The History of Solar Energy: The Big Picture
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Solar energy is one of our fastest-growing renewable energy sources with low levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Its history dates back centuries, and it has evolved into our third-largest renewable technology today. So, we had to ask: What is the history of solar energy?
Solar energy began in 700 BC with active reflection and passive absorption of the sun’s rays. Then, the photoelectric solar cell was invented in 1883, the silicon solar cell in 1954, large solar production facilities started in 2010, and now solar energy is our third-largest renewable technology.
One way to combat the current global climate crisis threatening Earth’s environmental, economic, and social health is to transition away from traditional fossil fuels and toward renewable energy sources, such as solar energy. Keep reading to learn how solar energy came to be, who and what pioneered its development, how effective it has been thus far, and what the future of solar energy could entail.
Here’s the History of Solar Energy in a Nutshell
Solar energy is the conversion of solar radiation into electrical energy either through the use of photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar radiation-concentrating mirrors. The energy produced is then used to generate electricity or can be stored in batteries or thermal storage for use at a later time.
“Solar Energy: energy that uses the power of the sun to produce electricity”
Cambridge Dictionary
The main way of harnessing the power of the sun with solar energy is via photovoltaic (PV) solar cells. These are photovoltaic cells in solar panels that absorb energy from sunlight, creating an electrical charge. This charge moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
Solar energy has gone through three distinct development phases in its development:
- Early market formation and innovation: The early history of solar energy dates back to the 7th century BC, when common ancient uses of the sun included actively reflecting the sun’s rays and passively allowing the sun to act as a source of heat.
- Consolidation and strengthening: The discovery of the photovoltaic effect, the invention of the solar cell, and technological advances to increase the efficiency of solar cells helped to shape the solar energy market.
- Mainstreaming: Solar energy began to establish itself as a part of the mainstream electricity industry in 2010, with increases in investments and the establishment of large solar production facilities. The establishment of the International Energy Agency (IEA), the IEA Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (IEA PVPS), the International Solar Alliance (ISA), and the Global Solar Council (GSC) helped to regulate the solar energy market.
| Solar Energy Milestones | Historical Event |
| Initial start | The early history of solar energy dates back to the 7th century BC. Common ancient uses of the sun included actively reflecting the sun’s rays and passively allowing the sun to act as a source of heat. |
| Milestones in solar energy development | 1839: The photovoltaic effect was discovered. 1883: The first photoelectric (solar) cell was invented. 1954: The first silicon solar cell was invented. 1963: Sharp Corporation became the first mass-producer of silicon solar panels. 2007: Solar energy global investment tops $100 billion. 2007: Solar becomes the leading clean energy technology. 2010-2018: Large solar production facilities begin to become established. 2018: France opened Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant. 2022: PV solar accounted for roughly 4.5% of total global electricity generation. |
| Current status | Currently, solar energy is the third-largest renewable electricity technology behind hydropower and wind energy. PV solar accounted for roughly 4.5% of total global electricity generation in 2022. |
| Future outlook | The future of solar energy will be heavily influenced by ambitious government targets, policy support, increasing competitiveness of solar energy companies, and decreasing costs. |
| Key policy developments | 1974: International Energy Agency (IEA) 1993: The IEA Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (IEA PVPS) 2009: The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) 2015: Paris Climate Agreement 2015: International Solar Alliance (ISA) 2015: The Global Solar Council (GSC) |
Understanding solar energy’s history can provide insight into how it has evolved into the renewable energy source it is today.
When and How Did Solar Energy Get Started
Humans have been harnessing the power of the sun for centuries, dating all the way back to the 7th century BC. Common ancient uses of the sun included actively reflecting the sun’s rays and passively allowing the sun to act as a source of heat.
7th century BC: Humans focused sunlight with magnifying glasses to light fires.
3rd century BC: The Greeks and Romans lit torches for religious ceremonies by focusing sunlight with mirrors.
