Green Energy vs Alternative Energy: What’s the Difference?
Affiliate Disclosure
Hey fellow impactful ninja ?
You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts.
Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click.
But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend.
Why do we add these product links?
First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide.
And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases.
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you.
And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you.
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you).
And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself.
What does this mean for me personally?
You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money.
Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go.
Stay impactful,
Green and alternative energy sources are sustainable energy options to replace fossil fuels (e.g. coal and natural gas). These terms are commonly used synonymously, but did you know there are instances where they are not mutually exclusive? Identifying the differences between the two is crucial to make informed decisions about our energy usage. So we had to ask: What’s the difference between green and alternative energy?
Green energy is the generation of energy from infinite sources that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or negatively impact the environment. Alternative energy provides the same benefits, but the energy source may not be in infinite supply. Both aid in the fight against global climate change.
So, we know it is beneficial to use green and alternative energy, but how can we tell the difference between the two? What makes energy green? How about alternative energy? And can some energies be classified as both, or even as neither? You can find all of these answers below, where we will define both terms and have a look at which of the six major non-fossil energy sources fall into each category.
How Are Green Energy and Alternative Energy Defined
Green and alternative energy do not mean the same thing, although they may appear so at first glance. They both share the same end goals of reducing global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and preserving the environment, but the energy source supply is what separates these two.
What Does the Dictionary Say About Green Energy and Alternative Energy
Green and alternative energies are substitutes for fossil fuels (e.g., coal and oil) that have lower levels of GHG emissions and have less of a negative impact on the environment.
“Green Energy: energy that can be produced in a way that protects the natural environment, for example by using wind, water, or the sun”
Cambridge Dictionary
Green energy is a subset of renewable energy that includes a zero-emissions profile and carbon footprint reductions to provide the highest environmental benefit.
“Alternative Energy: electricity or power that is produced from the sun, wind, water, etc. in ways that do not use up the earth’s natural resources or harm the environment”
Oxford Dictionary
Alternative energy does not produce GHG emissions that contribute to global warming or cause substantial harm to the environment.
Both green and alternative energy sources do not produce GHG emissions or harm the environment, but only green energy sources are also in infinite supply.
What Do These Differences Between Green and Alternative Mean
The difference between green energy and alternative energy involves the longevity of the resource, and whether it is renewable or not.
- If energy is only green but NOT alternative: The energy source is in infinite supply AND does not produce GHG emissions or harm the environment, while alternative energy “only” does not emit greenhouse gases or harm the environment (but may or may not be in infinite supply).
- If energy is only alternative but NOT green: The generation of energy does not produce greenhouse gases or harm the environment, but the energy source supply is finite. For example, nuclear energy does not harm the environment or produce greenhouse gases, but there is a finite amount of Uranium required for nuclear energy generation.
Basically, green energy is in infinite supply and does not pollute the atmosphere or harm the environment. Alternative energy also does not pollute the atmosphere or harm the environment, but the energy source may not be in infinite supply.
What Are the Differences and Similarities Between Green Energy and Alternative Energy
Using an energy source that is either green or alternative is a great way to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere and to preserve the natural state of the environment. But an even better way to maximize these benefits is to utilize energy sources that are both green AND alternative!
| Energy type | Energy source |
| Both Green and Alternative Energy | Geothermal Solar Low-Impact Hydropower |
| Only Green but not Alternative Energy | Wind |
| Only Alternative but not Green Energy | Nuclear |
| Renewable Energy that is neither Green Nor Alternative | Large Hydropower, Biomass |
The following five energy sources can be classified as green, alternative, both, or neither following a detailed analysis into the longevity of the resource, carbon emissions profile, and impact on the environment.
Which Energies are Both Green Energy and Alternative Energy
If energy is both green AND alternative, the energy source is in infinite supply, and the generation of energy does not produce greenhouse gases or harm the environment. Below are the energy sources that are both green and alternative.
