Solar Energy: All 6 Pros and 4 Cons Explained
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Solar energy is one of our fastest-growing and most popular renewable energy technologies with a low carbon emissions profile. It can play an important role in the global energy transformation and help transition away from fossil fuels, but it can come with drawbacks as with any other energy source. So, we had to ask: What are the pros and cons of solar energy?
The main pros of solar energy include sustainability, a low carbon footprint, air quality protection, the generation of few waste products, and energy independence. However, the main cons of solar energy include intermittency, high upfront and maintenance costs, and specific land use requirements.
Keep reading to find out all about what the pros and cons of solar energy are, how effective and efficient it is, how it can mitigate climate change, and what better alternatives to reforestation carbon offsets are.
The Big Picture of Solar Energy
Solar energy is the conversion of solar radiation into electrical energy either through the use of photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar radiation-concentrating mirrors. The energy produced is then used to generate electricity or can be stored in batteries or thermal storage for use at a later time.
“Solar Energy: energy that uses the power of the sun to produce electricity”
Cambridge Dictionary
Harnessing the power of the sun falls into two main categories:
- Photovoltaic (PV) solar cells: photovoltaic cells in solar panels absorb energy from sunlight, creating an electrical charge. This charge moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
- Concentrating solar thermal plants (CSP): mirrors reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect and convert solar energy into heat. This is utilized in very large power plants.
Both systems take the energy from the sun and convert it to electricity, just by slightly different mechanisms. PV solar is the main mechanism used today to harness solar energy.
| 6 Pros of Solar Energy | 4 Cons of Solar Energy |
| Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable energy source | Solar energy is an intermittent energy source |
| Solar energy has a low carbon footprint | Solar energy has high upfront costs |
| Solar energy protects air quality | Solar energy can be expensive to maintain |
| Solar energy panels efficiently convert sunlight into electricity | Solar energy has specific land requirements |
| Solar energy generates few waste products | |
| Solar energy promotes energy independence and energy security |
What Are 6 Pros of Solar Energy
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable energy source, has a low carbon footprint, protects air quality, is efficient, generates few waste products, and promotes energy independence and security.
Pro #1: Solar Energy is a Renewable and Sustainable Energy Source
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable resource that can reduce emissions for generations to come.
Solar Energy Pro #1
Renewable energy sources are resources that naturally replace themselves over time.
“Renewable Energy: energy that is produced using the sun, wind, etc., or from crops, rather than using fuels such as oil or coal | types of energy that can be replaced naturally such as energy produced from wind or water”
Cambridge Dictionary
Solar energy is classified as a renewable energy source because the sun generates energy at a rate faster than we can consume it. We can also continue to harness the sun’s energy almost indefinitely, or until the sun goes supernova (which won’t be for another 5 billion years).
Solar energy is also classified as a sustainable energy source. Sustainable energy sources meet the needs of our current generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
“Sustainable: The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level | Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance”
Oxford Dictionary
Solar energy emits minimal greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) and has a minimal effect on the environment, provided that proper siting and disposal methods are followed. This means future generations can continue to harness solar energy for many years.
Pro #2: Solar Energy Has a Low Carbon Footprint
Solar energy has one of the lowest carbon footprints out of all energy types.
Solar Energy Pro #2
The carbon footprint is one of the ways we measure the effects of human-induced global climate change. It primarily focuses on the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with consumption and includes other emissions such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
“Carbon footprint: the amount of greenhouse gasses and specifically carbon dioxide emitted by something (such as a person’s activities or a product’s manufacture and transport) during a given period”
Merriam Webster
On a life-cycle basis, concentrating solar energy emits 38, PV roof solar energy emits 41, and PV utility solar energy emits 48 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced.
Have a look at the illustration below to see the average life-cycle CO2 equivalent emissions of different energy sources and how they compare to solar energy.
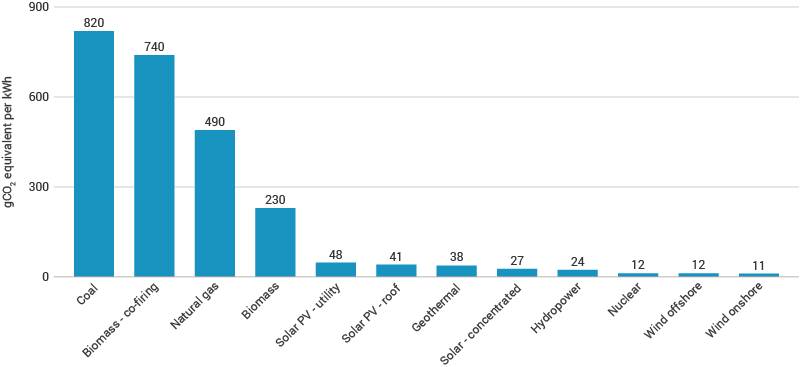
Overall, solar energy has the fifth-lowest carbon footprint out of all energy types, making it one of our cleanest energy sources.
