Is Eating Figs Ethical & Sustainable? Here Are the Facts
Affiliate Disclosure
Hey fellow impactful ninja ?
You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts.
Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click.
But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend.
Why do we add these product links?
First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide.
And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases.
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you.
And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you.
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it.
When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you).
And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself.
What does this mean for me personally?
You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money.
Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go.
Stay impactful,
Figs are a sweet, squishy fruit popular in Italian cuisine. They are also becoming increasingly popular in the US, with the fresh fig market valued at around $1.5 billion. However, there can be some very unethical and unsustainable aspects of the fig industry. So, we had to ask: Is eating figs ethical and sustainable?
Eating figs is somewhat ethical. Workers are generally paid a fair wage and there is no evidence of child labor within the industry. However, working hours can vary significantly and workers are often exposed to hazards such as wildfire smoke and unsafe environmental temperatures.
Eating figs is fairly sustainable. On the one hand, they require a significant amount of irrigation and have a moderate carbon footprint. However, their carbon sequestering properties and low pesticide use mean they are more sustainable than many other fruits.
In this article, we will assess both the ethical and sustainability practices of the fig industry. Through these two lenses, you will be able to gain in-depth knowledge of the overall impacts of the figs that you eat!
Here’s How We Assessed the Ethics & Sustainability of Figs
The Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture Systems (SAFA) is one of the ways we measure the externalities of our actions, like the consumption of figs. It is a holistic assessment based on the potential impact of food and agriculture operations on the environment and people. Those impacts are changes in our environment that can have adverse effects on the air, land, water, fish, and wildlife or the inhabitants of the ecosystem.
“Ethical: The discipline concerned with what is morally good and bad and morally right and wrong”
Encyclopedia Britannica
Ethics and sustainability are closely interconnected concepts that share a common objective: the well-being and preservation of our planet, including all its life and future generations.
“Sustainable: The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level | Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance”
Oxford Dictionary
Basically, all goods and services you buy—including figs—leave an impact on people, animals, and our environment. And when it comes to food in general—and figs in specific—the following are key factors for their ethics and sustainability:
- Social and economic conditions: The ethics of food crucially depends on the social and economic conditions of the farmers who grow them. Especially on fair labor practices, including fair wages and safe working conditions.
- Seasonality: Eating seasonally is a lever of sustainability. The two key reasons are that seasonal food is more likely grown in their “natural growing season” without using greenhouses, and also more likely to be grown locally.
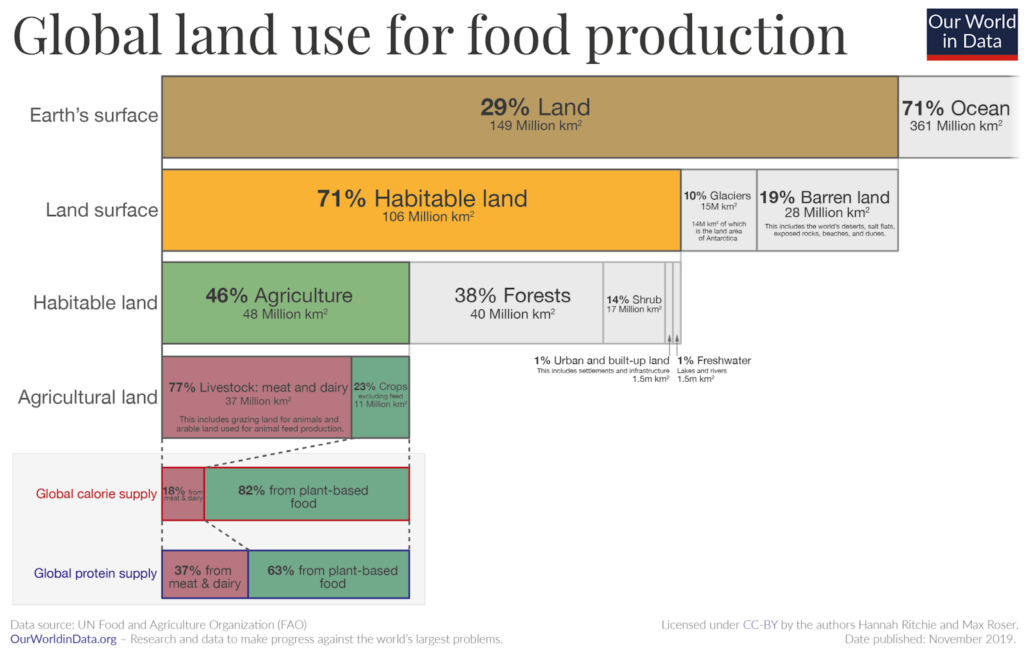
- Land requirements: Large parts of the world that were once covered by forests and wildlands are now used for agriculture. 10 million hectares of forest are destroyed annually and 50% of the world’s habitable land is now used for agriculture. This loss of natural habitat has been the main driver for reducing the world’s biodiversity.