- Geothermal Energy: drilling down to hot water reservoirs creates steam that rotates a turbine, which spins a generator to generate electricity. Geothermal is renewable because the Earth has an almost unlimited supply of heat generated by its core. This process is deemed green because although it does release minute amounts of carbon dioxide, the amount is, well, minute. It is also alternative because it minimizes any negative environmental impacts by only drilling to shallow depths and by recycling the water used.
- Low-Impact Hydropower: projects that generate 10 MW or less of power. Flowing water turns turbines, which spins a generator to generate electricity. This process is renewable because the water cycle is a continuous process that recharges itself. It is also green because, on a small scale, hydropower produces very few greenhouse gases and has little to no environmental impact. Installing small turbines in irrigation canals, water-treatment plant outfalls, and existing hydroelectric facilities mitigates emissions and environmental impact, making it alternative.
- Solar Energy: photovoltaic cells in solar panels absorb energy from sunlight, creating an electrical charge that moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell and creates electricity. Solar is renewable because the sun will continue to emit energy until it goes supernova. This process is green because no greenhouse gases are emitted during operation, and following proper disposal methods of hazardous chemicals associated with PVCs and placing solar panels in less populated areas or on top of buildings minimizes any negative environmental impacts, making it alternative.
Geothermal, low-impact hydropower, and solar are both green and alternative energies because the energy source is in infinite supply, and the generation of energy does not produce greenhouse gases or damage the environment.
Which Energies Are Only Green Energy But Not Alternative Energy
If energy is only green but NOT alternative, the energy source is in infinite supply and the generation of energy does not produce greenhouse gases, but it does harm the environment. Below are the energy sources that are green but not alternative.
- Wind Power: wind turns the blades of wind turbines around a rotor, which spins a generator to generate electricity. It is renewable because as long as the wind blows, wind power can be harnessed. This process is clean because no greenhouse gases are emitted during its operation. It is not alternative though because spinning turbine blades pose a threat to flying wildlife, and the land use requirement for wind farms is very high.
Wind power is clean energy but not alternative energy because its energy production negatively impacts the environment in some way.
Which Energies Are Only Alternative Energy But Not Green Energy
If energy is only alternative but NOT green, the generation of energy does not produce greenhouse gases or harm the environment, but the energy source supply is finite. Below are the energy sources that are alternative but not green.
- Nuclear Energy: in nuclear fission, an enormous amount of energy is released when electromagnetic radiation is used to split the nucleus of a uranium atom (U-235). The process of nuclear fission does not produce GHG emissions or harm the environment, but nuclear energy is not green because there is a finite supply of U-235, the uranium isotope used in nuclear power plants, on Earth. We have already used up most of our U-235 because it has a half-life of about 700 million years.
Nuclear power is green energy but not alternative energy because the Uranium used in the process of nuclear fission is not a renewable resource.
Which Non-Fossil Energies Are Neither Green Nor Alternative
If energy is NEITHER green NOR alternative, the energy source is either finite, produces GHG emissions, harms the environment, or all of the above. Below are the energy sources that are neither green nor alternative.
- Biomass: Wood, agricultural crops, biogenic materials, animal manure, and human sewage contain stored chemical energy from the sun which is burned for heat. This process is not green because the combustion of biomass materials releases sequestered greenhouse gases in the biomass material into the atmosphere. Albeit, the amount released is much less than is released from fossil fuels. It is also not alternative because the biomass industry is responsible for clearcutting forests and reducing both plant and animal biodiversity.
- Large Hydropower: facilities that have a capacity of more than 30 megawatts (MW). Flowing water turns turbines, which spins a generator to generate electricity. This process is not green because the construction of large hydroelectric facilities and biomass decomposition in the reservoirs produces GHG emissions (e.g. carbon dioxide and methane), although the rate of emissions is much lower than that of fossil fuels. It is also not alternative because dams that create reservoirs can obstruct fish migration, alter the water temperature and chemistry, and flood out adjacent lands.
So if an energy source is neither green nor alternative, does this mean we shouldn’t use it as a replacement for fossil fuels? Absolutely not!