Pro #3: Solar Energy Protects Air Quality
Solar energy produces a fraction of the pollution and toxic chemicals that fossil fuels produce, helping to protect air quality.
Solar Energy Pro #3
Air pollution can cause numerous health problems including asthma, breathing difficulties, brain damage, heart problems, and cancer. Fossil fuel (coal and natural gas) combustion emits coal ash residue, toxic heavy metals, CO2, carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, impairing public health.
Rather than combusting toxic materials like coal does, solar power plants harness the energy of the sun to generate electricity. PV panels and concentrating mirrors produce minimal greenhouse gasses and emit no sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides, thereby helping to protect air quality.
Pro #4: Solar Energy Panels Efficiently Convert Sunlight Into Energy
Solar energy is an efficient use of land and boasts a high-efficiency rate per solar panel.
Solar Energy Pro #4
Efficiency involves performing a task while using the least amount of resources and producing the least amount of waste possible.
“Efficient: working in a way that does not waste a resource (= something valuable such as fuel, water, or money)” Dictionary
Cambridge
Solar energy efficiency has drastically improved since the creation of the first PV solar cells in 1883 by American inventor Charles Fritts. His solar cells had an efficiency, also called an energy conversion rate, of 1-2%, meaning they converted only 1-2% of the total sunlight captured into usable energy.
Today’s PV solar cells have an average commercial energy conversion rate of 15-20% and an experimental conversion rate of more than 30%. High-efficiency panels can reach as much as 23%.
In order to increase the efficiency of solar energy we would have to increase the energy conversion rate. Experts have calculated the ceiling of solar cell efficiency, known as the Shockley-Queisser limit, as somewhere between 29% and 33%. So we are already approaching the limits of what is theoretically possible.
In addition, solar energy can require large amounts of land to establish solar farms, but it is an efficient use of that land, specifically farmland. One acre of solar panels can produce roughly 40 times more energy than one acre of corn devoted to ethanol production.
Pro #5: Solar Energy Generates Few Waste Products
Solar energy generates few waste products upon operation, and solar panels can be recycled.
Solar Energy Pro #5
In terms of emissions, solar energy produces few waste products, generating between 38 and 48 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced and zero sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxide emissions.
Solar panels themselves can be classified as hazardous waste depending on the type of metals present in the semiconductor and solder. For example, lead, arsenic, and cadmium are considered to be detrimental to human health and the environment, at high levels, and are therefore classified as hazardous. If solar panels containing toxic metals are dumped into landfills, the metals may leach out into the environment.
Recycling end-of-life solar panels can help ensure any toxic chemicals do not leach out into the environment. Many of the components of solar panels can be recycled, including glass, aluminum, copper wire, and the plastic junction box. Specialty metals and silicon cells can also be separated and purified via chemical and electrical techniques.
The solar panel recycling industry is still in its infancy and continues to evolve. Just in 2018, Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant opened in southern France. Previously, solar panels were recycled in traditional recycling facilities where the glass and aluminum were separated and the rest burned in cement ovens.
The International Renewable Energy Agency estimates that by 2030, the value of the recoverable raw materials from solar panels at the end of their lifespan will reach $450 million, which would be enough to produce approximately 60 million new solar panels. This highlights the importance of recycling solar panels.
Pro #6: Solar Energy Promotes Energy Independence and Energy Security
Solar energy can help us transition away from fossil fuels and toward an energy-independent future.
Solar Energy Pro #6
Being able to produce your own electricity without the aid of foreign countries is an important step in becoming more self-sufficient. For example, in the US, Former President George W. Bush signed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 to reduce US dependence on oil, expand the production of renewable energy, and confront global climate change.
Although solar energy alone cannot shoulder the burden of the world’s electricity needs, it can shoulder some. Solar energy is currently the third-largest renewable electricity technology behind hydropower and wind energy. PV solar accounted for roughly 4.5% of total global electricity generation in 2022, demonstrating the largest generation growth and surpassing wind energy for the first time in history.