- Water footprint: 70% of global freshwater is now used for agricultural purposes. By assessing the water footprint of a particular food, we can determine how our limited freshwater resources are being consumed and polluted.
- Pesticide and fertilizer usage: Pesticides and fertilizers provide a range of agricultural benefits. However, numerous studies link pesticides and fertilizers to serious effects on human health, along with disruptions to vital ecosystems and the spread of aquatic dead zones.
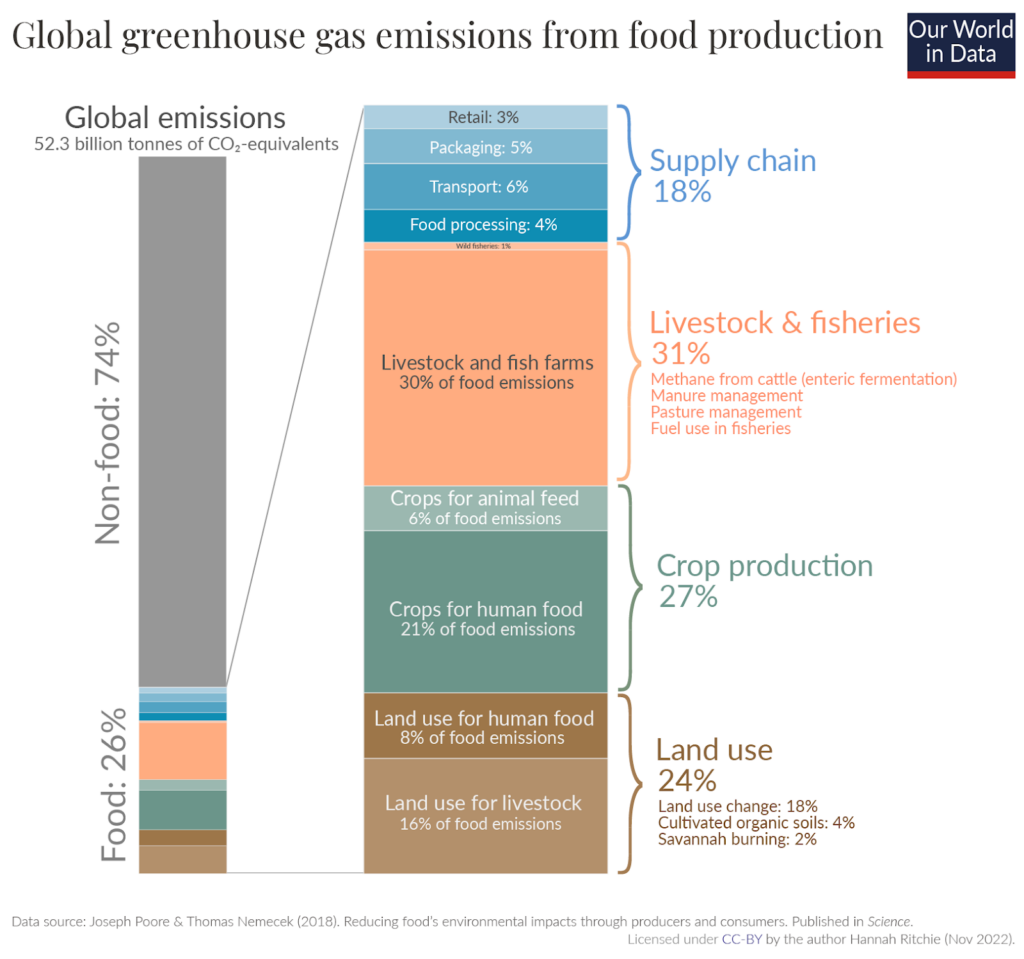
- Carbon footprint: The carbon footprint is one of the ways we measure the effects of our human-induced global climate change. Today, food production accounts for over a quarter (26%) of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste generation: Food and its packaging account for almost 45% of the materials landfilled in the US alone. And packaging sent to landfills, especially when made from plastics, does not degrade quickly or, in some cases, at all.