2nd century BC: Greek scientist Archimedes used bronze shields to reflect the sun’s rays and light wooden ships on fire.
1st – 4th century AD: The Romans used south-facing windows to allow sunlight to heat their bathhouses.
6th century AD: Sunrooms in houses and public buildings were so popular that Roman Emperor Justinian I initiated “sun rights” to ensure individual access to the sun.
How Has Solar Energy Developed Over Time
Solar energy is one of the fastest-growing and most popular renewable energy technologies with a low carbon emissions profile. It can play an important role in the global energy transformation and help transition away from fossil fuels.
What Are Milestones in Solar Energy Development
The discovery of the photovoltaic effect and the invention of the solar cell kickstarted the modern solar industry, which today has evolved into a $200+ billion industry.
1839: French physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, whereby photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity. His discovery would lead to the development of the photoelectric (PV solar) cell, which would become the basis of modern solar energy.
1866: French mathematician Augustin Mouchot invented the first solar-powered steam engine, which used metal to focus sunlight onto and heat a tube filled with water. The water turned into steam, which drove an engine.
1883: American inventor Charles Fritts created the first photoelectric (solar) cell by coating selenium in a thin layer of gold. His solar cells had an efficiency, called energy conversion rate of 1-2%, meaning they converted 1-2% of the total sunlight captured into usable energy. Today’s solar cells have an average commercial energy conversion rate of 15-20% and experimental conversion rate of up more than 30%.
1954: Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson of Bell Laboratories invented the first silicon solar cell, which had an energy conversion rate of 6%. Many solar panels today are based on this silicon cell model.
1957-1960: Hoffman Electronics improved PV solar efficiency from 8%-14%.
1958: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched Vanguard I, the world’s first solar-powered satellite, with a 1-watt panel to power its radios.
1963: Sharp Corporation became the first mass-producer of silicon solar panels; Japan installed a 242-watt PV solar array on top of a lighthouse, which was the largest array in the world at that time.
1964: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched the first Nimbus satellite with a 470-watt silicon solar array, enough to power the entire satellite.
1973: The University of Delaware (US) constructed the first solar building, nicknamed “Solar One”. Rather than using solar panels, it had solar power integrated into the roof.
1981: Paul MacCready built the first aircraft to run on solar power, named the “Solar Challenger”, which flew across the English Channel from France to the United Kingdom.
1985: The University of South Wales achieved 20% efficiency for silicon solar cells.
1999: The National Renewable Energy Laboratory and SpectroLab Inc. achieved 33.3% efficiency for PV solar cells. However, these solar cells were experimental and not yet scaled for commercial applications.
2007: Solar energy global investment tops $100 billion, and solar becomes the leading clean energy technology.
2010-2018: Chinese factories began to build large solar production facilities, which helped to reduce the cost of solar down to $.70 per watt.
2016: The University of South Wales achieved 34.5% efficiency for PV solar cells.
2016: Bertrand Piccard invented the world’s first solar-powered aircraft, named “Solar Impulse 2”. After completing a 25,000-mile journey around the world in 2018, it remains the world’s largest and most powerful solar-powered airplane to date.
2018: France opened Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant.
2022: PV solar accounted for roughly 4.5% of total global electricity generation.
How Has the Solar Energy Market Developed Recently
Starting in 2010, there was a push to increase solar energy capacity worldwide. Global installed solar capacity increased from 96 GW in 2012 to 1,180 GW in 2022.
Global solar energy capacity has continued to increase over recent years:
In 2019: 115 gigawatts (GW) of solar energy capacity were installed globally, increasing the total capacity for solar energy to over 590 GW.
In 2020: 139 GW of solar energy capacity were installed globally, increasing the total capacity for solar energy to over 760 GW.
In 2021: 175 GW of solar energy capacity were installed globally, increasing the total capacity for solar energy to over 940 GW.
