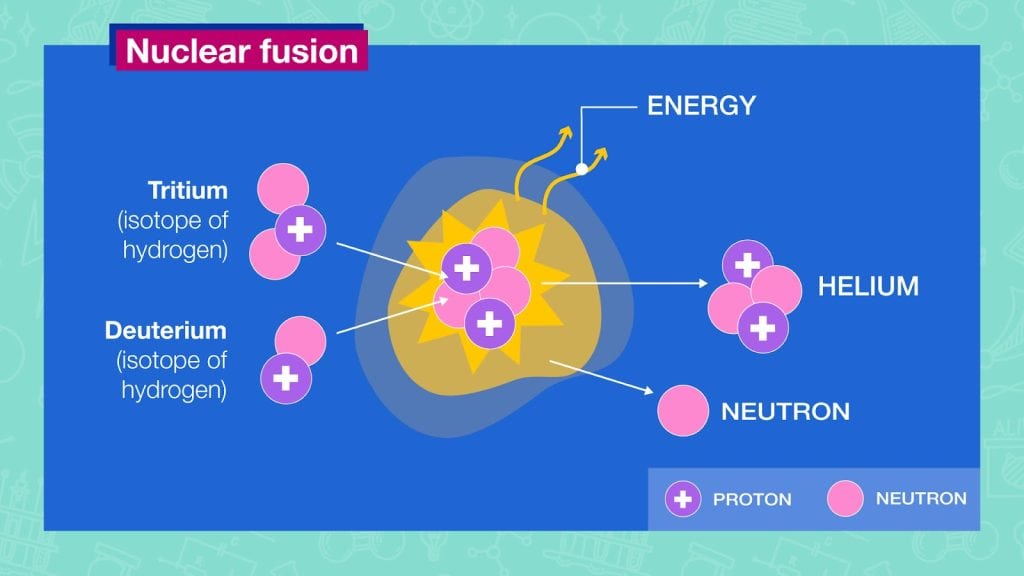
Nuclear fusion is the generation of energy produced when lighter atoms are combined or fused to create larger and heavier atoms.
“Nuclear fusion: the process of joining two nuclei to produce energy.”
Cambridge Dictionary
All operating nuclear power plants today utilize the process of nuclear fission, whereas nuclear fusion is still very much in the research and development phase and does not currently supply energy to our power grid.
In the table below, we highlight the pros and cons of nuclear power:
- When we refer to nuclear power: we refer to what both nuclear fission and fusion have in common
- When we refer to nuclear fission: we refer to just the splitting of atomic nuclei
- When we refer to nuclear fusion: we refer to just the joining of atomic nuclei
| 7 Pros of Nuclear Power | 4 Cons of Nuclear Power |
| Nuclear power has a low carbon footprint | Nuclear power generates nuclear waste |
| Nuclear power protects air quality | Nuclear fission is a nonrenewable energy source |
| Nuclear power is energy dense | Nuclear fusion is still in the research and development phase |
| Nuclear power generates few waste products | Nuclear fusion reactions are difficult to start and maintain |
| Nuclear power promotes energy independence and energy security | |
| Nuclear fusion cannot cause a nuclear accident | |
| Nuclear fusion cannot be used to produce nuclear weapons |
What Are 7 Pros of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power has a low carbon footprint, protects air quality, is extremely energy dense, generates few waste products, and promotes energy independence and energy security. In addition, nuclear fusion cannot cause a nuclear accident or be used to produce nuclear weapons.
Pro #1: Nuclear Power Has a Low Carbon Footprint
Nuclear power has one of the lowest carbon footprints out of all energy types.
Nuclear Power Pro #1
The carbon footprint is one of the ways we measure the effects of human-induced global climate change. It primarily focuses on the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with consumption and includes other emissions such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
“Carbon footprint: the amount of greenhouse gasses and specifically carbon dioxide emitted by something (such as a person’s activities or a product’s manufacture and transport) during a given period”
Merriam Webster
All operating nuclear power plants today utilize the process of nuclear fission. Because of this, nuclear fission is commonly referred to as ‘nuclear power’ in the data and literature.
