The Environmental Impact of Blackberries: From Farm to Table
Impactful Ninja is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Learn more
Learn more
.
Hey fellow impactful ninja ? You may have noticed that Impactful Ninja is all about providing helpful information to make a positive impact on the world and society. And that we love to link back to where we found all the information for each of our posts. Most of these links are informational-based for you to check out their primary sources with one click. But some of these links are so-called "affiliate links" to products that we recommend. First and foremost, because we believe that they add value to you. For example, when we wrote a post about the environmental impact of long showers, we came across an EPA recommendation to use WaterSense showerheads. So we linked to where you can find them. Or, for many of our posts, we also link to our favorite books on that topic so that you can get a much more holistic overview than one single blog post could provide. And when there is an affiliate program for these products, we sign up for it. For example, as Amazon Associates, we earn from qualifying purchases. First, and most importantly, we still only recommend products that we believe add value for you. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission - but at no additional costs to you. And when you buy something through a link that is not an affiliate link, we won’t receive any commission but we’ll still be happy to have helped you. When we find products that we believe add value to you and the seller has an affiliate program, we sign up for it. When you buy something through one of our affiliate links, we may earn a small commission (at no extra costs to you). And at this point in time, all money is reinvested in sharing the most helpful content with you. This includes all operating costs for running this site and the content creation itself. You may have noticed by the way Impactful Ninja is operated that money is not the driving factor behind it. It is a passion project of mine and I love to share helpful information with you to make a positive impact on the world and society. However, it's a project in that I invest a lot of time and also quite some money. Eventually, my dream is to one day turn this passion project into my full-time job and provide even more helpful information. But that's still a long time to go. Stay impactful,Affiliate Disclosure
Why do we add these product links?
What do these affiliate links mean for you?
What do these affiliate links mean for us?
What does this mean for me personally?
![]()
Blackberry picking is a favorite pastime of many Americans. The blackberry industry itself is worth over $38 million, with 51.3 million lbs produced every year. Hailed as a “superfood”, blackberries are teeming with many essential nutrients, not to mention their delicious tangy flavor. However, blackberries can also have a significantly negative impact on the environment, due to aspects of their manufacturing. So, we had to ask: What is the environmental impact of blackberries?
Blackberries have a moderately negative environmental impact. This is mainly because they use pesticides, nitrogen fertilizers, and plastic packaging, and have high irrigation rates. Nonetheless, some of their upsides include occasional polyculture farming and having a low carbon footprint.
In this article, we will examine the environmental impact of blackberries from several different angles. We will go through the life-cycle of blackberries, detailing their impact on the environment from growth to distribution to your plate to waste management. We will then compare the environmental impact of blackberries to that of other fruits. And, finally, we’ll share some tips with you on how you can reduce your own environmental impact and offset your own carbon emissions—both for your personal life and blackberry-related.
Here’s How We Assessed the Environmental Impact of Blackberries
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is one of the ways we measure the potential environmental effects of our actions, like the consumption of blackberries. It is a holistic assessment based on the environmental changes associated with our consumption. Those are changes in our environment that can have adverse effects on the air, land, water, fish, and wildlife or the inhabitants of the ecosystem.
