Solar Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Enough sunlight strikes the surface of the earth in an hour and a half to account for the world’s energy consumption in a year. Harnessing that sunlight and turning it into energy could play a major role in us transitioning away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy. So, we had to ask: What is solar energy really, and how can it help mitigate climate change?
Solar energy is the conversion of solar radiation into electrical energy. Per KWh produced, concentrated solar emits 38, PV roof solar emits 41, and PV utility solar energy emits 48 grams of CO2 on a life-cycle basis. Solar energy helps combat climate change and has various environmental benefits.
Keep reading to find out all about what solar energy is, its global capacity, its carbon footprint, its environmental benefits and drawbacks, and how it can mitigate climate change.
The Big Picture of Solar Energy
Solar energy contributes to the avoidance of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the burning of fossil fuels (e.g., coal, oil, natural gas). It is classified as a renewable energy source because the resource (the sun) naturally replaces itself over time.
How Is Solar Energy Defined
Solar energy is the conversion of solar radiation into electrical energy either through the use of photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar radiation concentrating mirrors. The energy produced is then used to generate electricity or can be stored in batteries or thermal storage for use at a later time.
“Solar Energy: energy that uses the power of the sun to produce electricity”
Cambridge Dictionary
The amount and availability of sunlight varies by location and time of day and is called. And the amount of solar radiation a surface receives in a designated amount of time – called insolation – is influenced by latitude, climate, and weather patterns. Lower latitudes and dry climates generally have higher amounts of insolation whereas higher latitudes and wet climates have lower amounts of insolation.
What Are the Different Types of Solar Energy
Harnessing the power of the sun falls into two main categories:
- Photovoltaic (PV) solar cells: photovoltaic cells in solar panels absorb energy from sunlight, creating an electrical charge. This charge moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
- Concentrating solar thermal plants (CSP): mirrors reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect and convert solar energy into heat. This is utilized in very large power plants.
Both systems take the energy from the sun and convert it to electricity, just by slightly different mechanisms.
There are three main types of PV solar cells:
- Silicon: The most common material used in solar panels today because silicon is reasonably priced and efficient in converting sunlight directly to electricity. These panels are typically assembled on roofs of homes and buildings or are mounted en masse on racks for large-scale electricity generation.
- Thin film: These solar panels are made of very thin layers, several millionths of a meter, of semiconductor materials including cadmium, telluride, or copper. This technology is commonly used in portable applications (i.e. backpacks, windows) because it is lightweight and flexible.
- III-V solar cells: These solar panels are generally much more expensive but also have much higher efficiency. They are made from periodic table Group III elements (gallium and indium) or Group V elements (arsenic and antimony). This technology is commonly used on satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles, and applications with a high power-to-weight ratio.
A group of PV solar panels clustered together forms a PV solar power plant. The largest PV solar power plant in the world is the Huanghe Hydropower Hainan Solar Park located in the Qinghai province of China. It has a capacity of 2.2 GW and 202.8 MW hours of storage capacity.
There are also three main types of concentrating solar thermal power plants:
- Linear: U-shaped mirrors focus sunlight onto tubes that span the length of the mirrors. The sunlight heats the fluid contained within the tubes, which is then sent to a heat exchanger. The heat boils water to produce steam, which spins a turbine and powers a generator to produce electricity. The two types of linear plants are parabolic trough systems and linear Fresnel reflector systems.
- Dish/engine: A mirrored dish, similar to a very large satellite dish, contains many flat mirrors formed into a dish shape. The dish focuses and concentrates sunlight onto a receiver which absorbs and collects the heat, transferring it to an engine generator. The fluid heated by the receiver moves pistons in the most common engine, the Stirling engine. This mechanical power powers a generator to produce electricity.
- Power tower: Heliostats, sun-tracking mirrors, reflect and concentrate sunlight onto a receiver that sits on top of a tower. The sunlight can be concentrated as much as 1,500 times. Water is most often used as the heat-transfer fluid which boils water to produce steam, spins a turbine, and powers a generator to produce electricity.