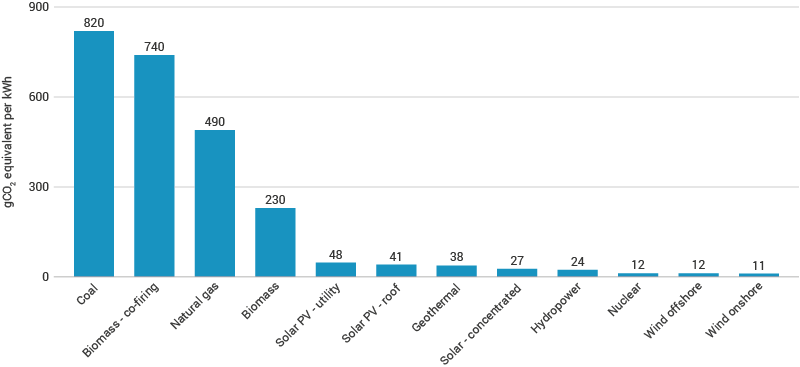
On a life-cycle basis, nuclear power emits 12 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced, the second lowest out of all fuel types.
Have a look at the illustration below to see the average life-cycle CO2 equivalent emissions of different energy sources and how they compare to nuclear power.
Nuclear fusion also produces little to no greenhouse gas emissions and toxic byproducts, making it one of our most environmentally friendly energy sources. One study on tokamak fusion power plants found that they emit less CO2 than photovoltaic solar systems and less than double those from nuclear fission reactors.
There are currently more than 10 stellarators and 50 tokamaks in operation worldwide, but there are currently no operating fusion reactors providing energy to our power grid. The focus remains on overcoming the two main challenges to nuclear fusion: keeping the reaction going and generating more energy from the reaction than was required to start the reaction.
Overall, nuclear power has one of the lowest carbon footprints out of all energy types, making it one of our cleanest sources of energy.
Pro #2: Nuclear Power Protects Air Quality
Nuclear power produces a fraction of the pollution and toxic chemicals that fossil fuels produce, helping to protect air quality.
Nuclear Power Pro #2
Air pollution can cause numerous health problems including asthma, breathing difficulties, brain damage, heart problems, and cancer. Fossil fuel (coal and natural gas) combustion emits coal ash residue, toxic heavy metals, CO2, carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere, impairing public health.
In terms of nuclear fission, every 1-inch pellet of nuclear fuel directly avoids the emission of over 2 tons of CO2 from our atmosphere. This is because each pellet contains the energy equivalent of 1 ton of coal, which creates 2.086 tons (4,172 lbs) of CO2 when it is burned.
Nuclear fusion also produces little to no greenhouse gas emissions and toxic byproducts, making it one of our most environmentally friendly energy sources in terms of air quality.
In short, nuclear power is a clean burning source of energy that produces minimal greenhouse gasses and emits no CO, SO2, or NOx, thereby helping to protect air quality.
Pro #3: Nuclear Power Is Energy Dense
Nuclear fuel is extremely energy dense, so you don’t need a lot of it to create a lot of energy.
Nuclear Power Pro #3
For nuclear fission, it would only take ten, U-235 pellets to power the average household for a year.
A single, 1-inch tall Uranium-235 pellet contains the energy equivalent of:
- 1 ton of coal
- 120 gallons of oil
- 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas
For nuclear fusion, it is theoretically possible to produce one terajoule of energy with just a few grams each of deuterium and tritium. This would be enough to meet the needs of an adult person living in the developed world for 60 years.
Estimates also suggest that nuclear fusion could generate:
- Up to 4 times more energy per kilogram of fuel than nuclear fission and
- Nearly 4 million times more energy than burning oil or coal
Because it is so energy dense, nuclear power is also incredibly energy-efficient. And energy efficiency is beneficial because it conserves resources, saves money, and increases the reliability of our energy grid as a whole.