“Environmental Impact: the effect that the activities of people and businesses have on the environment”
Cambridge Dictionary
Basically, all goods and services you buy—including blackberries—leave an impact on our environment. When it comes to food in general, and blackberries specifically, the following are key factors:
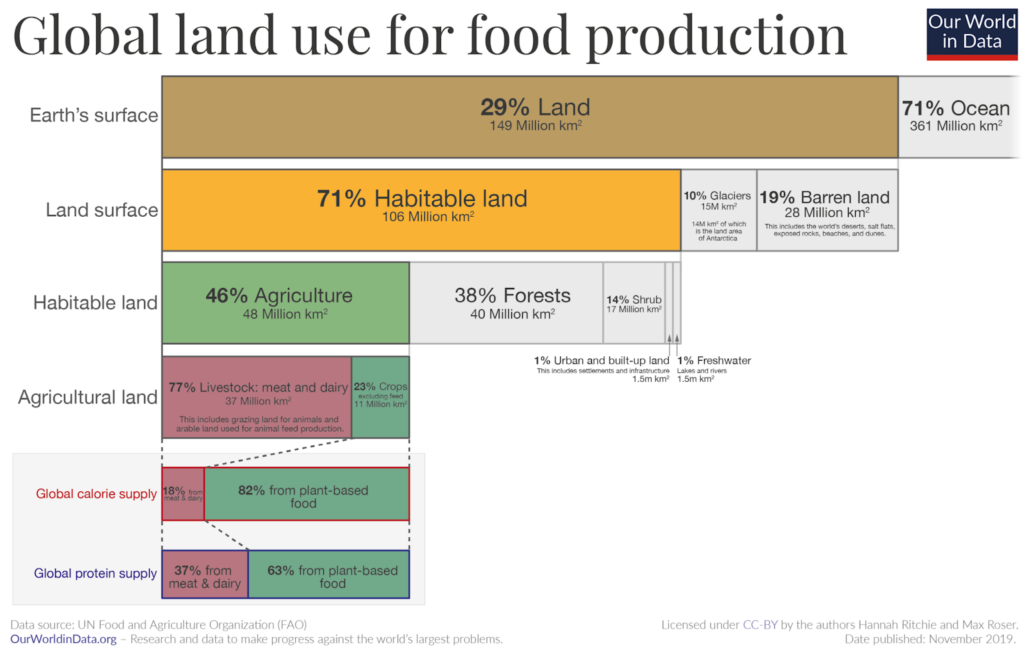
- Land requirements: Large parts of the world that were once covered by forests and wildlands are now used for agriculture. 10 million hectares of forest are destroyed annually and 50% of the world’s habitable land is now used for agriculture. This loss of natural habitat has been the main driver for reducing the world’s biodiversity.
- Water footprint: 70% of global freshwater is now used for agricultural purposes. By assessing the water footprint of a particular food, we can determine how our limited freshwater resources are being consumed and polluted.
- Pesticide and fertilizer usage: Pesticides and fertilizers provide a range of agricultural benefits. However, numerous studies link pesticides and fertilizers to serious effects on human health, along with disruptions to vital ecosystems and the spread of aquatic dead zones.
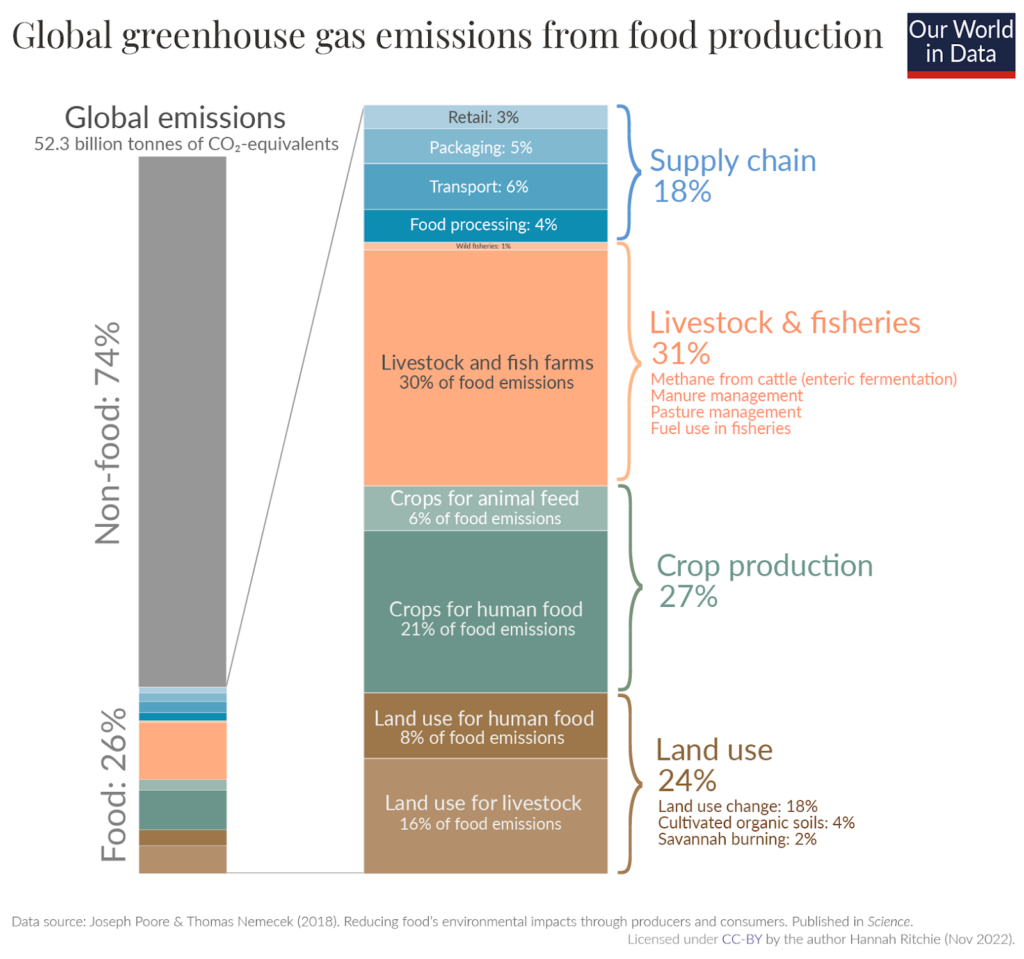
- Carbon footprint: The carbon footprint is one of the ways we measure the effects of our human-induced global climate change. Today, food production accounts for over a quarter (26%) of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste generation: Food and its packaging account for almost 45% of the materials landfilled in the US alone. And packaging sent to landfills, especially when made from plastics, does not degrade quickly or, in some cases, at all.