In 2022: 240 GW of solar energy capacity were installed globally, increasing the total capacity for solar energy to over 1,180 GW.
Experts predict we will install more than 280 GW of solar energy capacity in 2023, increasing the total capacity for solar energy to over 1,450 GW.
What Is the Present Status of Solar Energy
Solar energy is currently the third-largest renewable electricity technology behind hydropower and wind energy. PV solar accounted for roughly 4.5% of total global electricity generation in 2022.
The 5 countries that together account for nearly 800 gigawatts (GW), or two-thirds of our global PV solar energy capacity, are:
- China – 430 GW
- US – 142 GW
- Japan – 85 GW
- Germany – 69 GW
- India – 68 GW
China continues to dominate the PV solar market, adding 100 GW alone in 2022, 60% more than the year prior. The European Union, India, and Brazil have also added 38, 18, and 11 GW, respectively, as new policies and targets are set for renewable energy moving forward.
In 2022, electricity generation from solar energy increased by 270 TWh (26%) to reach 1,300 TWh. This was the largest generation increase for all renewable energy technologies, surpassing wind energy for the first time in history.
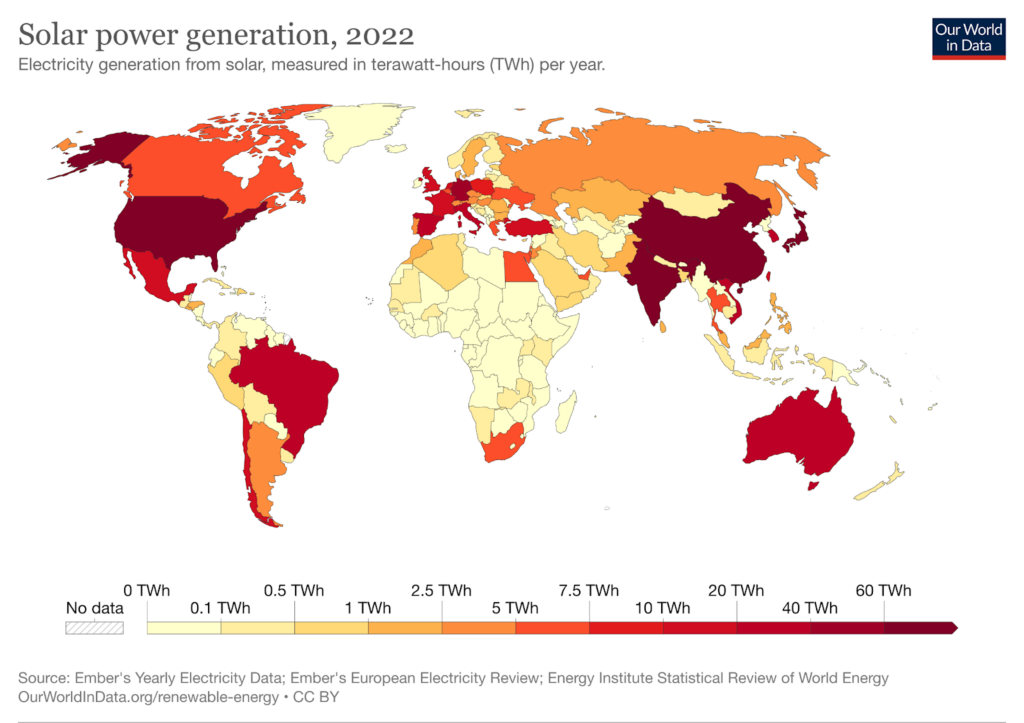
In terms of funding, global solar energy investment reached a record high of $320 billion in 2022, a 20% increase from the year prior and triple the amount spent on all fossil fuels combined.