What Are 4 Cons of Solar Energy
Solar energy is an intermittent energy source, faces high upfront and maintenance costs, and has specific land requirements.
Con #1: Solar Energy Is An Intermittent Energy Source
Solar energy production is heavily influenced by location, time of year, and weather patterns, making it unpredictable at times.
Solar Energy Con #1
Two of the main drawbacks associated with renewable energy are intermittency and lower levels of energy output, with solar energy being no exception.
The amount and availability of sunlight varies by location, time of day and year, and weather. The amount of solar radiation a surface receives in a designated amount of time—called insolation—is influenced by latitude, climate, and weather patterns. The unpredictable nature of solar means we cannot rely on it fully to produce all of our energy.
One way to combat intermittency is to store solar energy in batteries and draw from them in times when solar panels cannot produce energy, like at night.
Con #2: Solar Energy Has High Upfront Costs
Solar energy has a high upfront cost associated with solar panel installation.
Solar Energy Con #1
The cost of installing a residential solar system varies by location and system, but installation can cost thousands of dollars upfront. For example, the Solar Energy Industries Association estimates it costs roughly $25,000 to install an average-sized residential solar system in the US, before taking into account any tax incentives.
Solar batteries are another possible expense. Given that solar energy is intermittent, one way to ensure constant access to solar is to store unused solar energy in batteries for use in times when solar panels cannot capture sunlight, such as at night. However, solar batteries can cost between $12,000 and $20,000 to install, depending on the type and size.
Con #3: Solar Energy Can Be Expensive to Maintain
In addition to high upfront costs, solar energy can be expensive to maintain.
Solar Energy Con #3
Solar panels themselves have an average life expectancy of 25-30 years. This can be extended for many decades with proper maintenance because the panels do not have moving parts and are typically only damaged by poor installation or inclement weather events.
Routine solar panel maintenance can cost between $140-$180 per service, or $280-$720 annually, depending on the type of solar panels. Solar panel cleaning can cost $25 per panel, or $425-$525 for an average solar system with 17-21 panels.
In addition to regular maintenance, solar energy can come with hidden expenses such as optional solar system monitoring, roof and solar panel repairs, and tree trimming. Repairing solar panels can cost $300-$1300 on average, with external damage on the lower end and internal damage on the higher end of the price range.
Con #4: Solar Energy Has Specific Land Requirements
Utility-scale solar farms are site-specific and can require large amounts of land to produce energy.
Solar Energy Con #4
PV solar arrays constructed on top of residential or commercial buildings have a minimal land use impact. However, utility-scale solar projects can have a large land use carbon footprint. A utility-scale PV solar plant can require 5-10 acres per megawatt of generating capacity, and concentrating solar plants typically require 10-15 acres.
The type of land is also just as important as the amount of land. Flat, clear land close to major population centers is ideal for constructing solar farms because solar requires unobstructed sunlight, and electricity transmission lines get more expensive the longer they have to travel.
How Can Solar Energy Help Mitigate Climate Change
Climate change is a severe, long-term consequence of fossil fuel combustion. If left untreated, atmospheric CO2 can remain there for tens of thousands of years and exacerbate the negative effects of climate change. Solar energy emits less CO2 upon operation than fossil fuels and can therefore reduce our total emissions.
How is Climate Change Defined
Climate change is arguably the most severe, long-term global impact of CO2. Every year, we emit approximately 37 billion tons of CO2. The carbon found in fossil fuels reacts with oxygen in the air to produce CO2.
“Climate change: changes in the earth’s weather, including changes in temperature, wind patterns, and rainfall, especially the increase in the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere that is caused by the increase of particular gasses, especially carbon dioxide.”
Oxford Dictionary
When carbon enters the atmosphere, it absorbs sunlight and solar radiation, trapping the heat and acting as an insulator for the planet.
Since the Industrial Revolution, Earth’s temperature has risen a little more than 1 degree Celsius (°C), or 2 degrees Fahrenheit (°F). Between 1880-1980 the global temperature rose by 0.07°C every 10 years. This rate has more than doubled since 1981, with a current global annual temperature rise of 0.18°C, or 0.32°F, for every 10 years.