To understand the overall environmental impact of blackberries, we must assess each of their key factors. This Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a tool originally developed to identify the environmental impacts of a project prior to decision-making and also helps us to evaluate the environmental impacts of blackberries, from farm to table.
Here’s the Overall Environmental Impact of Blackberries
The overall environmental impact of blackberries is moderately negative. The main factors that contribute to their environmental impact are irrigation rates, pesticide usage, nitrogen fertilizers, and plastic packaging.
Blackberries have a lot going for them when it comes to their environmental impact. They occasionally use the more eco-friendly polyculture farming, don’t generate much organic waste, and have a very low carbon footprint. However, they can still cause significant environmental damage through other factors.
So, let’s have a look at the environmental impact of each key factor of blackberries!
| Key Assessment Factors | Environmental Impact |
| Land requirements for blackberries | Blackberries’ land requirements are moderate. They create some harm through things such as soil erosion and monocultures. However, they occasionally use polyculture farming and store carbon, so their environmental impact is only slightly negative at this stage. |
| Water footprint of blackberries | Blackberries have a moderate to high water requirement of 50–100 inches of water per year. Because of where they are grown, they also require a significant amount of irrigation, which significantly raises their harm to the environment and renders this stage of their impact as high. |
| Agrochemical usage for blackberries | Blackberries’ agrochemical use is high. They use a significant amount of pesticides and harmful nitrogen fertilizers, which cause their environmental impact to be very negative in this stage. |
| Carbon footprint of blackberries | Blackberries have an incredibly low carbon footprint at 0.07kg (0.15) of CO2e per pound of blackberries. The most significant factors contributing to this are their irrigation requirements, pesticide use, refrigerated trucking, and plastic packaging. |
| Waste generation of blackberries | Blackberries’ waste generation is moderate. While they don’t produce any organic waste, their plastic packaging is a major negative contributor to their environmental impact. |
These are the overall summaries, but there is a lot more to the story. In the next few sections, we will dive deeper into each stage to illustrate to you all the important aspects of blackberries’ environmental impact.
What Are the Land Requirements for Blackberries
Blackberries’ land requirements are moderate. They create some harm through things such as soil erosion and monocultures. However, they occasionally use polyculture farming and store carbon, so their environmental impact is only slightly negative at this stage.
Growing blackberries has a lot of variables that contribute to their environmental impact. The amount of land they use, the way in which they grow, and the amount of time they take to grow will all contribute to their environmental impact.
How do the land requirements of blackberries impact their environmental footprint?
- What is the land usage of blackberries: Blackberries yield around 22 tons per hectare. This is a moderately average yield for a fruit. For example, strawberries yield up to 25 tons per hectare, and bananas up to 100. Therefore, the land usage of blackberries contributes moderately to their environmental impact.
- Where and how are blackberries grown: Most blackberries grow in North America, with Oregon being the most common blackberry-growing state. Blackberries are grown on bushes. Blackberry bushes have good carbon-sequestering properties, storing around 1.6% more carbon than a grass-covered area. For this reason, blackberry growth methods don’t contribute significantly to their environmental impact.