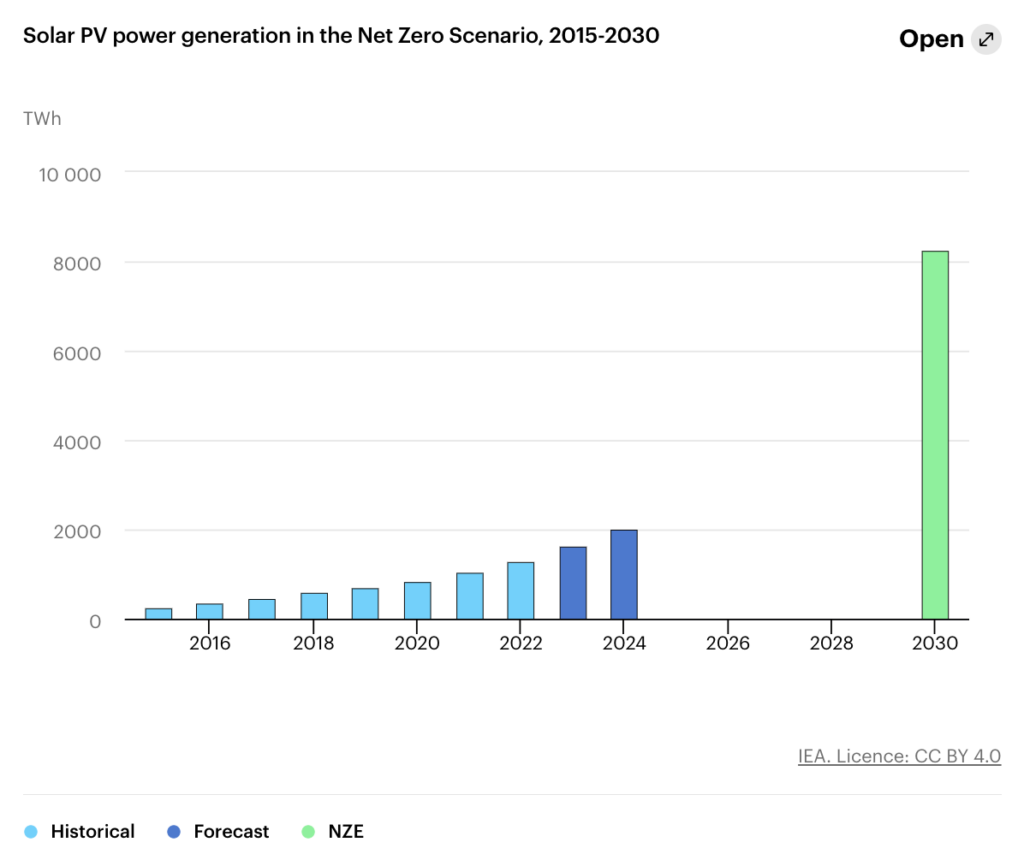
The IEA has deemed PV solar energy ‘on track’ in their net zero by 2050 scenario, so long as it can maintain an annual average generation growth of approximately 26% between 2023 and 2030.
How Will the Future of Solar Energy Look Like
Ambitious government targets, policy support, increasing competitiveness of solar energy companies, and decreasing costs will heavily influence the future of solar energy.
How Solar Energy Will Likely Develop in the Future
PV solar installed capacity is to exceed natural gas by 2026 and coal by 2027, becoming the largest in the world. This is because solar energy:
- Has a low carbon footprint: On a life-cycle basis, concentrated solar energy emits 38, PV roof solar energy emits 41, and PV utility solar energy emits 48 grams of CO2 equivalent per kWh of electricity produced. This is the highest out of all renewable energy types, but still significantly lower than fossil fuels (e.g., coal, oil, natural gas).
- Has low maintenance costs: Although there are high upfront costs associated with installing solar systems, these systems require very little maintenance once installed. If cleaned and inspected regularly, solar panels can function for 25 years without any additional measures.
- Promotes energy independence: Being able to produce your own electricity without the aid of foreign countries is an important step to becoming more self-sufficient.
- Protects air quality: Rather than combusting materials, solar power plants harness the energy of the sun to generate electricity. PV panels and concentrating mirrors do not produce greenhouse gasses and emit no sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides.