How Does Solar Energy Specifically Help Mitigate Climate Change
The global average concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere today registers at over 400 parts per million, the highest ever recorded. Solar energy can help lower this concentration because it can replace some of the burning of fossil fuels (e.g., coal, oil, natural gas) with a cleaner form of renewable energy.
Solar emits roughly 0.05%-0.08% of the amount of CO2 (grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh) as fossil fuels. Solar also has a life-cycle global warming emission between 0.08 and 0.2 pounds of CO2 equivalent per kilowatt-hour (kWh), whilst coal power plants have an estimated emission between 1.4-3.6 pounds of CO2 equivalent per kWh.
Increasing solar energy usage can reduce CO2 emissions, and the more we reduce CO2 emissions, the more we combat the negative effects associated with climate change including temperature rise, sea-level rise, ice melting, and ocean acidification. When these rates are slowed, the earth’s biodiversity does not have to struggle to adapt to temperature and pH changes. People will not be displaced due to the flooding of coastal areas. And icebergs will continue to provide climate regulation.
How Effective and Efficient Is Solar Energy
In terms of effectiveness, solar panels and concentrating mirrors are effective ways to convert sunlight into electricity. In addition, solar energy has a low carbon footprint, protects air quality, and promotes energy security and independence.
In terms of efficiency, solar panels are efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. In addition, solar energy is a renewable and sustainable energy source, increases the efficiency of the power grid, and generates few waste products.
Solar energy is effective because:
- Solar energy is an effective way to convert sunlight into energy. It is currently our third-largest renewable electricity technology behind hydropower and wind energy.
- Solar has the fifth-lowest carbon footprint out of all energy types. Concentrating solar energy emits 38, PV roof solar energy emits 41, and PV utility solar energy emits 48 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced, on a life-cycle basis.
- Solar produces a fraction of the pollution and toxic chemicals that fossil fuels produce, helping to protect air quality.
- Solar can help us transition away from fossil fuels and towards an energy-independent future.
Solar energy is efficient because:
- Solar energy boasts a high rate of efficiency per solar panel (15-20%) and is an efficient use of farmland.
- Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable resource that can reduce emissions for generations to come.
- Solar energy promotes the decentralization of our energy supply which increases power grid efficiency by reducing peak time usage and decreasing the likelihood of power outages.
- Solar energy generates few waste products upon operation, and solar panels can be recycled.
How Safe or Dangerous Is Solar Energy
Overall, solar energy is not considered to be dangerous. Holistically and throughout its life cycle, solar is safe and beneficial for human and animal health, the environment, and the energy grid. It is also significantly safer than fossil fuels and other types of renewable energy.
Here’s How Safe Solar Energy Is
Overall, solar energy is a safe form of energy regarding human and animal health, the environment, the energy grid, and throughout all stages of its life cycle.
| How Safe Is Solar Energy at a Holistic Level | Human and Animal Health: Solar energy is safe for human and animal health and can be made safer with proper siting, monitoring, and maintenance of solar facilities. Environment: Solar energy emits minimal greenhouse gas emissions and has a minimal effect on the environment. Energy Grid and Infrastructure: Solar energy is a safe and beneficial addition to our power grid. It promotes the decentralization of our energy supply, which increases power grid efficiency by reducing peak time usage and decreasing the likelihood of power outages. |
| How Safe Is Solar Energy Across Its Life-Cycle | Building: Safe work practices and proper training of solar professionals can mitigate any risks associated with constructing solar facilities. Operating and Maintaining: Solar energy is considered safe to operate and maintain because it does not harm human health or the environment when producing energy. Building Back: This final stage is considered to be safe overall, with the most common workplace hazards (lifting, trips and falls, electricity, and ladders) able to be mitigated by safe work practices. |
| How Safe Is Solar Energy In Comparison to Other Types of Energy | Solar energy is one of our safest forms of energy that has one of the lowest death rates from accidents and air pollution per unit of electricity generation. |
Here’s How Dangerous Solar Energy Is
Overall, solar energy is considered minimally dangerous in terms of human and animal health, the environment, the energy grid, and through all stages of its life cycle.