Biomass may not be green or alternative, but it is a renewable resource because it can be replenished by planting trees and agricultural crops. The quantity of greenhouse gases released and the level of environmental impact of biomass can be reduced by planting fast-growing trees, utilizing efficient stoves, and having strict air pollution control regulations.
Hydropower may not be green or alternative, but it is a renewable resource because the water cycle is a continuous process that recharges itself. The quantity of greenhouse gases released and the level of environmental impact of hydropower can be reduced by planning land use around river basins upstream of dams and constructing fish ladders that help with migration patterns.
By using hydropower instead of coal or natural gas we can still drastically reduce carbon emissions. To be more specific, per kilowatt-hour of electricity generated, hydropower only emits 2.3% of carbon dioxide-equivalent as compared to coal (18.5g vs 820g) and 3.8% as compared to natural gas (18.5g vs 490g) – when taking into account their whole life-cycle.
Why Is it Important to Differentiate Difference Between Green and Alternative Energy
Knowing the benefits and drawbacks of green and alternative energy allows us to make better-informed decisions about our energy usage.
| Green Energy | Alternative Energy | |
| Benefits | Reduces carbon footprint, air pollution, and water environmental impacts; infinite energy supply; promotes decentralization; potentially no GHG emissions and non-polluting | No GHG emissions, non-polluting, does not harm the environment |
| Drawbacks | High up-front cost; some have intermittent production, geographic limitations, lower quantities of energy produced | Some have intermittent production, geographic limitations, or nuclear waste byproducts |
Green Energy is a more specific category of renewable energy that provides higher environmental benefits than renewables. It can also reduce carbon footprints, air pollution, and water environmental costs. However, green energy possesses geographic limitations and offers intermittent production peaks depending on weather conditions (that could highly benefit from a smart grid).
Alternative energy does not produce greenhouse gases or negatively impact the environment, making it a good alternative to fossil fuels. On the other hand, it can have intermittent production and geographic limitations which could benefit from technology such as the smart grid. The impact of spinning turbine blades on wildlife and land use impact of various energies are other issues that need to be addressed when considering implementing this energy source.
How Do Green and Alternative Energy Benefit the Environment
Below are three ways in which green energy and alternative energy can help us overcome the current global climate crisis and lead us to a more sustainable future:
- Climate Change Mitigation: green and alternative energy do not emit carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxides, or mercury into the atmosphere, soil, or water. These pollutants are known to contribute to the thinning of the ozone layer, global sea-level rise, and the melting of our world’s glaciers. They also aim to cause the lowest level of environmental harm.
- Energy Independence: Being able to produce our own electricity in the U.S. without the aid of foreign countries is an important step to help us become more self-sufficient instead. Former President George W. Bush signed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 to reduce U.S. dependence on oil, expand the production of renewable fuels (and confront global climate change).
- Employment Opportunities: The renewable energy sector employed 11.5 million people worldwide in 2019, with solar energy making up the bulk of those jobs. Renewable energy jobs continue to increase as we start to realize just how beneficial renewable energy is for our environment.