- Are blackberries grown in a monoculture or polyculture: Blackberries are sometimes invasive, and as such, they can turn areas into monocultures even when they are wild. Generally, they are farmed in monocultures. However, they are also sometimes farmed in polycultures. Monocultures are very bad for the environment, and so the fact that they are only sometimes farmed in this style is good news for their environmental impact.
- How does the growing of blackberries affect soil fertility and erosion: Blackberries have fairly weak root systems, which means that they can leave soil vulnerable to erosion. As a result, blackberries’ relationship to soil contributes negatively to their environmental impact.
- How does the blackberries industry affect the loss of habitable land: Blackberries don’t contribute significantly to deforestation. However, they can have a particular effect on cleared areas after deforestation, damaging livestock and preventing healthy restoration.
- How does the blackberry industry affect wildlife and biodiversity: Monoculture farming can be harmful to wildlife. However, because blackberries don’t exclusively use monocultures, they don’t contribute too much to this harm.
In short, blackberries’ moderate land yield and occasional polyculture farming mean that they don’t have too big of an impact on the environment. However, they still contribute to erosion and decreases in land fertility, so they have a minor negative environmental impact.
What Is the Water Footprint of Blackberries
Blackberries have a moderate to high water requirement of 50–100 inches of water per year. Because of where they are grown, they also require a significant amount of irrigation, which significantly raises their harm to the environment and renders this stage of their impact as high.
Water usage is one of the most important factors in the environmental impact of a fruit. The amount of water used, as well as the way they affect the water sources around them, are all major contributing factors. Here, we will look at these different angles of blackberries’ water impact.
How does the water footprint of blackberries impact their environmental footprint?
- What is the overall water usage of blackberries: Blackberries need around 50–100 inches of water per year. This makes for a moderate to high water footprint. For example, cherry trees only need 35 inches of water per year, but watermelons need up to 100 inches per year. Therefore, blackberries’ water usage contributes moderately negatively to their environmental impact.
- What is the green water footprint of blackberries: The green water footprint is the amount of water from precipitation stored in the soil and used by plants for growth. Despite the fact that many blackberries are grown in Oregon, the majority of blackberries consumed in the US come from Mexico. In general, the annual average rainfall for Mexico is low at around 28 inches. This means that the majority of rainfall will be going towards fulfilling blackberries’ water requirements. Because of this, their green water footprint is significantly high.
- What is the blue water footprint of blackberries: The blue water footprint is the amount of water sourced from surface (such as rivers or lakes) or groundwater resources. Since Mexico’s annual rainfall doesn’t cover blackberries’ water requirements, they will need significant irrigation. This means that their blue water footprint is very high.
- What is the gray water footprint of blackberries: The gray water footprint is the amount of freshwater required to clean up water pollution to meet certain quality standards. Essentially, it’s the amount of water needed to make polluted water clean enough to be safe and healthy for humans and the environment. Blackberries have higher-than-average pesticide usage. This means that they require a significant amount of water to clean away their pesticide residues and so their gray water footprint is moderately high.
- How does the blackberries industry affect freshwater and ocean pollution: Irrigation can be very harmful to water systems, creating groundwater imbalances and over-salination. Pesticides are also major polluters to waterways. Blackberries also use plastic packaging, which contributes very significantly to ocean pollution. Between these factors, the blackberry industry has caused some serious damage to waterways over the years.
In short, blackberries’ need for significant irrigation and high use of pesticides means that their impacts on water systems are fairly significant.
What Is the Agrochemical Usage for Blackberries
Blackberries’ agrochemical use is high. They use a significant amount of pesticides and harmful nitrogen fertilizers, which cause their environmental impact to be very negative in this stage.
Pesticides and fertilizers are agrochemicals that can have a significant negative impact on the environment. They both require resources to create as well as have effects on the life around them. Here, we will look at how blackberries’ pesticide and fertilizer rates affect their environmental impact.
How does the agrochemical usage of blackberries impact their environmental footprint?
- What is the pesticide usage of blackberries: Blackberries use a high amount of pesticides. Pesticides can cause many kinds of environmental damage, including poisoning surrounding wildlife, and leakages getting into soil and groundwater. Therefore, blackberries’ environmental impact is very negative here.