Pro #4: Nuclear Power Generates Few Waste Products
Nuclear power produces substantially less waste than other forms of energy.
Nuclear Power Pro #5
Just as with any energy source, nuclear power generates some waste products. But the amount generated is substantially less than other forms of energy.
In terms of nuclear fission, a reactor supplying a person’s energy needs for an entire year produces only a brick-sized amount of nuclear waste. And only 5 grams of that, equivalent to the weight of a sheet of paper, is considered to be a high-level, radioactive waste.
In comparison, the average coal-fired power plant produces roughly 300,000 tons of coal ash and more than 6 million tons of CO2 every year. In the US alone, you could fit all of its used nuclear fuel over the past 60 years into a single football field at a depth of less than 10 yards (30 feet).
In terms of nuclear fusion, it does not produce CO2 or long-lived nuclear wastes. The only byproducts are helium (an inert gas) and tritium. Although tritium is radioactive, it is produced and consumed within the plant in a closed circuit and is used in low amounts.
Pro #5: Nuclear Power Promotes Energy Independence and Energy Security
Nuclear power can help us transition away from fossil fuels and toward an energy-independent future.
Nuclear Power Pro #5
Being able to produce your own electricity without the aid of foreign countries is an important step in becoming more self-sufficient. For example, in the US, Former President George W. Bush signed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 to reduce US dependence on oil, expand the production of renewable energy, and confront global climate change.
Although nuclear power alone cannot shoulder the burden of the world’s electricity needs, it can shoulder a substantial amount. Nuclear power accounted for roughly 10% of global electricity generation in 2023, generating approximately 2,600 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity from approximately 413 GW of installed capacity.
And if we can overcome previously unresolved engineering challenges, nuclear fusion offers the prospect of an inexhaustible energy source for future generations. In theory, it is possible to produce one terajoule of energy with just a few grams each of deuterium and tritium.
Pro #6: Nuclear Fusion Cannot Cause a Nuclear Accident
Nuclear fusion reactions cannot cause a nuclear accident because they are not based on chain reactions.
Nuclear Power Pro #6
Achieving and maintaining a nuclear fusion reaction is extremely difficult. There is only enough fuel present in the reactor to sustain the reaction for a few seconds at any given time, so a chain reaction cannot form.
“Chain reaction: a process yielding products that initiate further processes of the same kind, a self-sustaining sequence.”
Britannica
In addition, plasma must be kept at very high temperatures and pressures, with the support of external heating systems and magnetic fields. If there is a loss of pressure or temperature, the plasma cools and the fusion reactor shuts down, preventing a chain reaction from occurring and producing no adverse effects on the outside world.
This does not apply to nuclear fission because fission reactions are based on chain reactions, which can lead to the uncontrolled release of radioactive materials.
Pro #7: Nuclear Fusion Cannot Be Used to Produce Nuclear Weapons
Nuclear fusion cannot be used to produce nuclear weapons because it does not use fissile material and uses only a small amount of fuel.
Nuclear Power Pro #7
Nuclear fusion does not use fissile material (e.g., uranium and plutonium) in its reactor. Hydrogen bombs do use fusion reactions; however, they require an additional nuclear fission bomb to detonate. So on its own, fusion cannot solely be used to produce nuclear weapons.
In addition, nuclear fusion fuel is also continuously injected and consumed inside fusion reactors, so there is never enough fuel lying around to produce the instantaneous power required in a nuclear weapon.
This does not apply to nuclear fission because fission does use fissile material (e.g., uranium and plutonium) in its reactor.
What Are 4 Cons of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power generates nuclear waste with varying radioactivity. In addition, nuclear fission is a nonrenewable resource and nuclear fusion is still in the research and development phase because the fusion reaction is very difficult to start and maintain.