The largest solar power plant in the world is the Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan’s Jodhpur district, a state in India. It spans 14,000 acres and has a 2,250 GW capacity.
| What solar energy is | Solar energy is the conversion of sunlight into electrical energy. |
| What the different types solar energy are | The two types of solar energy are PV cell (silicon, thin film, or III-IV solar cells) and concentrating solar thermal plants (linear, dish/engine, or power tower). |
| How solar energy works | To harness solar energy, PV solar panels or solar radiation concentrating mirrors convert solar radiation into electrical energy which then turns turbines and spins a generator to create electricity. |
| The global capacity of solar energy | Solar energy accounts for roughly 13% of all renewable energy generation. China, the United States, Japan, Germany, and India are the top solar energy-producing countries in the world. |
| The carbon footprint of solar energy | On a life-cycle basis, concentrated solar energy emits 38, PV roof solar energy emits 41, and PV utility solar energy emits 48 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced. |
| The environmental benefits of solar energy | Solar energy protects air quality, mitigates climate change, promotes energy independence, and creates jobs. |
| The environmental drawbacks of solar energy | Solar energy can adversely impact land and water use and release hazardous materials into the environment. |
| Solar energy and climate change | Solar energy combats climate change by mitigating the temperature rise, sea-level rise, ice melting, and ocean acidification associated with global warming. |
How Does Solar Energy Work
To harness solar energy, PV solar panels or solar radiation concentrating mirrors convert solar radiation into electrical energy which then turns turbines and spins a generator to create electricity.
How Does Solar Energy Actually Produce Energy
Solar energy operates differently depending on the type of solar power plant (i.e. PV or concentrating).
PV solar power plants operate in the following way:
- Sunlight strikes a PV solar panel, creating an electrical charge
- The charge moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow
The electricity is then transported to a substation where it is transmitted to consumers by transmission lines. Transformers receive the electricity and either increase or decrease the voltage as needed before it can be delivered to consumers.
Concentrating solar power plants operate in the following way:
- Mirrors reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers
- Receivers collect and convert solar energy into heat
- In the case of linear and power tower systems, the heat boils water to produce steam. The steam then spins a turbine and powers a generator to produce electricity.
- In the case of dish/engine systems, a heated receiver moves pistons in an engine. This movement powers a generator to produce electricity.
The electricity is either stored for later use or is transported to a substation where it is transmitted to consumers by transmission lines. Transformers receive the electricity and either increase or decrease the voltage as needed before it can be delivered to consumers.
What Is the Global Capacity of Solar Energy
Globally, solar energy is a fast-growing renewable energy source, accounting for roughly 13% of all renewable energy generation in 2021.
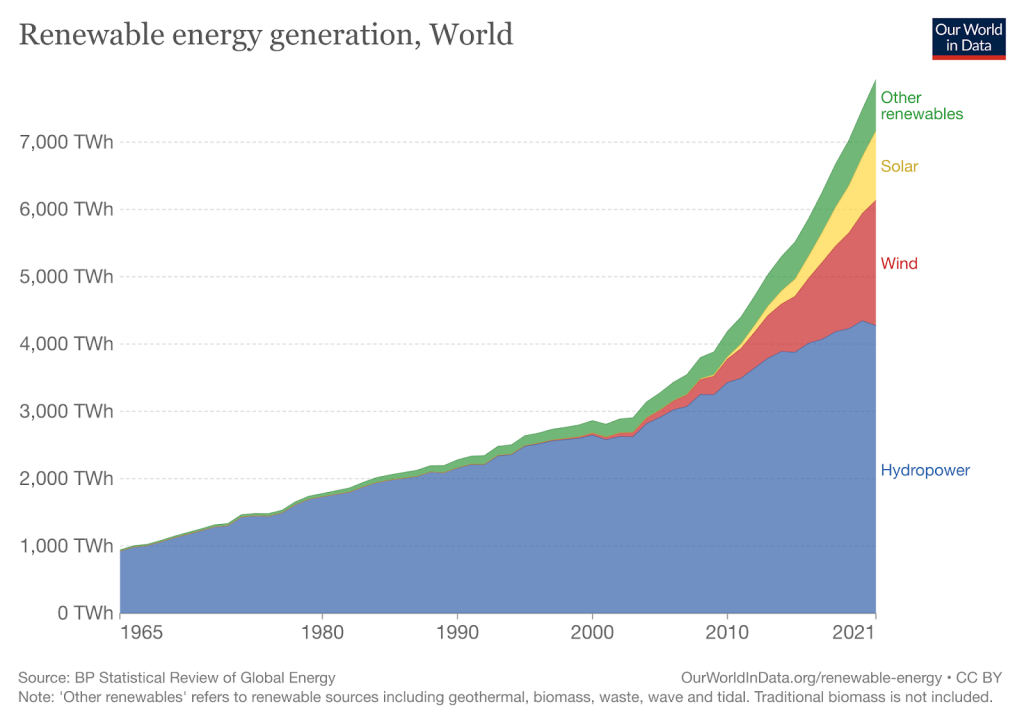
Initially, European countries drove solar growth. But with decreasing costs and technological improvements, more countries entered the market. China, the United States, Japan, Germany, and India are the top solar energy-producing countries in the world.