To understand the overall environmental impact of figs, we must assess each of their key factors. This Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture Systems (SAFA) is a tool developed for assessing the impact of food and agriculture operations on the environment and people. And this tool helps us to evaluate whether eating figs is ethical & sustainable.
Here’s How Ethical & Sustainable Eating Figs Is
The overall ethics & sustainability of figs is high. Their only unsustainable qualities are high irrigation needs amongst US-grown figs and a moderately high carbon footprint. The industry also has very few reports of ethical issues.
Figs are very sustainable and potentially ethical fruits. Fig plants sequester carbon very well, provide habitats and food for wildlife, and have even been used to restore rainforests. However, there are still a few unsustainable practices within the industry that you need to be aware of. Working conditions can also be improved.
So, let’s have a look at the ethics & sustainability impact of each key factor of figs!
| Key Assessment Factors | Ethics & Sustainability |
| Social and economic conditions of figs | Figs’ social and economic conditions are fair compared to other fruits. Their farming location in California means they may fall under many of the same ethical concerns as other California agriculture, such as poor working conditions. However, there are no reports of harmful child labor practices on fig farms. |
| Seasonality of figs | Figs’ seasonality is between May and November. They are more sustainable to buy in the US during this time because they are often locally grown. Out-of-season, figs are usually imported from Turkey. This requires longer travel distances which means higher fuel usage and thus a higher carbon footprint. |
| Land requirements for figs | Figs’ land requirements are somewhat high. However, their benefits for wildlife and biodiversity, such as habitat creation, means that they are fairly sustainable at this stage. |
| Water footprint of figs | Figs have a high water requirement of 50–75 inches of water per year. Considering that they grow in dry regions, figs require a significant amount of irrigation which can be fairly unsustainable. |
| Agrochemical usage for figs | Figs’ agrochemical use is low, especially on small, local farms. However, larger farms sometimes use certain fertilizers that can be harmful to the environment, notably nitrogen fertilizer. |
| Carbon footprint of figs | Figs have a moderate carbon footprint of 0.3kg (0.68lb) of CO2e per pound of figs. This is mainly because of their high irrigation requirements, mechanized harvesting processes, refrigerated trucking, and plastic packaging. |
| Waste generation of figs | Figs’ waste generation is fairly high. This is exacerbated by the fact that their waste has low composting rates and they are often packaged in plastic which is difficult to recycle. |
These are the overall summaries, but there is a lot more to the story. In the next few sections, we will dive deeper into each stage to illustrate to you all the important aspects of figs’ ethics & sustainability.
How Ethical & Sustainable Are the Social and Economic Conditions for Figs
Figs’ social and economic conditions are fair compared to other fruits. Their farming location in California means they may fall under many of the same ethical concerns as other California agriculture, such as poor working conditions. However, there are no reports of harmful child labor practices on fig farms.
Everything we consume was made or harvested by somebody. In past centuries, this was often someone who lived in your community and who you might have even known personally. But through the rise of globalized distribution systems, we have become increasingly alienated from the people who make our food. This leaves a lot of room for exploitation and abuse, both of which are rampant in the food industry. Here, we will look at how the fig industry fares in relation to these ethical questions.
How ethical & sustainable are the social and economic conditions of growing figs?
- Are farmers paid fair wages to grow figs: Most figs in the US are grown in California. The average California farm worker’s salary is around $30,000. However, they also tend to have more unstable hours than many other professions, meaning that income is actually much less than this. This means that their salary is far lower than what is needed to live comfortably in California.
- How safe are the working conditions to grow figs: The working conditions on California’s farms can be very bad. Many California farm workers have reportedly had to work amid wildfire smoke, in unsafe heat, and even with exposure to dangerous pesticides. Figs in general have low pesticide rates, so the latter might be to a lesser extent, but the first two dangers may be significant issues.
- Are there reports of child or forced labor to grow figs: There are no major reports of child labor within the fig industry specifically. However, child labor has been reported in the US farming industry in general.
- What is the wider economic impact on the communities that grow figs: Many agricultural workers in California are employed under the migrant worker program. Although they do make decent wages, they are also open to unique vulnerabilities and exploitation.