Con #1: Nuclear Power Generates Nuclear Waste
Nuclear power produces nuclear waste that is radioactive and can remain hazardous for many years, depending on the type.
Nuclear Power Con #1
Although nuclear power produces minimal waste, the waste that it does produce is radioactive. The level of radioactivity depends if we are talking about fission or fusion.
Overall, there are three types of nuclear wastes that are classified based on their radioactivity:
- High-level: Used nuclear fuel from the nuclear reactions accounting for 3% of the total volume of nuclear waste and containing 95% of the total radioactivity.
- Intermediate-level: Used filters, steel components, and effluents from reprocessing accounting for 7% of the total volume of nuclear waste and containing 4% of the total radioactivity.
- Low-level: Lightly contaminated items like tools and work clothing account for 90% of the total volume of nuclear waste and contain 1% of the total radioactivity.
Nuclear fission radioactive waste products include uranium mill tailings, spent (used) reactor fuel, and other radioactive wastes.
Nuclear fusion radioactive waste products include plasma vessel walls that become radioactive when high-energy neutrons activate the walls.
Most of the nuclear waste generated from nuclear power as a whole consists of low or intermediate-level nuclear waste (90%), which is significantly less dangerous and radioactive than high-level nuclear waste. But the small amount of high-level waste (3%) that is generated still must be contained and disposed of properly so as not to negatively impact public or environmental health.
Con #2: Nuclear Fission Is a Nonrenewable Energy Source
Nuclear fission is a nonrenewable energy source that will eventually be depleted.
Nuclear Power Con #2
Nonrenewable energy sources are those that will run out in our lifetime or will not be replenished in many, many lifetimes.
“Nonrenewables: existing in limited quantities that cannot be replaced after they have all been used”
Cambridge Dictionary
Nuclear fission is classified as nonrenewable energy because nuclear fuel (Uranium) is a finite material that can only be found in certain locations in the Earth’s crust.
Nuclear power plants use the second most common isotope of Uranium (U-235) which has a relative abundance of only 0.7%. And most of the original U-235 on earth has already decayed because it has a half-life of about 700 million years.
Although nuclear power plants use only tiny amounts of Uranium in the fission process and can be used as a reliable energy source for decades to come, we will still run out at some point. And once we run out of Uranium-235, we won’t be able to generate the nuclear fission reaction anymore.
This does not apply to nuclear fusion because fusion is considered to be renewable. Its input materials, deuterium and tritium, are virtually inexhaustible. Deuterium is found abundantly in water, and tritium can be synthetically produced by exposing lithium, a very common element, to high-energy neutrons.
Con #3: Nuclear Fusion Is Still in the Research and Development Phase
Nuclear fusion is still very much in the research and development phase because the fusion process is difficult to start, maintain, and control.
Nuclear Power Con #3
Nuclear fusion is still very much in the research and development phase because the fusion process is difficult to start, maintain, and control within a laboratory setting.
In terms of installed capacity, there are currently more than 10 stellarators and 50 tokamaks in operation worldwide, but there are currently no operating reactors that provide energy to our power grid.
Most experts agree that we are unlikely to achieve large-scale nuclear fusion energy generation before 2050. This means that fusion is not an option for meeting the short-term climate goals laid out in The Paris Climate Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius (C).
In order to achieve commercial energy generation, we must overcome the two main challenges to nuclear fusion: maintaining the reaction and generating more energy from the reaction than was required to start the reaction. This will require more research and development.
This does not apply to nuclear fission because fission is a well-established energy source in our energy mix. In 2023 it accounted for roughly 10% of global electricity generation, and it is currently our second-largest source of low-carbon energy.
Con #4: Nuclear Fusion Reactions Are Difficult to Start and Maintain
The two main challenges to nuclear fusion are maintaining the reaction and generating more energy from the reaction than was required to start the reaction.