- What is the fertilizer usage of blackberries: Blackberries use primarily nitrogen fertilizer. Nitrogen fertilizer is known to be one of the more harmful fertilizers out there, mainly due to pollution and chemical runoff. The fact that blackberries use this kind of fertilizer means that their environmental impact is very negative at this stage.
- Are there any known issues connected to the agrochemical usage for blackberries: Nitrogen fertilizer is well known for inadvertently stimulating the growth of invasive algae. This algae is harmful to wildlife in waterways and can spread widely. Blackberries cause a significant amount of damage through their nitrogen fertilizer use.
In short, the fact that blackberries use a high amount of agrochemicals means that their environmental impact is very negative in this category.
What Is the Carbon Footprint of Blackberries
Blackberries have an incredibly low carbon footprint of 0.07kg (0.15) of CO2e per pound of blackberries. The most significant factors contributing to this are their irrigation requirements, pesticide use, refrigerated trucking, and plastic packaging.
Carbon footprint is one aspect of the overall environmental impact of a fruit. It essentially measures how much carbon or other greenhouse gasses the production of strawberries emits into the atmosphere. Emissions from product manufacturing, irrigation, transportation fuel, and landfills all add up to create the overall carbon footprint of a fruit. Let’s see how the carbon footprint of blackberries breaks down and contributes to their environmental impact.
How does the carbon footprint of blackberries impact their environmental footprint?
- What is the overall carbon footprint of blackberries: The overall carbon footprint of blackberries is very low at 0.07kg (0.15) of CO2e per pound of blackberries. This means that for every pound of blackberries produced, 0.07kg of carbon is released into the atmosphere. This is a very low carbon footprint compared to other fruits.
- What are the main contributors to the carbon footprint of blackberries: The main factors that contribute to blackberries’ carbon footprint are pesticide and irrigation use, as well as refrigerated transportation and plastic packaging.
- Which life-cycle stage of blackberries has the highest carbon footprint: The stage that contributes the most to blackberries’ carbon footprint is growth. This is because of the resources, such as pesticides and irrigation, that blackberries consume during this stage.
In short, blackberries have a very small carbon footprint, despite some factors like refrigeration and irrigation that can drive up their emissions.
What Is the Waste Generation of Blackberries
Blackberries’ waste generation is moderate. While they don’t produce any organic waste, their plastic packaging is a major negative contributor to their environmental impact.
When fruit waste, either packaging or organic materials, is disposed of, it can have a major impact on the environment. Whether it’s damaging wildlife, getting into oceans, emitting methane, or dissolving into microplastics that contaminate groundwater, all these materials have their part to play. In this section, we will look at how blackberries’ waste affects the environment.
How does the waste generation of blackberries impact their environmental footprint?
- What is the packaging of blackberries: Berries are generally packaged in plastic clamshells for optimal protection of their delicate skins. Plastic has a very negative environmental impact during its production process. Therefore, blackberries’ negative environmental impact is raised significantly by using plastic.
- How is the packaging of blackberries disposed of: Plastic packaging has very low recycling rates, at around 9%. This means that the majority of blackberry packaging is ending up in landfills. Landfills cause significant environmental damage, including land clearance and chemical pollution. Furthermore, plastic can take up to 500 years to decompose. The quantity and longevity of blackberries in landfills contribute very negatively to their environmental impact.
- How are blackberries disposed of: Blackberries are generally consumed whole, so they don’t have significant food waste. However, blackberries—and berries in general—have a shorter shelf life than some other fruits. This may lead to them being thrown out more easily, but the waste is small.
In short, blackberries’ food waste contributes moderately negatively to their carbon footprint, mainly because of their use of plastic packaging.
What Have Been Historical Environmental Issues Connected to the Blackberries Industry
The blackberry industry has historically been somewhat harmful to land, wildlife, and water sources. Some contributing factors include nitrogen fertilizers, pesticides, and land usage.
All fruits have had a complex journey toward global distribution. They originate in one part of the world and often travel far to end up in your local supermarket. From farm to table, some of our favorite fruits have racked up some serious environmental damage along the way. Whether it’s deforestation to meet demand, water pollution, or disruption of wildlife, most fruits have left a path of destruction. Let’s see how blackberries have fared throughout history.
What have been the key environmental issues of the blackberry industry?
- How much land has been lost because of blackberry production: A significant amount of land has been used for blackberry farming. In Oregon alone, blackberry farming takes up just over 6,000 acres. Because blackberries are invasive, they also pose a threat to local plants, sometimes inadvertently choking out everything in their path.