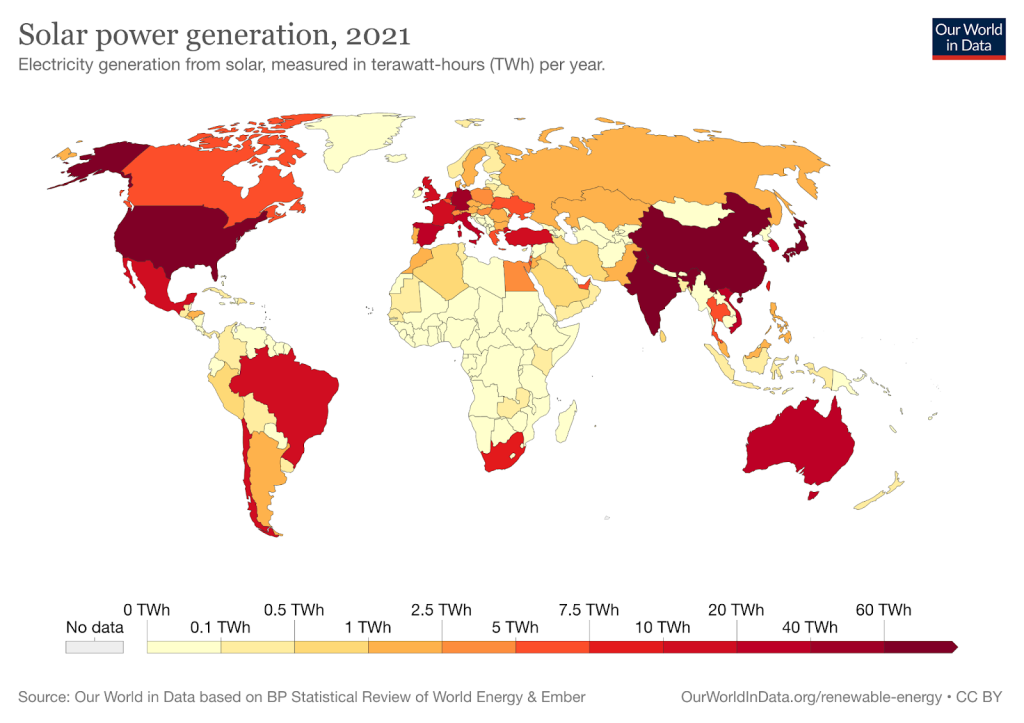
Solar energy is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy technologies with a low carbon emissions profile. The COVID-19 pandemic saw a decrease in fossil fuel emissions due to stay-at-home orders and supply chain disruptions. During this time, PV solar energy generation increased 23% to reach 821 TWh. Concentrating solar power only increased 0.2 GW, with additions occurring solely in China.
In order to meet targets set in the net zero by 2050 scenario, PV solar capacity must increase 24% annually, and concentrating solar must add roughly 6.7 GW of capacity annually. We are making progress with PV solar but still have a long way to go with concentrating solar.
What Is the Carbon Footprint of Solar Energy
The carbon footprint is one of the ways we measure the effects of human-induced global climate change. It primarily focuses on the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with consumption and includes other emissions such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
“Carbon footprint: the amount of greenhouse gasses and specifically carbon dioxide emitted by something (such as a person’s activities or a product’s manufacture and transport) during a given period”
Merriam Webster
Basically, it is the amount of carbon emitted by an activity or an organization. This includes GHG emissions from fuel that we burn directly (e.g., heating a home, driving a car) and GHG emissions from manufacturing the products that we use (e.g., power plants, factories, and landfills).
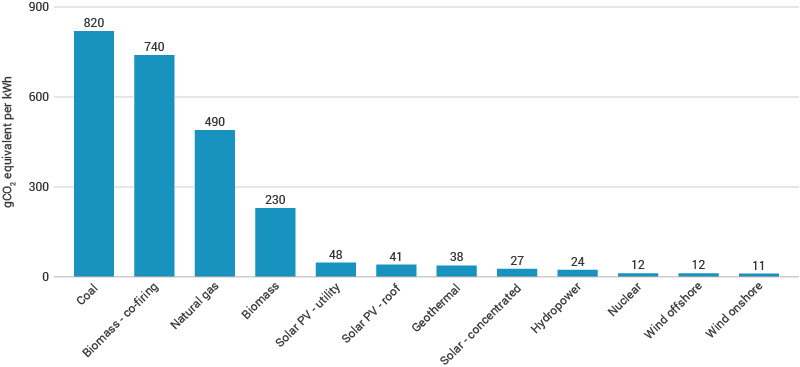
On a life-cycle basis, concentrated solar energy emits 38, PV roof solar energy emits 41, and PV utility solar energy emits 48 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced.