Nuclear Power Con #4
Nuclear fusion experiments themselves are relatively easy to achieve; however, the reaction typically only lasts a fraction of a second. The main challenge with nuclear fusion comes with sustaining fusion reactions for prolonged periods of time. To keep a nuclear fusion reaction going, hydrogen isotopes must be confined and maintained at extremely high pressures and temperatures that are several times hotter than the sun.
In 2021, JET held a nuclear fusion reaction for 5 seconds to produce 59 megajoules (MJ) of energy, almost double that of the previous record. However, scientists had to put 3x as much energy into the system as was created by the reaction.
In December 2022, The National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California (US) created a fusion reaction that produced more energy than was needed to spark the reaction. The machine’s laser fired 2 megajoules onto a target and produced 3 megajoules of energy. This demonstrated the viability of nuclear fusion energy for the first time ever.
This does not apply to nuclear fission because splitting apart atomic nuclei requires less pressure and lower temperatures than is required to join nuclei together.
How Can Nuclear Power Help Mitigate Climate Change
Climate change is a severe, long-term consequence of fossil fuel combustion. If left untreated, atmospheric CO2 can remain there for tens of thousands of years and exacerbate the negative effects of climate change. Nuclear power emits less CO2 upon operation than fossil fuels and can therefore reduce our total emissions.
How Is Climate Change Defined
Climate change is arguably the most severe, long-term global impact of CO2. Every year, we emit approximately 37 billion tons of CO2. The carbon found in fossil fuels reacts with oxygen in the air to produce CO2.
“Climate change: changes in the earth’s weather, including changes in temperature, wind patterns, and rainfall, especially the increase in the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere that is caused by the increase of particular gasses, especially carbon dioxide.”
Oxford Dictionary
When carbon enters the atmosphere, it absorbs sunlight and solar radiation, trapping the heat and acting as an insulator for the planet.
Since the Industrial Revolution, Earth’s temperature has risen a little more than 1 degree Celsius (°C), or 2 degrees Fahrenheit (°F). Between 1880-1980 the global temperature rose by 0.07°C every 10 years. This rate has more than doubled since 1981, with a current global annual temperature rise of 0.2°C, or 0.36°F, for every decade.
How Does Nuclear Power Specifically Help Mitigate Climate Change
The global average concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere today registers at 419 parts per million (ppm), the highest ever recorded. Nuclear power can help lower this concentration because it can replace some of the burning of fossil fuels (e.g., coal, oil, natural gas) with a cleaner form of renewable energy.
Nuclear power helps to avoid 1.5 gigatons of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions per year and 180 billion cubic meters of global gas demand per year. In the past 50 years, nuclear power has helped avoid over 70 gigatons of GHG emissions.
Increasing nuclear power energy usage can reduce CO2 emissions, and the more we reduce CO2 emissions, the more we combat the negative effects associated with climate change including temperature rise, sea-level rise, ice melting, and ocean acidification. When these rates are slowed, the earth’s biodiversity does not have to struggle to adapt to temperature and pH changes. People will not be displaced due to the flooding of coastal areas. And icebergs will continue to provide climate regulation.
How Effective and Efficient Is Nuclear Power
In terms of effectiveness, nuclear power effectively generates nuclear energy by having a low carbon footprint, protecting air quality, being energy dense, generating few waste products, and promoting energy independence and security.
In terms of efficiency, nuclear power uses energy-dense input materials to efficiently generate nuclear energy and has a small land-use carbon footprint when compared to other energy types.
Nuclear power is effective because:
- Nuclear power has become one of our largest global contributors of carbon-free electricity, accounting for roughly 10% of the world’s energy generation.
- Nuclear power has the second-lowest carbon footprint out of all fuel types. On a life-cycle basis, nuclear fission emits 12 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced.
- Nuclear power produces a fraction of the pollution and toxic chemicals that fossil fuels produce, helping to protect air quality.