In short, the fig industry is linked to some poor working conditions, making them slightly unethical.
How Ethical & Sustainable Are the Seasonality for Figs
Figs’ seasonality is between May and November. They are more sustainable to buy in the US during this time because they are often locally grown. Out-of-season, figs are usually imported from Turkey. This requires longer travel distances which means higher fuel usage and thus a higher carbon footprint.
Every fruit has a natural season in which they grow, usually lasting a couple of months, which can range depending on the region. However, international demand for every kind of fruit is year-round. This demand is often met by importing fruits from tropical places which can grow year-round, or by growing them in greenhouses. Both of these methods use more resources and are thus less sustainable than conventional farming. Here, we will look at how the fig industry accommodates year-round demand.
How ethical & sustainable is it to grow figs in-season vs out-of-season?
- When is the natural season for growing and harvesting figs: Figs have a long season in the US, being available generally from May until November. This means that you will be able to find the most widely-available domestic figs during this time.
- How are figs naturally grown in-season: During their season, most figs in the US are grown in California and Texas. This means that they will need to be transported smaller distances and are thus more sustainable than out-of-season figs.
- How are figs grown out-of-season: Out-of-season, much of the US imports figs from Turkey. So, they have to be shipped across the ocean, which comes with high emissions. Thus they are far less sustainable than in-season figs.
In short, figs are much more sustainable during their US season, since they use less emissions for transportation.
How Ethical & Sustainable Are the Land Requirements for Figs
Figs’ land requirements are somewhat high. However, their benefits for wildlife and biodiversity, such as habitat creation, means that they are fairly sustainable at this stage.
The growth stage has a major impact on fruits’ sustainability. The amount of land used, especially in relation to its expansion, the method with which they are grown, and their effect on surrounding land and wildlife are all important factors. In this section, we will look at the ways in which figs’ land usage affects their sustainability.
How ethical & sustainable are the land requirements for growing figs?
- What is the land usage of figs: Figs yield around 12 tons per hectare. This is a fairly low yield amongst fruits. For example, bananas can yield up to 100 tons per hectare. Though it is not the lowest of all, since watermelons only yield around 2–3 tons per hectare. This makes them moderately unsustainable compared to other fruits.
- Where and how are figs grown: Most figs are grown in Turkey on trees in orchards, however they are also commonly grown in the US during certain months of the year. All trees sequester carbon, meaning that they capture carbon from the atmosphere and store it in the ground. Fig trees have particularly excellent carbon sequestering properties, which is good news for their carbon footprint and thus their sustainability. Fig trees tend to naturally occur in monocultures. However, their monocultures are not as harmful to wildlife as other monocultures can be, since they fruit year-round, so they don’t limit pollinators.
- How does the growing of figs affect soil fertility and erosion: Fig trees are generally considered beneficial to the environment and are heavily used in forest restoration projects. However, figs can also have negative impacts on the surrounding area and the soil, mainly through their roots’ invasiveness. Therefore, if planted responsibly, figs can help restore biodiversity to an area, but if not, they can choke out other plants and make soil uninhabitable.
- How does the figs industry affect the loss of habitable land: Fig trees use a significant amount of land because of their low yield. However, they are also excellent at attracting biodiversity and reforesting depleted areas. Because fig trees are tropical and a natural habitat for many tropical species, they are a favorite for rainforest reforestation projects in particular.
- How does the figs industry affect wildlife and biodiversity: Fig trees are very beneficial to wildlife and biodiversity. This is mainly because they are an excellent food source for a variety of species. They especially support wasps and any fruit-eating animals with their constant-fruiting growth method.
In short, figs are actually fairly sustainable when it comes to land. Though they use a significant amount of land, they bring considerable benefits to it.
How Ethical & Sustainable Is the Water Footprint of Figs
Figs have a high water requirement of 50–75 inches of water per year. Considering that they grow in dry regions, figs require a significant amount of irrigation which can be fairly unsustainable.
Water usage is one of the most important factors in a fruit’s sustainability. Practices like irrigation use significant resources and can cause pollution, and as such, factors like the amount of water used, where it is sourced, as well as the way they affect the water sources around them, are all important. Here, we will look at these different angles of figs’ water footprint.
How ethical & sustainable is the water footprint of growing figs?