Have a look at the illustration below to see the average life-cycle CO2 equivalent emissions of different energy sources and how they compare to solar energy.
When discussing the carbon footprint of solar energy, we must take into account carbon emissions across the energy’s building, operating, and building back phases.
| The life-cycle stages of solar energy | Each stage’s carbon footprint |
| Building of solar energy | CO2 emissions from the construction of solar power plants and electricity delivery mechanism |
| Operating of solar energy | Little to no CO2 emissions or waste products |
| Building back of solar energy | CO2 emissions from decommissioning the solar farms and land restoration |
Throughout its life cycle, concentrated solar energy produces 0.04%, PV roof solar energy produces 0.05%, and PV utility solar energy produces 0.06% of the CO2 emissions per unit of electricity than coal produces. It also creates jobs and promotes energy independence, making it an environmentally friendly energy source.
Solar panels themselves have an average life expectancy of 25-30 years. And this can be extended for many decades with proper maintenance because the panels do not have moving parts and are typically only damaged by poor installation, wind, debris, or other inclement weather events. Also, solar panel output generally decreases by 0.8% each year. At the end of 25 years, solar panels can still operate at around 82.5%, and some panels have even lower degradation rates so they can remain in operation for longer.
Solar energy makes up an ever-growing amount of total energy consumption and plays a vital role in combating climate change. Therefore it is important to understand what its carbon footprint is and how its carbon emissions affect the global climate change process.
How Environmentally Friendly Is Solar Energy
The environmental impacts of solar energy largely depend on where solar power plants are constructed and how hazardous materials are disposed of.
“Environmentally friendly: (of products) not harming the environment.”
Cambridge Dictionary
Overall, solar energy is sustainable because it does not emit greenhouse gasses, and land use, water use, and hazardous material threats can be mitigated by proper disposal methods and siting of solar power plants.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
Here are the ways in which solar energy benefits the environment:
- Protects air quality: Rather than combusting materials, solar power plants harness the energy of the sun to generate electricity. PV panels and concentrating mirrors do not produce greenhouse gasses and emit no sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides.
- Climate change mitigation: Solar energy has an average life-cycle CO2 equivalent emission value that is much less than coal, 27 (concentrated), 41 (roof), and 48 (utility) g of CO2 equivalent per kWh compared to 820g of CO2 equivalent per kWh, respectively. This reduction in CO2 emissions, in turn, reduces the effects of global climate change including increasing temperatures, rising sea levels, melting of sea ice, changing precipitation patterns, and ocean acidification.
- Energy independence: Being able to produce our own electricity in the U.S. without the aid of foreign countries is an important step to help us become more self-sufficient. Former President George W. Bush signed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 to reduce U.S. dependence on oil, expand the production of renewable fuels (and confront global climate change).
- Employment opportunities: The renewable energy sector collectively employed 12 million people worldwide in 2020. Renewable energy jobs continue to increase as we start to realize just how beneficial renewable energy is for our environment.
What Are the Environmental Drawbacks of Solar Energy
The three main concerns associated with solar energy are land use, water use, and hazardous materials.
- Land use: The scale of land degradation and habitat loss depends on the technology, site topography, and intensity of the solar resource. Siting large-scale solar farms on abandoned land and small-scale farms on top of buildings or homes can minimize negative environmental impacts.
- Water use: Water is used to construct PV components, and CSPs require water for cooling. Wet-recirculating, once-through, and dry-cooling methods are utilized to reduce the amount of water used.
- Hazardous materials: Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen fluoride, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, and acetone are all used to manufacture PV cells. If not handled and disposed of properly, they could present a serious risk to environmental and public health. Strict laws are in place to reduce the likelihood of this occurring.
Proper siting and disposal methods can help mitigate these environmental drawbacks.
Why Is Solar Energy Important to Fight Climate Change
Climate change is arguably the most severe, long-term, global impact of fossil fuel combustion. Every year, approximately 33 bt of CO2 are emitted from burning fossil fuels. The carbon found in fossil fuels reacts with oxygen in the air to produce CO2. This warms the earth by acting as a heating blanket, and a warmer earth comes with a host of negative side effects.