- Which wildlife species have been negatively impacted or displaced because of blackberries production: Pesticide use has had a significantly negative historical impact on wildlife populations. Pesticides get into soil and water, rising up the food chain and being consumed by many different species. This has caused wildlife to have limited or contaminated food sources, resulting in declining populations. Blackberries’ high use of pesticides has been particularly damaging to wildlife over the years.
- Have water sources and soil been contaminated because of blackberry production: Nitrogen fertilizer is particularly damaging to waterways. The algae that are promoted in their growth can be very damaging to aquatic life and can spread easily to nearby rivers, streams, and lakes. Blackberries’ heavy use of nitrogen fertilizer means that they have caused some serious harm to waterways over the years.
In short, blackberries have had some major negative impacts on the environment over the years. This is mainly due to their land use, pesticides, and nitrogen fertilizers.
What Is the Overall Environmental Impact of Food and Agriculture
Food production in general has a high environmental impact. Everything from the amount of land used to the energy involved in irrigation to its effect on plant and animal biodiversity can be a factor in this. In the chart below, you can see how food production is one of the biggest influences on these areas of the environment.
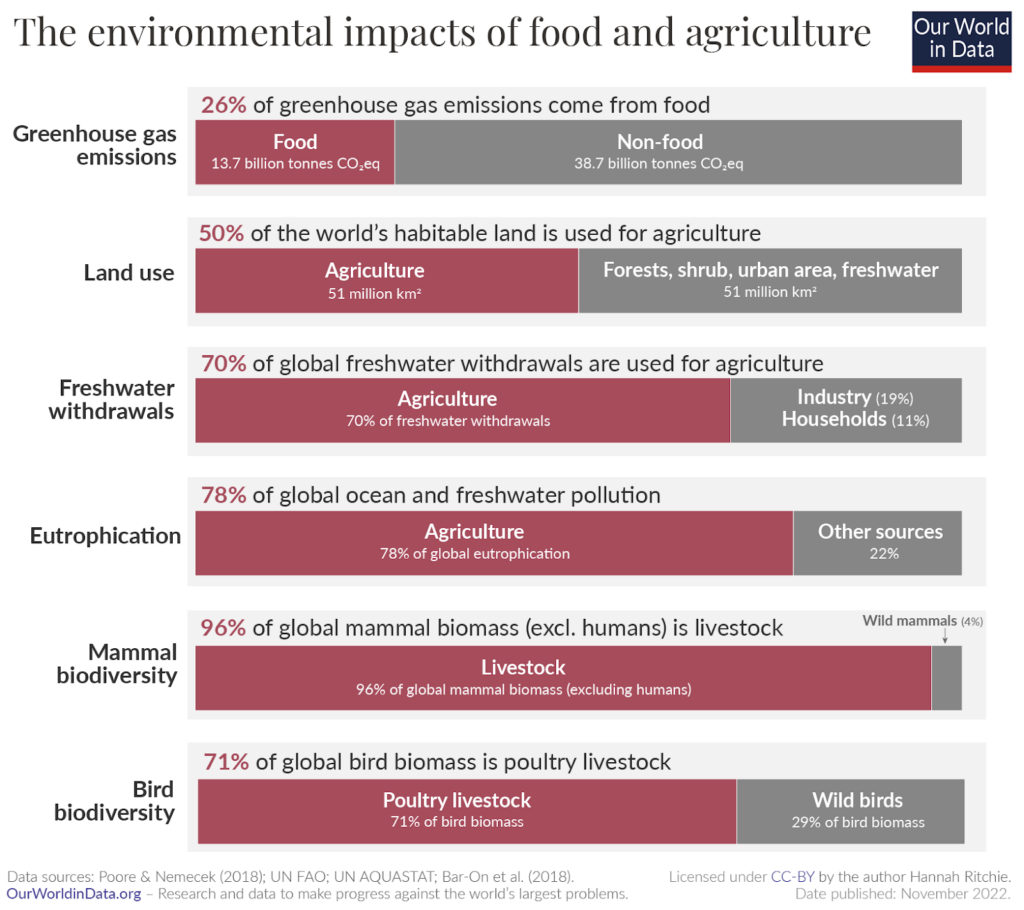
Agriculture alone accounts for over a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions, while using half of the world’s habitable land and 70% of the global freshwater withdrawals. Agriculture also causes 78% of the global ocean and freshwater pollution.