- What is the overall water usage of figs: Figs require around 50–75 inches of water per year. This is a fairly high water requirement amongst fruits. For example, cherries only need around 35 inches of water per year, though watermelons require up to 100.
- What is the green water footprint of figs: The green water footprint is the amount of water from precipitation stored in the soil and used by plants for growth. Most US-consumed figs are grown in California and Texas. California only gets around 23 inches of rain per year and Texas only about 27 inches. Thus, all of the regions’ rainfall needs to go towards figs’ water requirements.
- What is the blue water footprint of figs: The blue water footprint is the amount of water sourced from surface (such as rivers or lakes) or groundwater resources. Because figs’ water requirements are far above what Texas or California’s rainfall can provide, they need significant irrigation. Irrigation is very detrimental to the environment for several reasons, but mainly because it creates groundwater imbalances.
- What is the gray water footprint of figs: The gray water footprint is the amount of freshwater required to clean up water pollution to meet certain quality standards. Essentially, it’s the amount of water needed to make polluted water clean enough to be safe and healthy for humans and the environment. Figs have low pesticide use and so don’t need a significant amount of water to clean up their pesticide residues.
- How does the figs industry affect freshwater and ocean pollution: The fact that figs don’t use a significant amount of pesticides means that they will pollute waterways less than fruits with high pesticide use. However, their use of significant irrigation can pollute waterways through excess salt.
In short, figs’ use of considerable irrigation lowers their sustainability. However, their low pesticide use reduces their potential for a larger impact.
How Ethical & Sustainable Is the Agrochemical Usage for Figs
Figs’ agrochemical use is low, especially on small, local farms. However, larger farms sometimes use certain fertilizers that can be harmful to the environment, notably nitrogen fertilizer.
Pesticides and fertilizers are agrochemicals that are very unsustainable and damaging to ecosystems. This is because they require resources to create and can easily run off into groundwater and soil systems. Here, we will look at how sustainable figs’ pesticide and fertilizer rates really are.
How ethical & sustainable is the agrochemical usage of growing figs?
- What is the pesticide usage of figs: Figs have low pesticide usage in general. This means that they avoid many of the unsustainable qualities of pesticides.
- What is the fertilizer usage of figs: Fig trees generally don’t need a significant amount of fertilizer, unless the soil they are growing in is particularly barren. However, more major farms may use fertilizer, often a general purpose NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) fertilizer. Potassium is actually somewhat sustainable, whereas nitrogen has been found to be very unsustainable. However, fig trees’ use of nitrogen fertilizer is minimal and so not as impactful as a fruit tree which primarily uses nitrogen fertilizer, such as avocados.
- Are there any known issues connected to the agrochemical usage for figs: Nitrogen fertilizers can cause many problems with waterways in particular. This is because they promote invasive algae growth, which can harm many kinds of aquatic life.
In short, figs’ minimal pesticide and fertilizer use, despite the inclusion of nitrogen fertilizer, means their agrochemical footprint is fairly low overall.
How Ethical & Sustainable Is the Carbon Footprint of Figs
Figs have a moderate carbon footprint of 0.3kg (0.68lb) of CO2e per pound of figs. This is mainly because of their high irrigation requirements, mechanized harvesting processes, refrigerated trucking, and plastic packaging.
Carbon footprint is one aspect of the overall sustainability of a fruit. It essentially measures how much carbon or other greenhouse gasses the production of fruits emits into the atmosphere. Emissions from product manufacturing, irrigation, transportation fuel, and landfills all add up to create the overall carbon footprint of a fruit. Let’s see how the carbon footprint of figs contributes to their overall sustainability.
How ethical & sustainable is the carbon footprint of figs?
- What is the overall carbon footprint of figs: The overall carbon footprint of figs is 0.3kg (0.68lb) of CO2e per pound of figs. This means that for every pound of figs produced, 0.3kg of carbon is released into the atmosphere. 0.3kg is a moderate carbon footprint compared to other fruits.
- What are the main contributors to the carbon footprint of figs: The main factors that contribute to figs’ carbon footprint are their mechanized harvesting, high irrigation requirements, low land yield, refrigerated trucking, low composting rates, and the use of plastic packaging.
- Which life-cycle stage of figs has the highest carbon footprint: The stage that contributes the most to figs’ carbon footprint is harvesting, processing, and packaging. This is because almost every step of this process requires energy, from harvesting machines to refrigerators. The use of plastic in their packaging process also creates emissions through plastic manufacturing.