- Nuclear power is extremely energy dense, so you don’t need a lot of it to create a lot of energy.
- Nuclear power produces substantially less waste than other forms of energy.
- Nuclear power can help us transition away from fossil fuels and towards an energy-independent future.
- Nuclear fusion reactions are not based on chain reactions and therefore cannot cause a nuclear accident
However, nuclear power can lack effectiveness because:
- Nuclear fission is classified as a nonrenewable resource. Once we run out of Uranium-235, we won’t be able to generate the nuclear fission reaction anymore.
- Nuclear fusion is still very much in the research and development phase because the fusion process is difficult to start, maintain, and control.
Nuclear power is efficient because:
- Nuclear power uses fuel that is extremely energy dense, so you don’t need a lot of it to create a lot of energy.
- Nuclear power has a small land-use footprint, using only 0.3 square meters of land per megawatt-hour of electricity produced, the lowest out of all energy types.
However, nuclear fusion can lack efficiency because the two main challenges to fusion are maintaining the reaction and generating more energy from the reaction than was required to start the reaction.
How Safe or Dangerous Is Nuclear Power
Overall, nuclear power is considered to be minimally dangerous. Holistically and throughout its life cycle, nuclear power is safe and beneficial for human and animal health, the environment, and the energy grid. It is also significantly safer than fossil fuels and some other types of renewable energy.
Here’s How Safe Nuclear Power Is
Overall, nuclear power is a safe form of energy regarding human and animal health, the environment, the energy grid, and throughout all stages of its life cycle.
| How Safe Is Nuclear Power at a Holistic Level | Human and Animal Health: Nuclear power is considered safe when it comes to human and animal health due to the rarity of nuclear accidents. Environment: Nuclear power emits minimal greenhouse gas emissions and has a minimal effect on the environment, provided that proper siting of nuclear facilities and disposal of nuclear waste occurs. Energy Grid and Infrastructure: Nuclear power is not only safe, but it is also a beneficial addition to our energy grid and supporting infrastructure. |
| How Safe Is Nuclear Power Across Its Life-Cycle | Building: Safe work practices and proper training can mitigate the risks associated with the building stage of nuclear power. Operating and Maintaining: Nuclear power is generally considered safe to operate and maintain, if proper precautionary measures are followed. Building Back: This final stage is considered to be safe overall, with the hazard of handling, containing, and disposing of spent nuclear materials able to be mitigated with proper procedures and safe work practices. |
| How Safe Is Nuclear Power In Comparison to Other Types of Energy | Nuclear power is one of our safest forms of energy that has one of the lowest death rates from accidents and air pollution per unit of electricity generation. |
Here’s How Dangerous Nuclear Power Is
Overall, nuclear power is considered minimally dangerous in terms of human and animal health, the environment, the energy grid, and through all stages of its life cycle.
| How Dangerous Is Nuclear Power at a Holistic Level | Human and Animal Health: Nuclear power can be dangerous to human and animal health if proper measures are not in place. Environment: Nuclear power is minimally dangerous to the environment, provided that proper siting of nuclear facilities and disposal of nuclear waste occurs. Energy Grid and Infrastructure: Nuclear power is not considered to be dangerous to our energy grid and supporting infrastructure. |
| How Dangerous Is Nuclear Power Across Its Life-Cycle | Building: Nuclear power plant construction and uranium mining come with the danger of radiation exposure. Operating and Maintaining: Nuclear power is considered minimally dangerous to operate and maintain if proper precautionary measures are followed. Building Back: Decommissioning nuclear power facilities comes with risks involving direct contact with spent nuclear fuel and radioactive plasma vessel walls. |
| How Dangerous Is Nuclear Power in Comparison to Other Types of Energy | Nuclear power is one of our safest forms of energy that has one of the lowest death rates from accidents and air pollution per unit of electricity generation. |
Final Thoughts
Nuclear power has a low carbon and land footprint, protects air quality, is energy dense, generates few waste products, and promotes energy independence and security. However, nuclear power does produce nuclear waste which can negatively impact the environment if not properly dealt with.