Livestock accounts for the vast majority of non-human mammal and bird biomass. Mammal livestock outweighs wild mammals by a factor of 15-to-1, and poultry livestock outweighs wild birds by a factor of more than 3-to-1.
These statistics highlight the need for sustainable and responsible practices in food production to reduce its impact on the environment. And the need for us to shift toward more environmentally-friendly foods.
How Can You Reduce Your Environmental Impact and Offset Your Personal Carbon Footprint
There are a few things you can do to mitigate some of the negative environmental effects of consuming blackberries, while still enjoying them. You can also consider offsetting your personal and blackberry-related carbon emissions, which will work to remove carbon emissions elsewhere that are then attributed to you. Here, we will walk you through how to accomplish both of these things.
How Can You Reduce Your Environmental Impact When Shopping for Blackberries
In this section, we give you a short list of ways you can reduce the negative environmental effects of oranges, based on those parts of the life-cycle of blackberries that would otherwise most negatively impact the environment:
- Buy organic blackberries: Pesticides are one of the biggest concerns when it comes to blackberries’ environmental impact. Organic farms generally avoid high amounts of chemical pesticides and nitrogen fertilizers and so they are good to support if you want to reduce your pesticide and fertilizer impact.
- Avoid plastic packaging: Most blackberries come in plastic packaging. However, there are still a significant amount that come in open-top cardboard containers, especially ones from local farmers. Cardboard has a far higher recycling rate than plastic—89%—and so is far less likely to end up in a landfill. It can also be composted.
- Consume your blackberries as soon as you buy them: Because blackberries have a shorter shelf life than many other fruits, they are more likely to go to waste. Making sure that you eat them as soon as you buy them will help you avoid adding blackberry waste to the landfill.
Following some of these methods can really help you to cut down on your environmental impact of eating blackberries. None of these will completely eradicate these negative impacts, since there are always effects that may be outside of your control. But some reduction is always better than nothing!
Which Organizations Can You Support to Help Alleviate Your Environmental Impact
While blackberries can cause a wide range of environmental damage, there are also some organizations that help you reduce parts of your impact that would otherwise be outside of your control. These organizations are working hard to prevent and reverse damage to the environment caused by industries like blackberry agriculture.
In the table below are some of the best environmental charities that work in the areas where blackberries production has affected the environment – and beyond:
Though it is helpful to reduce the environmental impact of your personal blackberry consumption, supporting these organizations takes your positive impact a step further. You will be reaching far beyond your own consumption impacts and helping to build a better world for everyone!
How Can You Offset Your Personal Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint is a key part of your environmental impact. And it is one of the ways we measure the effects of our human-induced global climate change. Yes, even from eating blackberries!
“Carbon footprint: the amount of greenhouse gasses and specifically carbon dioxide emitted by something (such as a person’s activities or a product’s manufacture and transport) during a given period”
Merriam Webster
Basically, it is the amount of carbon emitted by you as an individual or an organization providing you with goods and services – including blackberries:
- This includes GHG emissions from producing the products that we use and foods that we eat (e.g., power plants, factories or farms, and landfills)
- GHG emissions from fuel that we burn directly or indirectly (e.g., logistics and transportation, cooling or heating facilities),
- as well as the GHG emissions attributed to how we consume these products and foods.
Carbon offsets are reductions in carbon emissions that are used to compensate for carbon emissions occurring elsewhere – for example for the carbon emissions that are associated with blackberries. They are measured in tons of CO2 equivalents and are bought and sold through international brokers, online retailers, and trading platforms on what is known as the global carbon offset market.
“Carbon Offset: a way for a company or person to reduce the level of carbon dioxide for which they are responsible by paying money to a company that works to reduce the total amount produced in the world, for example by planting trees”
Oxford Dictionary
In terms of blackberries—and indeed all food types—there will always be a carbon footprint, because of the resources it takes to get your food from farms to the place where you’ll eventually eat them. And while there are ways to reduce your carbon footprint when shopping for blackberries, carbon offsets would be a way to reduce your CO2e emissions all the way down to net zero (or even to become climate positive).