| How Dangerous Is Solar Energy at a Holistic Level | Human and Animal Health: Solar energy is not dangerous to humans and is minimally dangerous to animals, with the main concerns being habitat loss and fragmentation of natural habitats. Environment: Solar energy is minimally dangerous to the environment, with land degradation and solar panel toxicity being the two main concerns. Energy Grid and Infrastructure: Solar energy is not considered to be dangerous to our energy grid or supporting infrastructure. |
| How Dangerous Is Solar Energy Across Its Life-Cycle | Building: Building solar facilities can expose workers to arc flashes (arc flash burn and blast hazards), electric shock, falls, and thermal burns. Operating and Maintaining: Solar energy has minimal dangers associated with this stage, with burns and electric shock being the most common. Building Back: The most common workplace hazards of this stage include those resulting from lifting, trips and falls, electricity, and ladders. |
| How Dangerous Is Solar Energy In Comparison to Other Types of Energy | Solar energy is significantly less dangerous than fossil fuels and other types of renewable energy. In fact, solar is one of the, if not the, safest forms of energy with a death rate of only 0.02 deaths per terawatt-hour of electricity produced. |
Final Thoughts
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable energy source, has a low carbon footprint, protects air quality, efficiently converts sunlight into energy, generates few waste products, and promotes energy independence and security. However, solar energy is also an intermittent energy source, faces high upfront and maintenance costs, and has specific land requirements.
Despite this, the pros of solar energy outweigh the cons. Beginning to reverse the climate crisis means we have to cut CO2 emissions now, and solar energy can help us do that. It has the fifth-lowest carbon footprint out of all energy types and emits a fraction of the CO2 and air toxics that fossil fuels emit. Although its unpredictable nature means we cannot rely on it solely for energy generation, incorporating more of it into our power grid has many environmental benefits.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- US Department of Energy: How Does Solar Work?
- How Does Solar Energy Work? From Source Til Energy Generation
- Advantages and Disadvantages – Renewable Energy
- What is renewable energy? | United Nations
- Arizona State University: Will the Sun Ever Stop Shining?
- Britannica: Carbon footprint | Definition, Examples, Calculation, Effects, & Facts
- World Nuclear Association: Carbon Dioxide Emissions From Electricity
- World Nuclear Association: Average life-cycle CO2 equivalent emissions
- Impactful Ninja: What Is the Carbon Footprint of Solar Energy? A Life-Cycle Assessment
- Coal Power Impacts | Union of Concerned Scientists
- Smithsonian Magazine: A Brief History of Solar Panels | Sponsored
- Ecoflow: Solar Panel Efficiency Over Time
- Enel X: What is solar panel energy efficiency?
- Wired: New Designs Could Boost Solar Cells Beyond Their Limits
- Columbia Climate School: Solar Panels Reduce CO2 Emissions More Per Acre Than Trees — and Much More Than Corn Ethanol
- US Environmental Protection Agency: End-of-Life Solar Panels: Regulations and Management
- Reuters: Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant opens in France
- US Environmental Protection Agency: Solar Panel Recycling
- US Environmental Protection Agency: Summary of the Energy Independence and Security Act
- International Energy Agency: Solar PV
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary: Intermittent Definition & Meaning
- Solar Reviews: Solar Energy Pros and Cons in 2024
- US Energy Information Administration: Where solar is found
- NerdWallet: What Do Solar Panels Cost and Are They Worth It?
- Solar Reviews: Solar Batteries: Are They Worth the Cost?
- EnergySage: How Long Do Solar Panels Last? Solar Panel Lifespan 101
- Forbes: How Much Do Solar Panels Cost In 2024?
- Solar Energy Industries Association: Land Use & Solar Development
- Our World of Energy: How much land does a solar power plant require?
- Natural Resources Defense Council: Global Warming 101
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: The Paris Agreement
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Climate Change – Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
- Impactful Ninja: Fossil Fuel Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Coal Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Oil Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Natural Gas Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- National Wildlife Federation: Climate Change
- Impactful Ninja: Renewable Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Impactful Ninja: Sustainable Energy Explained: All You Need to Know
- Electrical Academia: Difference between Traditional Power Grid and Smart Grid
- Impactful Ninja: How Effective and Efficient Is Solar Energy?
- How Safe Is Solar Energy? A Holistic Life-Cycle Analysis
- How Dangerous Is Solar Energy? A Holistic Life-Cycle Analysis
- Ipsun Solar: Are Solar Panels Harmful to Your Health?
- Republic Of Solar: The Impact of Solar Energy on Wildlife and Biodiversity: Ensuring a Sustainable Balance
- Global Solar Council: Solar Energy and its Countless Benefits for the Power Grid
- DuraLabel: Solar Power Hazards & Safety Infographic
- Union of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Solar Power
- Our World in Data: What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?