What Policies Are Put in Place to Support Solar Energy Usage
The most well-known piece of legally binding, international climate mitigation legislation is The Paris Agreement, the goal of which is to limit global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius (C), preferably to 1.5C, compared to pre-industrial levels.
The Paris Agreement specifically notes a transition towards renewable energies, such as solar energy, as being a critical part of meeting these goals.
Check out the highlights of the 2015 COP21 directly from the UN Climate Change channel:
In addition, The International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario is one framework for the global energy sector to achieve net zero CO2 emissions by 2050 and universal energy access by 2030.
There are many global and country-specific solar energy policies and organizations aimed at meeting the 2050 net zero scenario, including:
- 1974 – International Energy Agency (IEA): The IEA was founded in response to the major oil disruptions in 1974. They promote international energy cooperation, including solar energy, and are made up of 31 member countries.
- 1993 – The IEA Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (IEA PVPS): The IEA PVPS is a collaborative research and development agreement established within the IEA. There are 31 member countries around the world collaborating on solar energy projects.
- 2009 – The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA): IRENA was founded as a global intergovernmental agency focused on scaling renewable energy. It is comprised of 167 member countries as well as the European Union.
- 2015 – International Solar Alliance (ISA): The ISA is a treaty-based organization established to create cooperation among solar-resource-rich countries and the rest of the world. There are currently 94 member countries.
- 2015 – The Global Solar Council (GSC): The GSC is an international, nonprofit organization that aims to promote rapid adoption of solar energy worldwide through market development, partnerships, and education.
If you are interested in learning more about country-specific solar energy policies, you can visit the IEA’s solar policy database.
What Are Currently the Different Types of Solar Energy
Harnessing the power of the sun falls into two main categories. Both systems take the energy from the sun and convert it to electricity, just by slightly different mechanisms.
- Photovoltaic (PV) solar cells: photovoltaic cells in solar panels absorb energy from sunlight, creating an electrical charge. This charge moves in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
- Concentrating solar thermal plants (CSP): mirrors reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect and convert solar energy into heat. This is utilized in very large power plants.
PV solar cells are by far the preferred method of harnessing solar energy today. Because CSP only makes up a fraction of the solar energy market, data on solar energy focuses mainly on PV solar.
There are three main types of PV solar cells:
- Silicon: The most common material used in solar panels today because silicon is reasonably priced and efficient in converting sunlight directly to electricity. These panels are typically assembled on roofs of homes and buildings or are mounted en masse on racks for large-scale electricity generation.
- Thin film: These solar panels are made of very thin layers, several millionths of a meter, of semiconductor materials including cadmium, telluride, or copper. This technology is commonly used in portable applications (i.e. backpacks, windows) because it is lightweight and flexible.
- III-V solar cells: These solar panels are generally much more expensive but also have much higher efficiency. They are made from periodic table Group III elements (gallium and indium) or Group V elements (arsenic and antimony). This technology is commonly used on satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles, and applications with a high power-to-weight ratio.
A group of PV solar panels clustered together forms a PV solar power plant. The world’s largest PV solar power plant is the Bhadla Solar Park in India. It spans 14,000 acres and has a 2,250 GW capacity.
There are also three main types of concentrating solar thermal power plants:
- Linear: U-shaped mirrors focus sunlight onto tubes that span the length of the mirrors. The sunlight heats the fluid within the tubes, which is then sent to a heat exchanger. The heat boils water to produce steam, which spins a turbine and powers a generator to produce electricity. The two types of linear plants are parabolic trough systems and linear Fresnel reflector systems.
- Dish/engine: A mirrored dish, similar to a very large satellite dish, contains many flat mirrors formed into a dish shape. The dish focuses and concentrates sunlight onto a receiver which absorbs and collects the heat, transferring it to an engine generator. The fluid heated by the receiver moves pistons in the most common engine, the Stirling engine. This mechanical power powers a generator to produce electricity.