Despite this, the pros of nuclear power outweigh the cons. Beginning to reverse the climate crisis means we have to cut CO2 emissions now, and nuclear power can help us do that. Nuclear power has the second-lowest carbon footprint out of all energy types and emits a fraction of the CO2 and air toxics that fossil fuels emit.
Although its future remains uncertain due to negative public opinion, incorporating more nuclear power-generated energy into our power grid has many benefits.
Stay impactful,
Sources
- Impactful Ninja: Nuclear Power Explained: All You Need to Know
- International Atomic Energy Agency: What is Nuclear Energy? The Science of Nuclear Power
- World Nuclear Association: Nuclear Fusion Power
- Impactful Ninja: How Does Nuclear Fission Work? From Source Till Energy Generation
- Impactful Ninja: How Does Nuclear Fusion Work? From Source Til Energy Generation
- Britannica: Carbon footprint | Definition, Examples, Calculation, Effects, & Facts
- World Nuclear Association: Carbon Dioxide Emissions From Electricity
- World Nuclear Association: Average life-cycle CO2 equivalent emissions
- IOP Science: Evaluation of CO2 emissions in the life cycle of tokamak fusion power reactors
- International Atomic Energy Agency: Tokamaks, Stellarators, Laser-based and Alternative Concepts
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Nuclear Power? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Union of Concerned Scientists: Coal Power Impacts
- University of Michigan Center for Sustainable Systems: Nuclear Energy Factsheet
- Freeing Energy: How much CO2 and pollution comes from burning coal?
- World Nuclear Association: Nuclear Energy and Sustainable Development
- Visual Capitalist: The Power of a Uranium Pellet Compared to Fossil Fuels
- Nuclear Energy Institute: Nuclear Fuel
- International Atomic Energy Agency: What is nuclear fusion
- US Department of Energy: Energy Efficiency – Buildings and Industry
- World Nuclear Association: What is nuclear waste, and what do we do with it?
- US Department of Energy: 3 Reasons Why Nuclear is Clean and Sustainable
- International Atomic Energy Agency: Fusion – Frequently asked questions
- US Environmental Protection Agency: Summary of the Energy Independence and Security Act
- International Energy Agency: Nuclear
- Impactful Ninja: Nuclear Power Explained: All You Need to Know
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Nuclear Power 101
- ITER: Advantages of fusion
- World Nuclear Association: What is nuclear waste, and what do we do with it?
- US Energy Information Administration: Nuclear power and the environment
- Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists: Fusion reactors – Not what they’re cracked up to be
- National Geographic: Nonrenewable Energy
- National Grid Group: Why is nuclear a clean energy?
- World Nuclear Association: Uranium Mining Overview
- Scientific American: What Is the Future of Fusion Energy?
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: The Paris Agreement
- Science: European fusion reactor sets record for sustained energy
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: National Ignition Facility
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Global Warming 101
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: The Paris Agreement
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Climate Change – Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
- Impactful Ninja: Fossil Fuel Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Coal Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Oil Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Natural Gas Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- International Energy Agency: Executive summary – Nuclear Power and Secure Energy Transitions
- Impactful Ninja: How Effective and Efficient Is Nuclear Fission? A Holistic Life-Cycle Analysis
- Impactful Ninja: How Safe Is Nuclear Fission? A Holistic Life-Cycle Analysis
- Impactful Ninja: How Dangerous Is Nuclear Fission? A Holistic Life-Cycle Analysis
- Impactful Ninja: The History of Nuclear Fission – The Big Picture
- Nuclear Energy Institute: Here’s How a Nuclear Reactor Actually Works
- World Nuclear Association: Occupational Safety in Uranium Mining
- Beyond Nuclear International: Nuclear power and harm to animals
- US Energy Information Administration: Delivery to consumers
- Our World in Data: What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?