In short, figs have a fairly average carbon footprint amongst fruits. Their emissions mainly come from their irrigation requirements, plastic packaging, and refrigeration needs.
How Ethical & Sustainable Is the Waste Generation of Figs
Figs’ waste generation is fairly high. This is exacerbated by the fact that their waste has low composting rates and they are often packaged in plastic which is difficult to recycle.
When fruit waste, either in the form of packaging or organic materials, is disposed of, it can cause a lot of problems. Whether it’s damaging wildlife, getting into oceans, emitting methane, or dissolving into microplastics that contaminate groundwater, all these materials have their part to play. The sheer amount of waste we produce is reaching a crisis point and won’t be able to continue much longer. In this section, we will look at how sustainable figs’ waste generation is.
How ethical & sustainable is the waste generation of figs?
- What is the packaging of figs: Figs are mainly packaged in plastic clamshells. Plastic creates significant environmental damage just in its manufacturing process. These damages include extracting and burning fossil fuels, runoffs harming local wildlife, and emissions harming the health of nearby people.
- How is the packaging of figs disposed of: Plastic is one of the worst materials to dispose of. Though some plastic is recyclable, only 9% of plastic is actually successfully recycled, leaving the other 91% for landfill. Landfills are very unsustainable and so the more un-recycled plastic there is, the more damage it can do. Plastic is also notorious for breaking down into microplastics, which pollute groundwater and can even end up in food.
- How are figs disposed of: Figs have peels that can be eaten, however, some people don’t like the texture. Unfortunately, despite the fact that they can be composted, only 4% of food actually ends up in the compost. This means that a good portion of figs are put in landfills, either because people don’t eat the peels or because the figs themselves have gone bad. When food goes into landfills it creates methane, a greenhouse gas, which can be harmful to the environment.
In short, the disposal of figs is very unsustainable. The low composting rates of food waste and low recycling rates of plastic mean most fig waste ends up in landfills.
What Have Been Historical Ethics & Sustainability Issues Connected to the Fig Industry
The fig industry has historically had a minimal impact on people and the environment. They have not contributed majorly to land loss or water pollution.
All fruits have had a complex road toward global distribution. They originate in one part of the world and often travel far to end up in your local supermarket. From farm to table, some of our favorite fruits have racked up some serious damage along the way. Whether it’s exploiting labor, deforestation to meet demand, water pollution, or disruption of wildlife, most fruits have left a path of destruction. Let’s see how figs have fared throughout history.
What have been the key ethical & sustainable issues of the fig industry?
- Has labor been exploited because of fig production: There have been many labor disputes on California farms over things like wages, overtime, and hours. However, fig farms have not been specifically named in these reports.
- How much land has been lost because of fig production: Figs have a low land yield, so their land use is high. However, figs are not as popularly farmed as more common fruits like oranges and apples. Global fig farming only amounts to around 1 million tons a year, whereas oranges are valued at 50 million tons a year and apples at around 76 million tons. Therefore, they have not had as much of a historical burden on land use as other fruits.
- Which wildlife species have been negatively impacted or displaced because of fig production: Since fig trees make excellent habitats for wildlife by providing food sources and pollination, they have had some positive impacts over the years. They also have had historically low pesticide rates which has helped them to minimize their negative impact on wildlife.
- Have water sources and soil been contaminated because of fig production: The fact that fig trees have used small amounts of pesticides and fertilizer means that their impact on water sources has been low. However, the small amount of nitrogen fertilizer they use may have had some impacts on waterways.
In short, figs have historically had very little impact on people and the environment. Their low pesticide and fertilizer rates, and positive relationship with wildlife have resulted in a small negative impact on the environment.
How Can You Reduce Your Environmental Impact and Offset Your Personal Carbon Footprint
There are a few things you can do to make your fig consumption more ethical and sustainable, while still enjoying them. You can also consider offsetting your personal and fig-related carbon emissions, which work to remove carbon emissions elsewhere that are then attributed to you. Here, we will walk you through how to accomplish both of these things.
How Can You Shop for Figs More Ethically & Sustainably
In this section, we give you a short list of ways you can consume figs in a more sustainable way. This list is designed to target the most unsustainable parts of figs’ life-cycle:
- Buy in-season figs: One of the more unsustainable components of figs is that they are typically imported out-of-season. To avoid the unsustainable emissions from these shipments, try to limit your fig consumption to between May and November.