- Power tower: Heliostats, sun-tracking mirrors, reflect and concentrate sunlight onto a receiver that sits on top of a tower. The sunlight can be concentrated as much as 1,500 times. Water is most often used as the heat-transfer fluid which boils water to produce steam, spins a turbine, and powers a generator to produce electricity.
The largest CSP is the Noor Complex, located in Morocco on the edge of the Sahara Desert. It has a 580-megawatt capacity and provides electricity for over 1 million people.
Final Thoughts
Solar energy has a lengthy history that dates back to 7,000 BC when common ancient uses of the sun included actively reflecting the sun’s rays and passively allowing the sun to act as a source of heat. The discovery of the photovoltaic effect and the invention and development of the solar cell were instrumental in forming the modern solar energy industry.
Currently, solar energy is the third-largest renewable electricity technology behind hydropower and wind energy. The formation of the International Energy and International Renewable Energy Agency plus the implementation of the Paris Climate Agreement Climate has propelled solar energy into the spotlight as one replacement for traditional fossil fuels.
Solar energy is poised to see continued growth in the future as we look to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to levels stated in the Paris Agreement. Ambitious government targets, policy support, increasing competitiveness of solar energy companies, and decreasing costs will heavily influence the future of solar energy.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy: How Does Solar Work?
- The National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Solar Energy Basics
- The International Energy Agency: Homepage
- The IEA Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme: Homepage
- The International Solar Alliance: Homepage
- The Global Solar Council: Homepage
- The US Department of Energy – Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: The History of Solar
- The International Renewable Energy Agency: Solar Energy
- Science Direct: Photovoltaic Effect
- Fortune Business Insight: The global solar power market is projected to grow from $234.86 billion in 2022 to $373.84 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 6.9% in forecast period, 2022-2029
- Solar Energy World: Solar History – Alexandre Edmond Becquerellar
- The Guardian: The French solar power pioneer who was light years ahead
- Smithsonian Magazine: A Brief History of Solar Panels
- Solar.com: Solar Panel Efficiency – Pick the Most Efficient Solar Panels
- American Physical Society: April 25, 1954: Bell Labs Demonstrates the First Practical Silicon Solar Cell
- EnergySage: History of Solar Energy – Timeline
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Homepage
- SolarReviews: The history of solar energy
- Smithsonian Magazine: Inside the First Solar-Powered Flight Around the World
- Reuters: Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant opens in France
- The International Energy Agency: Solar
- Our World in Data: Renewable Energy
- IEA Photovoltaic Power System Programme: Snapshot 2021
- IEA Photovoltaic Power System Programme: Snapshot 2020
- IEA Photovoltaic Power System Programme: Snapshot 2022
- IEA Photovoltaic Power System Programme: Snapshot 2023
- The International Energy Agency: Executive summary – Renewables
- Ornate Solar: The Top 5 Solar Countries in the World (2023)
- Our World in Data: Solar Power Generation, 2022
- International Energy Agency: Solar PV power generation in the Net Zero Scenario, 2015-2030
- World Nuclear Association: Carbon Emissions from Electricity
- Forbes: Solar Energy Pros And Cons – What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages?
- Union of Concerned Scientists: Environmental Impacts of Solar Power
- EnergySage: How long do solar panels last? Solar panel lifespan explained
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: The Paris Agreement
- The International Energy Agency: Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario
- The International Energy Agency: Policies Database
- The National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Solar Photovoltaic Technology Basics
- NS Energy: Profiling the top five largest solar power plants in the world
- Solar Energy Industries Association: Concentrating Solar Power
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Solar Explained – Solar thermal power plants
- Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy: Dish/Engine System Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power Basics
- Britannica: Heliostat
- Cable News Network: Morocco’s megawatt solar plant powers up
- Impactful Ninja: Solar Energy Explained: All You Need to Know