However, when you purchase carbon offsets, it’s important that they actually make a difference in offsetting (aka reducing) total carbon emissions. To achieve that, the following are key criteria:
- Carbon offset projects have to be effective (different projects have different effectiveness rates)
- Carbon offset projects have to be additional
- Carbon offset projects have to be permanent
- The claims from carbon offset projects have to be verifiable
To find the best carbon offsets for you personally, check out our full guide on the best carbon offsets for individuals, where you’ll also learn more about how these carbon offset projects work, what their respective offsetting costs are, and what your best way would be to offset your own carbon emissions.
Final Thoughts
Blackberries may have a very low carbon footprint, but that doesn’t tell the whole story when it comes to the environment. Using harmful practices like excessive pesticides and plastic packaging can negatively impact ecosystems, waterways, and soil fertility alike. Fortunately, there are many things you can do to mitigate these damages, such as buying organic blackberries or supporting ecological organizations.
Stay impactful,

Sources
- Raspberry Blackberry: Overview of the Caneberry Industry
- Just Fun Facts: Interesting Facts About Blackberries
- UN Environment Programme: Environmental Impact Assessment and Strategic Environmental Assessment: Towards an Integrated Approach
- UN: Forests, desertification and biodiversity
- Our World in Data: Food production is responsible for one-quarter of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions
- World Health Organization: Preventing disease through healthy environments: a global assessment of the burden of disease from environmental risks
- ScienceDirect (Biological Conservation): Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers
- EPA: The Sources and Solutions: Agriculture
- EPA: Reducing Food Waste and Packaging
- FoodPrint: The Environmental Impact of Food Packaging
- Our World in Data: The environmental impacts of food and agriculture
- Our World in Data: Global land use for food production
- CA Garden Web: Blackberry Plants Irrigation
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Blackberries
- OK State: Commercial Blackberry Production
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Strawberries
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Bananas
- AGMRC: Blackberries
- Gardeners Path: Blackberries
- JAHR: Opportunities for Carbon Sequestration
- Sussex Wildlife Trust: Blackberry Bushes
- Hort Science: Performance of Component Species
- The Independent: Avocado, Coffee, and Citrus Fruits Threaten Global Food Security
- EMSWCD: Blackberry
- Southworth Forest: Noxious Weeds
- Gallant Intl: Environmental Impacts of Monoculture
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Cherries
- Impactful Ninja: What is the Carbon Footprint of Watermelons
- Water Footprint Network: What Is a Water Footprint?
- Raspberry Blackberry; Where Do Your Berries Come From
- Climate Knowledge Portal: Mexico Climate Data
- Express: Pesticides Plague EU
- Permaculture News: Pesticides Water Pollution
- IUCN: Marine Plastic Pollution
- Friends of the Earth: Effects of Pesticides on Our Wildlife
- USGS: Pesticides in Groundwater
- Gardeners Path: When and How to Fertilize Blackberries
- Mitsui: Reducing the Environmental Impact of Chemical Fertilizers
- EPA: The Problem With Nitrogen Fertilizers
- Rubus: Postharvest Handling and Storage of Blackberries and Raspberries
- Packaging Strategies: Berries Traced From Farm to Store
- ITP Packaging: Is Plastic Packaging Bad for the Environment
- Also Known As: 12 Interesting Facts About Packaging Waste
- Colorado: The Hidden Damage of Landfills
- Forge Recycling: How Long It Takes Everyday Items to Decompose
- Eat Delights: Blackberries Shelf Life
- AGMRC: Blackberries
- J and C Lawn Care: How Invasive Blackberries Can Destroy Your Yard
- SN Applied Sciences Journal: Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem
- Our World in Data: Global greenhouse gas emissions from food production
- UVM: Sources of Nitrogen for Organic Farmers
- Gardening Knowhow: Composting Cardboard
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that fight to protect our environment
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities for reforestation
- Impactful Ninja: Best wildlife conservation charities
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities for protecting the Amazon rainforest
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that protect our national parks
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that fight for clean water
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that help conserve our rivers
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities to save our oceans
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that help farmers
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities for helping farm animals
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities for climate change
- Impactful Ninja: Best carbon offsets for individuals
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that fight to reduce food waste
- Impactful Ninja: Best charities that fight to end plastic pollution
- Our World in Data: Emissions from food alone would take us past 1.5°C or 2°C this century
- Impactful Ninja: Why Is a Carbon Footprint Bad for the Environment
- Impactful Ninja: Best Carbon Offsets for Individuals