Using solar energy instead of fossil fuel energy helps mitigate the following negative effects of climate change:
- Increasing temperatures: Earth’s atmosphere has warmed 1.5℃ since 1880. This may not seem like a lot, but these degrees create regional and seasonal temperature extremes, reduce sea ice, intensify rainfall and drought severity, and change habitat ranges for plants and animals.
- Rising sea levels: Global sea levels have increased approximately 8-9 inches since 1880, displacing people living along coastlines and destroying coastal habitats. Roads, bridges, subways, water supplies, oil and gas wells, power plants, sewage treatment plants, and landfills remain at risk if sea level rise goes unchecked.
- Melting of sea ice: Since 1979, arctic sea ice has declined by 30%. Sea ice plays a major role in regulating the earth’s climate by reflecting sunlight into space and providing habitat for animal species. If all of the glaciers on Earth melted, sea levels would rise by approximately 70 feet, effectively flooding out every coastal city on the planet.
- Changing precipitation patterns: Extreme weather events (e.g., hurricanes, floods, droughts) are becoming more common and more intense. Storm-affected areas will experience increased precipitation and flooding whereas areas located further from storm tracks will experience decreased precipitation and droughts.
- Ocean acidification: The ocean absorbs 30% of the CO2 released into the atmosphere, which decreases the pH (increases the acidity) of the ocean. In the past 200 years, the pH of oceans has decreased by 0.1 pH units, which translates to a 30% increase in acidity. Aquatic life unable to adjust to this rapid acidification will die off. A prime example of this is coral bleaching, where coral expel the algae (zooxanthellae) living in their tissues as a result of changes in temperature, light, or nutrients.
The more we reduce CO2 emissions, the more we slow the rate of temperature rise, sea-level rise, ice melting, and ocean acidification. When these rates are slowed, the earth’s biodiversity does not have to struggle to adapt to temperature and pH changes. People will not be displaced due to the flooding of coastal areas. And icebergs will continue to provide climate regulation.
To help keep global temperature rise below 1.5C, as outlined in the Paris Agreement, we must shift at least 80% of our electricity generation to low carbon sources. Over 120 countries have already stated their net-zero carbon emissions ambitions for 2050 or 2060. But only 12 countries have thus far proposed or enacted any legislation, indicating that there is more work to be done.
Final Thoughts
Solar energy currently makes up 13% of all renewable energy generation. Solar radiation is converted into electrical energy via PV solar cells or solar radiation concentrating mirrors. That energy is then used to turn turbines and spin a generator to produce electricity.
Solar energy is an environmentally friendly energy source with a low carbon footprint across its building, operating, and building back phases. It mitigates climate change, improves air quality, creates jobs, and promotes energy independence. Proper siting and disposal methods can mitigate environmental concerns such as land and water usage.
As we look towards a future powered by renewables, solar energy is a sustainable energy source that benefits both our atmosphere and Earth’s biota.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Impactful Ninja: Renewable Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Coal Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Oil Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Natural Gas Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy: How Does Solar Work?
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Solar Explained – Where solar is found and used
- The National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Solar Photovoltaic Technology Basics
- NS Energy: Profiling the top five largest solar power plants in the world
- Solar Energy Industries Association: Concentrating Solar Power
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Solar Explained – Solar thermal power plants
- Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy: Dish/Engine System Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power Basics
- Britannica: Heliostat
- Our World in Data: Renewable energy
- Our World in Data: Renewable energy generation, World
- Nasdaq: The Top Five Nations Leading in Solar Energy Generation
- Our World in Data: Solar Power Generation
- World Health Organization: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic
- International Energy Agency: Solar PV
- International Energy Agency: Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
- Britannica: Carbon Footprint
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: System of Registries
- World Nuclear Association: Carbon Emissions from Electricity
- Our World in Data: Solar Power Generation
- EnergySage: How long do solar panels last? Solar panel lifespan explained
- The National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Photovoltaic Degradation Rates — An Analytical Review
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Solar Energy?
- Union of Concerned Scientists: The Hidden Costs of Fossil Fuels
- White House Archives: Fact Sheet – Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Summary of the Energy Independence and Security Act
- International Renewable Energy Agency: Renewable Energy and Jobs Annual Review 2021
- Union of Concerned Scientists: How it Works – Water for Power Plant Cooling
- National Resources Defense Council: Global Warming 101
- The National Wildlife Federation: Climate Change
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Climate Change – Global Temperature
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Climate Change – Global Sea Level
- United States Geological Survey: How would sea level change if all glaciers melted?
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration, U.S.A.: How does climate change affect precipitation?
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Ocean Acidification
- National Ocean Service: What is coral bleaching?
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: The Paris Agreement
- International Energy Agency: Oil 2021