- Avoid plastic packaging: Both at the manufacturing stage and the disposal stage, plastic packaging is very unsustainable. Buy figs with alternative or biodegradable packaging, or no packaging at all, to make your fig consumption significantly more sustainable.
- Compost and recycle: If it isn’t possible to avoid plastic packaging altogether, then you should make the effort to recycle or reuse it as much as possible. Likewise, you should try to compost your fig waste. If your city doesn’t have a composting system, then you can consider building one yourself!
Following some of these methods can really help you to make your fig-eating more sustainable. None of these will completely eradicate the negative impacts, since there are always effects that may be outside of your control. But some reduction is always better than nothing!
Which Organizations Can You Support to Help Promote Ethics & Sustainability
While fig production engages in some very unsustainable practices, there are also some organizations that help you change the parts of these processes that would otherwise be outside of your control. These organizations are working hard to prevent and reverse damage to the environment caused by industries like fig agriculture, towards a more sustainable future.
In the table below are some of the best charities that work in the areas where fig production are very unsustainable—and beyond:
Though it is helpful to boost the sustainability of your personal fig consumption, supporting these organizations takes your positive impact a step further. You will be reaching far beyond your own consumption impacts and helping to build a better world for everyone!
How Can You Offset Your Personal Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint is a key part of how sustainable we live. And it is one of the ways we measure the effects of our human-induced global climate change. Yes, even from eating figs!
“Carbon footprint: the amount of greenhouse gasses and specifically carbon dioxide emitted by something (such as a person’s activities or a product’s manufacture and transport) during a given period”
Merriam Webster
Basically, it is the amount of carbon emitted by you as an individual or an organization providing you with goods and services – including figs:
- This includes GHG emissions from producing the products that we use and foods that we eat (e.g., power plants, factories or farms, and landfills)
- GHG emissions from fuel that we burn directly or indirectly (e.g., logistics and transportation, cooling or heating facilities),
- as well as the GHG emissions attributed to how we consume these products and foods.
Carbon offsets are reductions in carbon emissions that are used to compensate for carbon emissions occurring elsewhere – for example for the carbon emissions that are associated with figs. They are measured in tons of CO2 equivalents and are bought and sold through international brokers, online retailers, and trading platforms on what is known as the global carbon offset market.
“Carbon Offset: a way for a company or person to reduce the level of carbon dioxide for which they are responsible by paying money to a company that works to reduce the total amount produced in the world, for example by planting trees”
Oxford Dictionary
In terms of figs – and indeed all food types – there will always be a carbon footprint, because of the resources it takes to get your food from farms to the place where you’ll eventually eat them. And while there are ways to reduce your carbon footprint when shopping for figs, carbon offsets would be a way to reduce your CO2e emissions all the way down to net zero (or even to become climate positive).
However, when you purchase carbon offsets, it’s important that they actually make a difference in offsetting (aka reducing) total carbon emissions. To achieve that, the following are key criteria:
- Carbon offset projects have to be effective (different projects have different effectiveness rates)
- Carbon offset projects have to be additional
- Carbon offset projects have to be permanent
- The claims from carbon offset projects have to be verifiable
To find the best carbon offsets for you personally, check out our full guide on the best carbon offsets for individuals, where you’ll also learn more about how these carbon offset projects work, what their respective offsetting costs are, and what your best way would be to offset your own carbon emissions.
Final Thoughts
Figs are one of the most sustainable fruits out there, with few known ethical issues. Their impacts on land and water sources are very low, mainly because of their minimal pesticide and fertilizer rates, as well as their positive relationship with surrounding wildlife. However, they do require higher amounts of irrigation when grown in the US, and their carbon footprint is moderate. But with some reduction methods, such as cutting down on packaging and even potentially growing your own figs, you can become a much more responsible fig consumer!
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Italian Food Forever: All About Figs
- Future Market Insights: Fresh Figs Market
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: SAFA (Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture systems) Guidelines
- Food Ethics Council: What is food ethics?