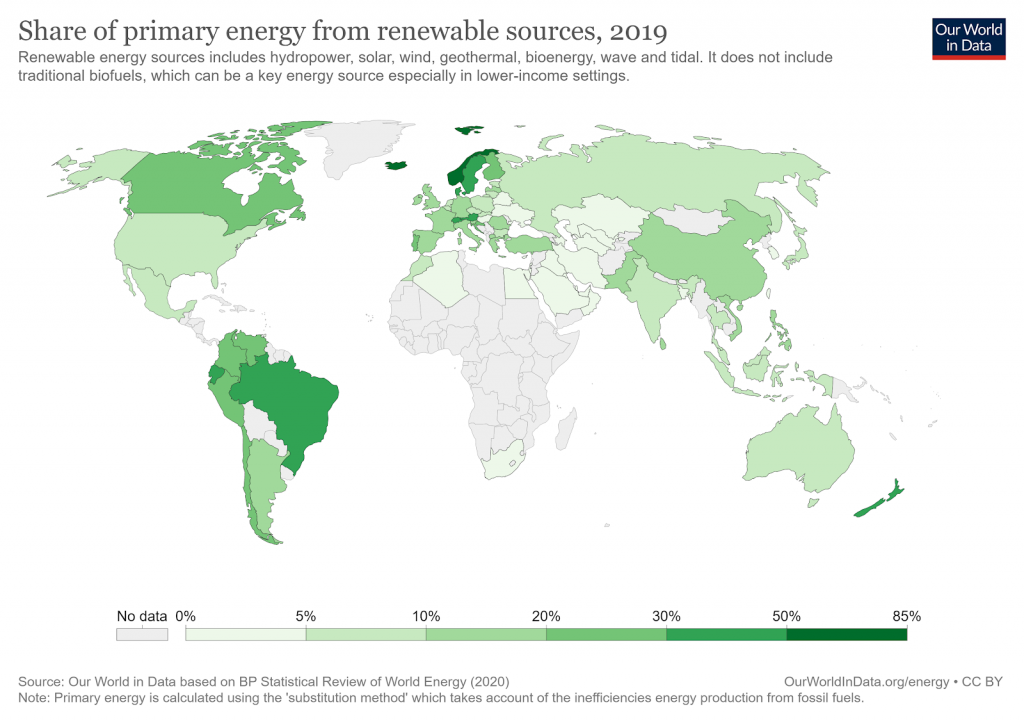
Renewable energy accounted for 11% of total energy consumption in the United States in 2019. This was equal to the amount of coal consumption and was nearly three times greater than consumption in 2000. Experts predict renewable resource consumption will continue to increase through 2050 as more and more effort is put into reducing global GHG emissions.
However, we still have a long way to go to make green or renewable energy sources our primary form of energy. Only a very few countries have renewables as their primary energy source, while the vast majority of countries still have a long way to go.
Final Thoughts
Green energy and alternative energy do not mean the same thing! Green energy is a more specific category that includes resources that are in infinite supply, while this is not necessarily the case for alternative energy. Both are important in the fight against global climate change though because they do not pollute the atmosphere or harm the environment. Knowing their differences, benefits, and drawbacks is important when deciding which energy to use.
Of the energy sources described above, large hydropower and biomass energy are neither green nor alternative. But this doesn’t necessarily make them a bad choice as a substitute for fossil fuels! They are both still renewable resources, and proper planning can mitigate carbon emissions and environmental impacts.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: What is Green Power?
- New World Encyclopedia: Alternative Energy
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Geothermal FAQs
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Geothermal Electricity Production Basics
- Brittanica: Geothermal Energy – Environmental Effects And Economic Costs
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: How Hydropower Works
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Types of Hydropower Plants
- National Hydropower Association: Small Hydro
- High Country Conservation Center: What’s the Difference Between Clean & Renewable Energy?
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: How Does Solar Work?
- Union Of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Solar Power
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Advantages and Challenges of Wind Energy
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: How Do Wind Turbines Work?
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Environmental Impacts and Siting of Wind Projects
- National Geographic: Non-Renewable Energy
- Brittanica: Nuclear Fission
- World Nuclear Association: Uranium Mining Overview
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Biomass Explained
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Biomass – Not Carbon Neutral and Often Not Clean
- Leonardo DiCaprio Foundation: Dangerous delusions – biomass is not a renewable energy source
- Synapse Energy Economics Inc.: Hydropower Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Union Of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Hydropower
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Biomass and the environment
- International Hydropower Association: Greenhouse gas emissions
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Guide to Purchasing Green Power
- Impactful Ninja: How Does the Smart Grid System Benefit the Environment
- White House Archives: Fact Sheet – Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Summary of the Energy Independence and Security Act
- International Renewable Energy Agency: Renewable Energy Jobs Continue Growth to 11.5 Million Worldwide
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Renewable Energy Explained
- Our World in Data: Share of Primary Energy from Renewable Sources