- The Fair Labor Association: Agriculture Standards
- MDPI Sustainability: Eating in Season—A Lever of Sustainability? An Interview Study on the Social Perception of Seasonal Consumption
- MDPI Foods: The Role of Local Seasonal Foods in Enhancing Sustainable Food Consumption: A Systematic Literature Review
- UN Environment Programme: Environmental Impact Assessment and Strategic Environmental Assessment: Towards an Integrated Approach
- Our World in Data: The environmental impacts of food and agriculture
- Our World in Data: Global land use for food production
- World Health Organization: Preventing disease through healthy environments: a global assessment of the burden of disease from environmental risks
- ScienceDirect (Biological Conservation): Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers
- EPA: The Sources and Solutions: Agriculture
- EPA: Reducing Food Waste and Packaging
- FoodPrint: The Environmental Impact of Food Packaging
- Gardening Know How: Water Requirements for Fig Trees
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Figs
- EPI: Farmworker Wages in California
- Sofi: What is a Good Salary for a Single Person Living in California
- Cal Matters: Farmworker Conditions in California Report
- Hello Magazine: The Food You Should Always Buy Organic
- Vox: Child Labor Laws
- The Guardian: California Migrant Workers
- ILO: Migrant Workers May Face Discrimination
- California Figs: Fresh Figs are Available in May
- Volza: Import in United States
- Agrifarming: Fig Farming Project Report
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Bananas
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Watermelons
- World Mapper: Fig Production by Country
- RHS: How to Grow Figs
- Woodland Trust: How Trees Capture and Store Carbon
- Pubmed: Using Fig and Eucalyptus for Restoration
- Sweets on Groves: Limes
- Saveur: Evolution is so Cool and so Gross
- Food Unfolded: How Fig Trees Restore Forests and Biodiversity
- Permaculture News: Dig the Fig
- Agrifarming: Fig Farming Project Report
- Mongabay: Can Fig Trees Regrow Lost Rainforests
- Water Footprint Network: What Is a Water Footprint?
- Gardening Knowhow: How to Water a Cherry Tree
- The Spruce Eats: History of Figs
- OEHHA: Oregon Precipitation
- Weatherstem: Texas Annual Precipitation
- Gardening Knowhow: Irrigating Fig Trees
- National Geographic: Environmental Impacts of Agricultural Modification
- Hello Magazine: The Foods You Should Always Buy Organic
- FAO: Environmental Considerations in Irrigation
- GOV.BC: Environmental Protection and Pesticides
- Wilson Bros Gardens: How to Fertilize and Water a Fig Tree
- Fig Nut: How to Fertilize a Fig Tree
- Direct Farm: Potassium
- Mitsui: Reducing the Environmental Impact of Chemical Fertilizers
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Avocados
- Figs 4 Fun: Crop Profile for Figs in California
- Actahort: Effect of Temperature on the Shelf Life of Figs
- EPA: Reducing the Impact of Wasted Food
- The Produce Nerd: Fresh Fig Harvesting and Packing
- OECD: Increased Plastic Leakage and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Biological Diversity: The Plastic Production Problem
- Also Known As: 12 Interesting Facts About Packaging Waste and Disposal
- Colorado: The Hidden Damage of Landfills
- UNEP: How Tiny Plastic Particles Are Polluting Our Soil
- BBE: How Plastic is Getting Into Our Food
- Taste of Home: How to Eat Figs
- GOV.BC: Waste Management
- Techno-Preneur: Fig Farming
- Habbas Law: Farm Worker Overtime
- World Atlas: Top Orange Producing Countries in the World
- Agribenchmark: World Apple Production
- SN Applied Sciences Journal: Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem
- Our World in Data: Global greenhouse gas emissions from food production
- Our World in Data: The environmental impacts of food and agriculture
- Earth Easy: Composting
- Our World in Data: Greenhouse Gas Emissions per 1,000 kilocalories
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Climate Change Terms
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Advance Ethics Worldwide
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Promote Sustainability
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Help Farmers
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Fight to Protect our Environment
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities for Reforestation
- Impactful Ninja: Best Wildlife Conservation Charities
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities for Protecting the Amazon Rainforest
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Fight for Clean Water
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Help Conserve Our Rivers
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities to Save Our Oceans
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities for Helping Farm Animals
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities for Climate Change
- Impactful Ninja: Best Carbon Offsets for Individuals
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Fight to Reduce Food Waste
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Fight to End Plastic Pollution
- Impactful Ninja: Best Charities That Promote Recycling
- Impactful Ninja: Why Is a Carbon Footprint Bad for the Environment?
- Impactful Ninja: Best Carbon Offsets for Individuals